Archive for the 'Asian cinema' Category
The ten best films of … 1926
The Adventures of Prince Achmed.
Kristin (with some help from David) here:
David and I have been offering this greatest-of-90-years-ago series almost as long as this blog has existed. For earlier annual entries, see 1917, 1918, 1919, 1920, 1921, 1922, 1923, 1924, and 1925.
I approached 1926 with the assumption that it would present a crowded field of masterpieces; surely it would be difficult to choose ten best films. Instead it turned out that some of the greatest directors of the era somehow managed to skip this year or turn in lesser films. Eisenstein had two masterpieces in 1925 but no film in 1926. Dreyer made a film that is a candidate for his least interesting silent feature, The Bride of Gromdal. Chaplin did not release a film, and Keaton’s Battling Butler, while a charming comedy, is not a plausible ten-best entry. The production of Lang’s Metropolis went over schedule, and it will appear on next year’s list, for certain.
Still, the Soviet directors were going full-tilt by this time and contribute three of the ten films on this year’s list. French directors on the margins of filmmaking created two avant-garde masterpieces. Two comic geniuses of Hollywood already represented on past lists made wonderful films in 1926. A female German animator made her most famous work early in a long career. I was pleased to reevaluate a German classic thanks to a sparkling new print. Finally, Japan figures for the first time on our year-end list, thanks to a daring experimental work that still has the power to dazzle.
The Russians are coming
Vsevolod Pudovkin’s Mother was a full-fledged contribution to the new Montage movement in the Soviet Union. By the 1930s, that movement would be criticized for being too “formalist,” too complex and obscure for peasants and workers to understand. Nevertheless, being based upon a revered 1906 novel of the same name by Maksim Gorky, Mother was among the most officially lauded of all Montage films. It tells the story of a young man who is gradually drawn into the Russian revolutionary movement of 1905. His mother, the protagonist of the novel, initially resists his participation but eventually herself joins the rebellion.
Along with Potemkin, Mother was one of the key founding films of the Montage movement. Its daring style is no less impressive now than it must have been at the time. One brief scene demonstrates why. Fifteen years before Mother, D. W. Griffith was experimenting in films like Enoch Arden (1911) with cutting between two characters widely separated in space, hinting that they were thinking of each other. By 1926, Pudovkin could suggest thoughts through editing that challenged the viewer with a flurry of quick mental impressions.
As the Mother sits beside her husband’s dead body, her son, a participant in the 1905 failed revolution, comes in. He is about to bend down and open a trap-door in the floor (73 frames). A cut-in shows her horrified reaction (12 frames), and there follows a brief close shot of some guns she had seen him hide under the floor in an earlier scene (11 frames). Even shorter views of a man clutching his chest (8 frames), two jump-cut views of the dead husband (3 frames and 2 frames), and a tight framing of the son being shot follow (8 frames). We return to her face, registering even greater horror (15 frames). A return to the initial long shot shows her leaping up to try and stop her son from taking the guns out to participate in a seditious act (31 frames).
The series of five shots goes by in a few seconds, and we are challenged to grasp that the guns are a real memory, while the shots of the man’s chest and her son’s anguished face are visions of what might happen. The shots of her husband’s body suggest that she could soon end up sitting by her son’s corpse as well. The jumble of recollection, imagination, and reality are remarkably bold for this relatively early era.
Mother also contains two of Pudovkin’s most memorable scenes, the breaking up of ice in the spring as a symbol of the Revolution and the final violent attack on the demonstrators, including the heroine.
Mother was released on DVD by Image Entertainment in 1999, but it seems to be very rare. An Asian disc, perhaps a pirated edition of the Image version, is sold on eBay. I’ve never seen the film on DVD and can’t opine on these. The time is ripe for a new edition.
Pudovkin was one of the filmmakers who had studied with Lev Kuleshov during the early 1920s, when Kuleshov made the famous experiments that bear his name. Pudovkin played the head of the gang of thieves in The Adventures of Mr. West in the Land of the Bolsheviks, which I included in the ten-best list of 1924.
Kuleshov had moved on as well to direct his most famous film and probably his best silent, By the Law, based on Jack London’s story “The Unexpected.” Set in the Yukon during the gold rush, it involves five people who are cooperatively working a small claim and discover gold. Taking advantage of a warm autumn, they stay too long and are trapped for the winter. One of the men kills two of the others, and the heroine, Edith and her husband Hans are left to determine the fate of the killer, Dennin. Edith insists on treating him strictly according to the law. After enduring the harsh winter and a spring flood, the couple finally act as judge, jury, witnesses, and, after finding Dennin guilty, executioners.
The great literary critic and theorist Viktor Shklovsky (one of the key figures of the Russian Formalist school) adapted the short story, condensing it by eliminating the opening section of Edith’s backstory and a few scenes in which a group of Indians appear occasionally to help the prospectors. The result is a concentration on the tense drama of a three people trapped together in a tiny cabin.
In the 1924 entry, I mentioned that Kuleshov’s team emphasized biomechanical acting and that Alexandra Kokhlova was adept at eccentric acting. She delivers a bravura performance here, as Edith moves closer to a breakdown as the months go by.
Kuleshov also puts into practice the experiments in imaginary geography that his classes had made. Although in this film he didn’t unite shots made in widely separate spaces, he did favor scenes built up of a considerable number of detail shots before finally revealing the entire space in an establishing shot. Edith, for example, though glimpsed briefly asleep early on, is introduced in a later scene by a shot of her boots and Bible, followed by a shot of her head as she read the Bible. The scene also contains close shots of the other characters before a general view of the cabin interior shows where each of them is.
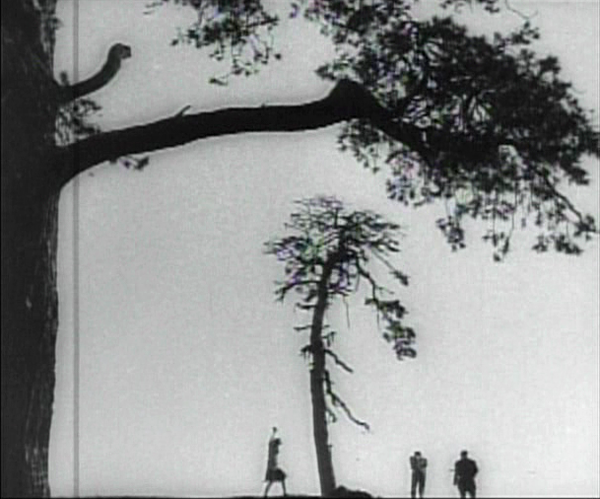
The scene of the execution includes one of the most famous images of the Monage movement, a framing with the horizon line at the bottom edge of the frame and the sky dominated by trees (see bottom). Any number of framings of tall features such as trees and telephone poles against a huge sky appeared in Montage and non-Montage films, and this device became so common as to be a trait of the Soviet cinema of the late 1920s and early 1930s.
The desire to hide the actual hanging led Kuleshov to stage is behind the larger of the two trees, as Edith and Hans struggle to carry out their sentence on Dennin. This leads to some eccentric framings, such as our view only of Edith’s legs as she teeters on the box where Dennin stands, presumably adjusting the noose (see top of this section).
A beautiful print of By the Law is available on DVD from Edition-Filmmuseum.
Grigori Kozintzev and co-director Leonid Trauberg did not study with Kuleshov, but they shared a passion for eccentricity. Having started out in the theater, in 1921 both contributed to the “Manifesto for an Eccentric Theater,” a dramatic approach based on popular forms like circus and music-hall. In 1922 they founded the “Factory of the Eccentric Actor” group and two years later transformed it into FEKS, devoted to making films.
The Overcoat (also known in English as The Coat), their second feature, was based on a combination of two short stories by Gogol, an author whose grotesque creations were very much in tune with their own tastes. It tells the story of a poor, middle-aged low-level government clerk, Akaky Akakievich, who is bullied over his shabbiness, particularly his worn-out overcoat. Scrimping to buy a new one, he finally purchases a magnificent new coat and finds his status suddenly raised–until the coat is stolen.
Andrei Kostrichkin was a mere twenty-five years old when he played the fiftyish clerk, but he was highly effective and provided another model of the eccentric actor. As Akakievich he stands with bent legs and twisted torso, as if flinching away from a blow, and walks in tiny steps along perfectly straight lines through the hallways in his office building. When he applies to a Person of Consequence for help in recovering his stolen coat, the official leans over his desk to look downward, with a high-angle point-of-view framing of Akakievich appearing dwarfed by the other’s superiority.
The script of The Overcoat was adapted by another Russian Formalist critic and theorist, Yuri Tynjanov.
Unfortunately The Overcoat does not seem to be available on any form of home video.
Petit mais grand
The IMDb lists 23 directing credits for Dimitri Kirsanoff from 1923 to the year of his death, 1957. He is largely remembered, however, for one film, the 37-minute Ménilmontant, a melodrama about the travails of two sisters orphaned as children by a violent crime. Each is later seduced by a callous young man who leaves the heroine a single mother and her sister reduced to prostitution. It belongs to the French Impressionist moment. (We deal with Impressionist films in other entries: La roue, L’inhumaine, L’affiche, Coeur fidèle, The Smiling Madame Beudet, Le brasier ardent, Crainquebille, and El Dorado, as well as DVD sets of Impressionist films by the Albatros company and by director Jean Epstein.)
The story itself is simple and indeed might be thought clichéd were it not for two factors. First, there’s the performance of the delicately beautiful Nadia Sibirskaïa as the protagonist. There’s also the lyrical, melancholy use of the settings, initially in the countryside and later in the desolate working-class Parisian district whose name gives the film its title. The simplicity of the narrative also makes it one of the most successful of the attempts to tell a story visually, eschewing intertitles.
The film’s most famous scene is its abrupt, shocking opening. With no establishing shot, there is a series of rapid shots of details of faces, hands, a window, and an ax, during which we can barely discern that a man has committed a double murder. The spectator cannot possibly know who these people are and why the murders occur.
Instead of offering an explanation, the action then shifts to two little girls playing in the woods. As they return home, the camera begins to concentrate on one of them, apparently the younger, as she arrives at the murder scene and reacts in horror. Kirsanoff presents her expression in a series of five shots, linked by what David has termed axial cuts, from medium shot to extreme close-up as she gradually realizes what has happened.
There had certainly been axial cuts before this, including in Potemkin, but Kirsanoff probably went further than anyone of the era by including so many shots, by making each so short, and by moving his camera forward in such small increments. It is difficult to notice every cut, particularly the one from the third to the fourth shot, and the effect adds an unsettling quality to an already intense moment.
After this opening, a funeral scene reveals through labels on the grave that the murdered man and woman are the children’s parents. We might have suspected that the killer was a jealous husband discovering his wife with her lover. As it is, we never learn whether the crime was the result of a love triangle or the random act of a madman.
The rest of the film establishes the sisters now grown up, working in a workshop making artificial flowers and sharing a small flat in Menilmontant. The heroine’s brief romance leads to a baby, and superimpositions and other Impressionist techniques depict her despair and contemplation of suicide. Beautifully melancholy atmospheric shots of the streets of the neighborhood punctuate the action and underscore the dreariness and hopelessness that the heroine faces. The ending, though an improvement in the heroine’s lot, does little to dispel the overall grimness of the story.
Menilmontant is included in the out-of-print set “Avant-garde – Experimental cinema of the 1920s & 1930s.” It has been posted twice on YouTube in a low-rez format.
Even shorter is Anémic cinéma, the only venture into film directing by the great French Dadaist, Marcel Duchamp. It’s hard to compare a roughly seven-minute abstract film with narrative features, but this short is so innovative and influential that it’s also hard to leave it off the list.
Duchamp went through a phase of spinning artworks, including some “Rotoreliefs” that he attempted to sell as toys. These were similar to some Victorian optical toys, such as the Phenakistopscope and the bottom disks of Zoetropes. See Richard Balzer’s website for a collection of such devices, as well as “The Richard Balzer Collection” on tumblr, which contains gifs that animate some of the disks, done by Brian Duffy. Some of these resemble the spinning spirals and embedded circles that Duchamp used for his short. (See the top of this section.)
These spinning abstract circular images alternate with slowly spinning disks with sentences laid out as spirals. These involve either alliteration or puns or both. Unfortunately the English subtitles cannot render these in a way that conveys the original intent. For example, “Esquivons les ecchymoses des esquimaux aux mots exquis” becomes “Let us dodge the bruises of Eskimos in exquisite words.” The meaning is the same, and even the echo of the first syllables of “Eskimos” and “exquisite” is retained. Nevertheless, the similar syllables in two other words in the original are lost, as are the echoes of “moses,” “maux,” and “mots.” It is rather as though someone attempted to render “Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers” into another language quite literally. (The Wikipedia entry includes a complete list of the sentences in French.)
Duchamp’s purpose was presumably to create an artwork with minimal means, including quasi-found objects, the disks he had made for another purpose. His idea is clearly reflected in the title, Anémic cinéma, which suggests a weakness or thinness of means. “Anémic” is also an anagram for “cinéma.”
Anémic cinéma is available in the same collection as Menilmontant, linked above. it is also available in the similarly out-of-print set, “Unseen Cinema.” There are numerous versions on YouTube, varying in quality. Some of these have been manipulated by other artists.
Lloyd and Lubitsch
Though Chaplin and Keaton might have had off-years in 1926, Harold Lloyd did not. Over the past several years, Lloyd has gradually been gaining the admiration he deserves. He used to be known largely for Safety Last (1923) and The Freshman (1925), two excellent films which, however, are not his finest. Girl Shy (1924) and The Kid Brother (1927) are better known now for the masterpieces they are. For Heaven’s Sake (directed by Sam Taylor), which clocks in at a mere 58 minutes, is just as good.
Lloyd plays a breezy millionaire, J. Harold Manners, who unintentionally helps Brother Paul found a mission in the downtown slums of Manhattan. He falls in love with Hope, the missionary’s daughter, and decides to help out around the place. By this time Lloyd was known for his spectacular chase scenes, and there are two here. Initially he puts a twist on the chase, luring a growing crowd of criminals into racing after him, ending in the mission. Gaining their respect, Harold makes the mission a happy social center.
The romance provides one of my favorite comic intertitles, leading into a love scene: “During the days that passed, just what the man with a mansion told the miss with a mission–is nobody’s business.” The love scene in turn includes a visual joke that emphasizes the rich boy – poor girl contrast.
Harold’s rich friends hear that the pair are to be married and determine to kidnap him to prevent the inappropriate match. The result is a lengthy chase through the streets of Manhattan, with the drunken thugs rescuing Harold and using a variety of means to get him back to the mission in time for the wedding–as when the drunken leader of the group demonstrates his tightrope-walking abilities on the upper railing of a double-decker bus (see above).
Two years ago, when I put Girl Shy on my list, the New Line Cinema boxed set of Lloyd films was out of print and hard to find, and the separate volumes appeared to be going out of print as well, with Volume 1 not being available at the time. The situation has changed, and the boxed set, though apparently still out of print, is now available at reasonable prices from various third-party sellers on Amazon and Barnes & Noble. The set contains a “bonus disc” with extras, including interviews and home movies. The same is true for the three individual volumes (here, here, and here). For Heaven’s Sake is in Volume 3.
Inevitably, coming directly after Lady Windermere’s Fan, probably Ernst Lubitsch’s greatest silent film, So This Is Paris does not quite live up to its predecessor. Still, it’s a very fine, clever, and funny film, and it marks Lubitsch’s last appearance in these lists until sound arrives.
The opening scene, running nearly twenty-five minutes, is as good as anything Lubitsch did in this era. Set in Paris, it’s a slow build-up of misunderstandings and deceptions involving two affluent couples in apartments across the street from each other. One couple, Maurice and Georgette Lalle, are practicing a melodramatic dance in Arabian costumes. Their marriage seems to be a rocky one. Across the street, Suzanne Giraud is reading one of the lurid “Sheik” novels that were popular at the time, involving “burning kisses” in its final scene. Put into a romantic mood by this, she looks out her window and sees the head of a man in a turban at the window opposite–Maurice relaxing after his strenuous rehearsal.
Her husband Paul arrives home, and she kisses him passionately. Apparently not used to such affectionate greetings, he is puzzled until he, too, looks out the window. By now Maurice has doffed his turban and necklaces and appears to be not only naked but also examining a piece of his anatomy.
Paul jumps to the conclusion that this sight is what caused Suzanne’s unaccustomed display of passion. He calls her to the window, and we see Maurice in depth through the two windows.
Suzanne then asks if Paul is going to stand for such a thing, and he goes to the other apartment to confront Maurice. Instead he finds Georgette, who turns out to be an ex-lover of his. She introduces him to Maurice, who is very friendly and charms Paul. The latter who returns home and claims that he has beaten Maurice and even broken his cane on him, though in fact he had simply forgotten it. Shortly thereafter Maurice visits Suzanne to return the undamaged cane and takes the occasion to flirt with her. It’s a beautifully plotted and developed farcical scene. The film is based on a French play and could easily have become stagey in its adapted form. Yet the byplay between the two apartments via the windows allows Lubitsch to avoid any such impression; the misunderstandings based on optical POV recall the racetrack scene of Lady Windermere.
The rest of the film develops the two potentially adulterous affairs, primarily with Paul secretly taking Georgette to the Artists’ Ball. Here Lubitsch uses an elaborate montage sequence to convey the wild party, with superimpositions and shots taken through prismatic lenses.
Such sequences were primarily developed in German films and were still fairly rare in American ones in 1926. Similar techniques convey Paul getting drunk on the champagne he and Georgette are awarded when they win a dance contest–the announcement of which on the radio broadcast of the ball alerts Suzanne to her husband’s presence there with another woman.
So This Is Paris is less famous than Lubitsch’s earlier American comedies primarily because it has never appeared on DVD. Marilyn Ferdinand, in a blog entry that gives a detailed description of the film, writes that Warner Bros. claims not to own the rights to the film anymore and therefore has made no effort to bring it out on home video. On the other hand, a four-minute excerpt of the dance montage sequence was included in the Unseen Cinema set (disc 3, number 18), and the credit there is “Courtesy: Warner Bros., Turner Entertainment Company.” Whatever the rights situation is, a home-video version of this film is in order. A beautiful 35mm print is owned by the Library of Congress, so there is hope.
Two German flights of fancy
I must confess that I was disappointed the first time I saw F. W. Murnau’s Faust, and I have never warmed up to it in later viewings. I am delighted at having occasion to look at it again for this 1926 list, since a recently discovered and restored print reveals that the main problem before was the poor visual quality of the print formerly in circulation.
Different local release prints survived in a number of countries, but there were basically two original versions made: the domestic negative for German release and the export negative. These were shot using two camera side-by-side on the set, as was the standard practice in much of the silent era, given the lack of an acceptable negative-duplicating stock. The primary camera contributed most of the shots to the domestic negative, though in some cases where the second camera yielded a superior take, that was used in the domestic negative. Conversely, inferior takes from the primary camera sometimes made their way into the export negative. The result, as we now know, was that both the visual quality and in many cases the editing of the scenes was markedly different in the two negatives.
The version familiar for decades originated from the export negative. Recently the domestic negative was rediscovered, and the Friedrich Wilhelm Murnau Stiftung restored the that version using the that negative, supplemented with material from a variety of other prints. The result closely approaches the original German release version, including the original decorated intertitles. The contrast in quality between this restoration and the old, familiar Faust is remarkable.
Given how dark the film is, details in the backgrounds could easily be lost. The scene in which Faust is called to help a woman dying of the plague is revealed to have dramatic staging in depth against a very dark room contrasted with the stark foreground underlighting of the woman’s haggard face. Faust enters from behind the daughter and comes forward to her, after which his movement is balanced by the daughter retreating into that same dark background.
The famous aerial journey of Mephisto and Faust from Germany to Italy (below left) always looked rather hokey, but the detail revealed in the extraordinarily extensive model makes it far more impressive. Similarly, when one can actually see the sets, visual echoes become apparent. For example, Faust first encounters Gretchen and follows her into the church, where he finds himself barred from entering by his pact with Mephisto. Later, when Gretchen has been abandoned, she laments when not permitted to enter there.
No doubt some motifs of this sort were visible in the earlier print, but their clarity here enhances both the beauty and the craft of Murnau’s film.
Faust is available in several editions on DVD and Blu-ray. DVDBeaver ran a detailed comparison among seven of these, including a selection of frame grabs. To my eye, the 2006 DVD “Masters of Cinema” version of the domestic print, released by Eureka!, looked the best. (The two-disc set also includes the export version.) The Blu-ray from the same source, released in 2014, looked slightly darker. The box for the Blu-ray also includes the DVD, however. These releases are Region 2. The film is available on Blu-ray in the USA from Kino.
Both Eureka! releases’ supplements include a booklet, a commentary track, a Tony Rayns interview, and a lengthy comparison of the domestic and export versions. One particularly striking example is drawn from the scene in which Mephisto talks with Gretchen’s brother in a beer hall, with the domestic version on the left.
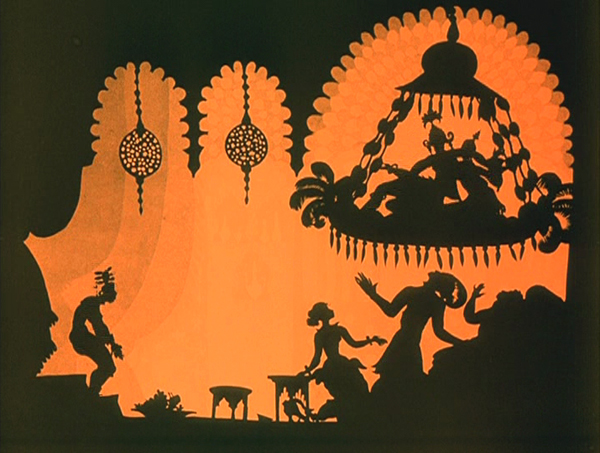
While watching Faust, I kept grabbing frames, far too many to be used in this entry. They were simply too beautiful or impressive to be passed over, and they made my final selection of illustrations difficult. The only other film for which this was true this year is Lotte Reiniger’s silhouette-animated feature, The Adventures of Prince Achmed. The restored, tinted print that is currently available is even lovelier than the older black-and-white version.
Reiniger seems to have invented the use of jointed silhouette puppets, and she still is the first artist one thinks of in relation to this form of animation. She continued to practice it until the 1970s. (See the link below to a collection of many of her short films.) Her one feature film remains her most famous and is probably her masterpiece.
It involves far more than simple black figures moving against a light background. As the frame at the top of this entry shows, her characters, furnishings, and locations, all rendered in paper with scissors, were often elaborate indeed. Characters wore feathers, jewelry, fancy wigs, and other decorative elements. The hanging platform has many little tassels, and the lamps are rendered in delicate filigree. The backgrounds are not blank but have varying layers of saturation that suggest a depth effect, the equivalent of atmospheric perspective. At the left in the top image, a series of identical curtains start out a dusky orange and in three stages lighten until there is a bright, solid glow at the center.
In the frame at the left below, the same sort of shading creates the depth of a cavern, setting off the tracery of the foliage and the kiosk in which the hero finds the magic lamp. On the right, very simple shading suggests a vast and elaborate palace in the background, while Reiniger fills the foreground with many small figures, all marching out to surround the procession of the caliph.
By choosing a classical fantastic tale, Reiniger found the perfect subject matter to fit the technique that she invented. Both the subject matter and the sophistication of the animation give her films a timeless look. Her reputation remains high today as a result. One scene in Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows Part 1, “The Tale of the Three Brothers,” was made in a style inspired by Reiniger’s work. (I discuss it here.)
A restored, tinted version of The Adventures of Princes Achmed is available from Milestone. A combination Blu-ray/DVD release of the film is available from the BFI. (I have not seen this version.) Note that these have somewhat different content. The BFI version has five Reiniger shorts from across her career along with a booklet. The Milestone version has only one of the shorts, but it includes a documentary about Reiniger. (This documentary was on the 2001 BFI release of the film on DVD but is not listed among the extras on its Blu-ray.) See also the BFI’s collection of many of her shorts, “Lotte Reiniger: The Fairy Tale Films,” which I discussed here.
[Dec 27: Thanks to Paul Taberham for pointing out that Prince Achmed also has no intertitles and gets along without them very well.]
Into the asylum
David here:
Few western viewers of 1926 saw any Japanese films, but Japanese audiences had been watching imported films for a long time. Hollywood films could easily be seen in the big cities, and The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari (released in 1922), La Roue (released in early 1926), and other films from Europe had made a strong impression on local filmmakers. One fruit of this influence was the wild Page of Madness (Kurutta ichipeiji, aka “A Crazy Page”).
Directed by Kinugasa Teinosuke and based on a story by the renowned experimental writer Kawabata Yasunari, the film bore the influence of German Expressionist and particularly French Impressionist cinema. Page of Madness set out to be a bold exercise in subjective filmmaking. But it wasn’t widely seen at the time, and wasn’t revived until 1971, when Kinugasa discovered a print in his house (reportedly, among cans of rice). Apparently the version we have is slightly edited.
A woman has been confined to a madhouse, and her husband has taken a job as a janitor there to stay in touch with her. Many of the scenes are presented as the hallucinations of the wife and other inmates, while abrupt flashbacks attached to the husband fill in the past. But this story is terribly difficult to grasp. There are no intertitles (perhaps an influence of The Last Laugh, shown in Japan earlier in 1926), and the film is a blizzard of images, choppily cut or dissolving away almost subliminally.
Viewers of the period had the advantage of a synopsis printed in the program, and there was a benshi commentator accompanying the screening to explain the action. Because we lack those aids, the film seems more cryptic than it did at the time. Even when you know the story, though, Page of Madness often surpasses its foreign counterparts in its free, unsignalled jumps from mind to mind and time to time. It remains a powerful example of narrative and stylistic experiment, from its canted framings and single-frame cutting to its frenzied camera movements and abstract planes of depth (thanks to scrims à la Foolish Wives, 1922).
For nearly fifty years it has remained a milestone, a grab-bag of advanced techniques and likely the closest Japan came to a silent avant-garde film.
Page of Madness is not commercially available on home video. It is occasionally shown on TCM, and a reasonably good print is on YouTube. Aaron Gerow’s A Page of Madness: Cinema and Modernity in 1920s Japan is an indispensable guide to Kinugasa’s eccentric masterpiece.
By the Law.
Il Cinema Ritrovato: revelations from India and Iran
Pather Panchali
Kristin here:
The second half of my week at the Cinema Ritrovato festival in Bologna was centered around two Asian events: a small program of Iranian films from the 1960s and 1970s and the restored Apu trilogy. In between those screenings I tried to fit in some programs of pre-1920s cinema.
Bringing the Apu Trilogy back from the ashes
That was the title of a panel presentation during the festival, one which I missed because I was watching the first of the four Iranian films. In this case the metaphor is literal. The original negatives of the Apu films were stored in a London warehouse, and in 1993 a fire damaged them extensively.
In 2013, The Criterion Collection and the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences began a collaborative restoration. Working meticulously by hand and employing an innovative rehydration technique, experts at L’Immagine Ritrovata in Bologna rescued the images for about 40 percent of Pather Panchali and 60 percent of Aparajito. The negative of Apu Sansar (The World of Apu) was wholly lost. For it and the missing parts of the other two films, footage from fine-grained masters and duplicate negatives from various archives was used. The restoration was done in 4K. (For an interview with Lee Kline, Criterion’s technical director, see here. There is a short but informative short film on the restoration, including some before-and-after comparisons, on Vimeo.)
The result is spectacular, far better than one would expect, given the dire circumstances the restorers faced. It was a privilege to see the entire trilogy over three days on the huge screen of the Cinema Arlecchino from the front row. There were times when the replacement footage was obvious, but for the most part, the images look pristine. They also look like film, with no hint of video-y quality about them.
I had seen the trilogy only once, in 16mm back in my graduate-school days. At the time, I admired it but wasn’t bowled over. Sitting through the Ritrovato screenings, I found it a profoundly moving and beautiful experience. Satyajit Ray manages both to maintain a quiet, leisurely pace and to compress the hero’s life, from birth to early adulthood, into three parts totalling less than six hours.
Apu’s strict but devoted mother (below left, in Aparajito) anchors the first two films, gaining our sympathy despite her scolding and worrying. Apu’s wife, Apurna (below right, in Apu Sansar), is in the third film for a remarkably short time. Yet we quickly come to understand her love for this unknown man whom she marries almost by accident, her sense of humor, and her compassion, all of which are vital to our sympathy for Apu’s utter devastation after her death. Indeed, the trilogy involves five major deaths, all of which makes the hopeful ending the more affecting.
Presumably The Criterion Collection will bring out a Blu-ray set of the three films, though no date has yet been announced.
Iran’s own New Wave
Admirers of Abbas Kiarostami, Mohsen Makhmalbaf, Asghar Farhadi, Jafar Panahi, and other notable directors of the Iranian cinema of the past few decades might be curious about their forerunners. Iranian film critic and historian Ehsan Khoshbakht has begun to satisfy that curiosity by programing a short series of classics of pre-Revolutionary cinema. According to his program notes (available in their entirety online), the four films shown in Bologna constitute about a quarter of the output of the Iranian New Wave. I hope there will be further screenings at future festivals.
As Khoshbakht warned in introducing the earliest film in the series, Shab-e Ghuzi (Night of the Hunchback, 1965), it is not a masterpiece and certainly not a forerunner of the filmmaking that would later bring Iran to prominence in international festivals and art cinema. Director Farrokh Ghaffari was a pioneer of Iranian filmmaking beginning in the 1950s, but he is perhaps equally important in having started the first Iranian film archive.
Night of the Hunchback is a black comedy with a story loosely derived from The Trouble with Harry. A player in a cheap entertainment troupe is accidentally killed, and the bulk of the film follows his corpse as it is passed from one group of characters to another; these include a pair of smugglers running a beauty salon, who provide much of the film’s humor (above). Most try to dispose of it, but a society woman trails it in the hope of retrieving an incriminating document in its jacket pocket. By Western standards it seems like a fairly mainstream commercial work, but it departed from commercial Iranian cinema, according to Khoshbakht, “with its respect for folklore and its bitter portrayal of the upper class.” It was a commercial flop but gained some attention at European film festivals.
The most famous film of the era is Gaav (The Cow, dir. Dariush Mehrjui, 1969). It centers around Hassan, the owner of his village’s sole cow. He dotes on the beast, as is quickly established in an early scene when he affectionately bathes her.
When the cow mysteriously dies (a cause is hinted at but never confirmed), the villages lament the loss of their only source of milk, but they also worry about how Hassan will react when he hears the news.
Although Hassan is the evident protagonist of the film, the drama centers more around the ignorance, lack of judgment, and even cruelty of the villagers. The film begins not by introducing Hassan and his cow but with a disturbing scene of the local children chasing and tormenting a mentally defective young man. This establishes the tone for several later scenes.
When the cow’s death is discovered, the small group of men who wield authority initially concoct a story of the cow having run away, and the villagers bury the carcass (bottom). As Hassan descends slowly into madness, the people supposedly trying to help him make every possible wrong decision, leading to disaster.
If the films I discussed in my previous entry extolled the virtues of village life and represented leaving home as unwise, The Cow is just the opposite. Cut off from the outer world, the villagers have little education or ability to come up with logical solutions to problems. It’s a theme repeated in the other two Iranian fiction films on the program as well.
Yek Ettefagh-e sadeh (A Simple Event, dir. Shrab Sahid Saless, 1973), the latest of the films shown, seems the most obvious forerunner of the wave of Iranian cinema that started in the 1980s. It closely follows the daily routine of a young, unnamed boy living in a small town on the edge of the Caspian Sea. We see him at school, helping sell the few fish that his father catches each day, eating and trying to study in the almost unfurnished house he shares with his father and sickly mother.
There’s little dialogue, apart from scenes in the school. I believe the boy speaks two lines in the entire film, and his father communicates with him only occasionally, to order him around: “Close the door” or “Study.” Much of the action consists of the boy running through the streets on errands, including his night-time visit to fetch a doctor for his ailing mother (below).
Although there’s a superficial resemblance between A Simple Event and the later films of the “child quest” genre, I see considerable differences as well. In films like Kiarostami’s Where Is My Friend’s Home? or Panahi’s The Mirror, the child protagonists have clear-cut goals which they have decided upon themselves. They are stubborn and determined, and as they doggedly pursue their goals we are never unsure about their motives.
In A Simple Event the boy has no goal, and we learn almost nothing about his character. Is he really as stupid as his teacher believes, or is he behind his classmates because he gets little chance to do his homework? Does he love his mother or is he indifferent to her declining health? Is he resentful but cowed by his elders? Or is he resigned and accepting of his lot? We have no way of knowing. His one independent action is to buy a bottle of Coca-Cola to go with his usual meager meal after his father uncharacteristically gives him a little money.
There’s certainly a suggestion, once again, that small-town life is deadening to people. The rote learning and lack of relevance in the subjects taught in school help explain the lack of imagination and the resignation to their situation among the students.
My suspicion is that later directors may have seen the potential in A Simple Event and built upon it, introducing a greater empathy with their child protagonists and certain greater drama and suspense.
To me, the surprise among the Iranian films was Oon Shab Ke Baroon Oomad Ya Hemase-Ye Roosta Zade-ye Gorgani (The Night It Rained or the Epic of the Gorgan Village Boy, dir. Kamran Shirdel, 1967). It’s a  sophisticated investigative documentary that reminded me of the work of Erroll Morris.
sophisticated investigative documentary that reminded me of the work of Erroll Morris.
The film begins with a written report on the making of the film itself, submitted to the authorities by Shirdel. It seems to describe earnest attempts to document an inspiring story that had been widely circulated in newspapers. On a rainy night, a boy in the village of Gorgon had discovered that flooding had undermined the local train tracks; he signaled an oncoming train by setting his jacket alight, successfully stopping it and saving 200 passengers’ lives.
Doubt begins to creep in, though. Among the many newspaper titles shown trumpeting the boy’s feat, we find one calling it a pack of lies. Shirdel’s report indicates that his team could not find the boy and set out to interview various people. Gradually it becomes apparent that the whole story was concocted and that the train–a cargo train with no passengers aboard–was stopped by local railway officials. Throughout the film, there are further passages from the production report, describing the filming work as if it were for a simple, laudatory documentary about the heroic boy. We see, however, that much of the filming undermines that heroism and satirizes the government’s willingness to perpetuate false accounts of it.
Shirdel carefully avoids making that point explicitly. He intercuts interview scenes, some of the boy rattling off his story and some of newspaper editors defending the story (above). In other scenes, we hear from indignant railway officials and an editor who dismisses the incident as pure fiction. The director seems to let us decide on the truth, but the the absurdity of boy’s supposed heroism becomes increasingly apparent.
Not surprisingly, Shirdel’s film was banned. Six years later, according to the program notes, “it was deemed harmless. It was then premiered at the Tehran International Film Festival where it won the Best Short Film award.” Clearly the officials who cleared it for release missed the ironic underpinnings of the film.
The Night It Rained (and perhaps others of Shirdel’s films) may have offered a model of reflexive filmmaking that later directors picked up on. Close-up, The Mirror, Salaam Cinema, and Through the Olive Trees all bring filmmaking into the stories they tell.
Thanks to Ramin S. Khanjani for some corrections concerning the Iranian section of this entry. His article on The Night of the Hunchback, “Actors and Conspiracies,” was published in Film International 15, 3/4 (Autumn 2009/Winter 2010): 66-71.
The Cow.
A second chance at childhood
DB here:
This year Ebertfest has been such a swirl of activity that I hardly know where to start. Jim Emerson’s reportage, here and here, decorated with neat photos and trim Tweets, has admirably hit the high points—the panels, the Q & A’s, and the young Web critics, or “foreign correspondents,” that Roger has summoned to his annual get-together. There’s even streaming of the panels and Q & A.
After participating in four events in rapid succession, I find that I’m still sorting out impressions. I hope to do justice to the broad swathe of doings in another entry after I get home tomorrow. For now, why not just let my impulses take over and write about my most enjoyable movie so far?
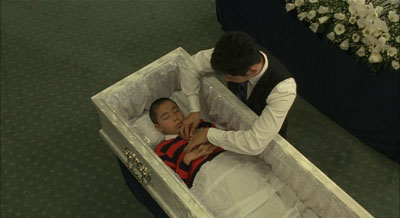
 Takita Yojiro’s Departures (2008) well deserves the standing ovation that greeted him when he stepped out on the Virginia Theatre stage. I mentioned the film last year, and since then I’ve seen it two more times, not counting the splendid projection Friday. I was happy that Roger shares my affection for the movie. In my remarks before the screening, I praised the movie’s willingness to go straight for the heart. This sort of sincerity, which John Ford or Frank Borzage would have understood, is hard to come by in today’s American cinema, where emotion tends to be framed by irony or self-consciousness cuteness (500 Days of Summer). My intro did mention the comedy in the film, but I didn’t stress it enough. Watching it with the Ebertfest audience again taught me that the film cleverly uses humor to lead us into its pathos.
Takita Yojiro’s Departures (2008) well deserves the standing ovation that greeted him when he stepped out on the Virginia Theatre stage. I mentioned the film last year, and since then I’ve seen it two more times, not counting the splendid projection Friday. I was happy that Roger shares my affection for the movie. In my remarks before the screening, I praised the movie’s willingness to go straight for the heart. This sort of sincerity, which John Ford or Frank Borzage would have understood, is hard to come by in today’s American cinema, where emotion tends to be framed by irony or self-consciousness cuteness (500 Days of Summer). My intro did mention the comedy in the film, but I didn’t stress it enough. Watching it with the Ebertfest audience again taught me that the film cleverly uses humor to lead us into its pathos.
The first half hour handles a lot of narrative business. We need to meet the main characters and learn their situation, of course. We also need an introduction to the trade of encoffinment, the practice of preparing the body of the deceased for cremation. But if the story proceeded chronologically, we wouldn’t get this introductory scene for quite a while. So the film provides a pre-credits flashforward that serves up the process, making it palatable with a dose of humor.
We see Daigo and his crusty boss Sasaki visiting a household and arranging a young woman’s corpse. No, it’s not a woman: Daigo discovers that the corpse has a penis. Should they apply male or female make-up? This bit of comedy undercuts the solemnity of the occasion and builds up curiosity: How to resolve the situation? Cut back to Daigo two months earlier, playing the cello in an orchestra that is about to be disbanded. The end of his musical career sends him and his wife back to his hometown seeking a new job.
Since the first scene shows Daigo practicing the “sending-off” trade, we know how that search will turn out. With our superior knowledge we can enjoy all the misunderstandings that fill the first scenes in Yamagata. A misprint in the newspaper ad makes Daigo think he’s applying to a travel bureau; Sasaki hires him without glancing at his résumé; Daigo becomes disturbed at the prospect of handling dead bodies, but the generous advance makes him decide to try. Moreover, in the opening we’ve watched him skillfully executing the routines of the ceremony, so we know that he will eventually succeed. The question is how.
One of the pleasures of movies is showing us how people work. (Think of Steve McQueen running the ship’s engine in The Sand Pebbles, or the arcana of sleight of hand in The Prestige.) So the opening fascinates by introducing us, matter-of-factly, to a craft. In doing so, the scene treats the ceremony fairly objectively. A second ceremony is staged for a video demo, with Daigo serving as the corpse. Here the comedy is even broader, but we’re still learning about the procedures.
A third ceremony, involving the decomposed body of an old woman, is skipped over, but it is heavy in consequences. It drives Daigo to the bathhouse to clean up, and there he reunites with an old friend and his mother, the bathhouse owner. The third encounter also makes Daigo return to playing the cello, using the instrument he was given as a boy. In a way, the whole story offers another chance at childhood. Daigo, feeling guilty for abandoning his mother and angry at the father who deserted them, will be granted a chance to reconcile with both.
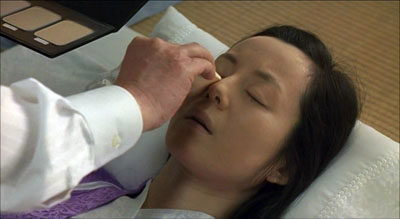
The film’s next sending-off ceremony is a turning point, for it’s Daigo’s first encounter with the dignity of Sasaki’s craft. With the young man we study the tender precision with which Sasaki tucks the dead wife’s garments around her, strokes her face and hands, and applies her favorite lipstick. The husband, initially enraged that Sasaki and Daigo arrived late, ends up moved to tears: “She never looked so beautiful.” Here, fifty minutes into the film, humor is suspended in order to present a compassionate gravity in the face of death. Characteristically, however, a certain lightness returns when in the car Sasaki and Daigo chew noisily on the snacks the husband has given them.
From a penis joke and Daigo’s humiliation at playing dead for the video, the film has led us to care about the characters. We can relax and start to appreciate the depths of what Sasaki and Daigo do. The film will busy itself with new problems—the shame Daigo faces in pursuing this craft, his stratagems for concealing it from his wife Mika, his revived memories of his father, a subplot involving another son impatient with his mother—but we are now ready for these enrichments of the central situation. Eventually too we will see the encoffinment ceremony though other characters’ eyes, as they arrive at our appreciation of its astringent tenderness.
The shrewd placement of the opening flashforward has gently pulled us into the story’s world and its key issue, the tie between the living and the dead. By the time that we return to that family and their transvestite son, the question of how to make up his face has gathered a thick array of associations. The parents’ quarrel anticipates all the other parent/ child relationships that accrue across the film, and the resolution of it, through a father acknowledging his guilt, provides a foretaste of the climax.
The unruffled exactness of Sasaki’s tradecraft is mirrored in Takita’s direction. This is classic Japanese filmmaking: Not a wasted shot, each angle precisely depicting what we need to see at any moment. After the fumbling and flailing displayed by most contemporary Hollywood directors, after filmmakers’ urge to “give a scene energy” manages to muff getting an actor out of a car, it’s a pleasure to watch powerful effects achieved delicately. How many movies can wring tears from uncurling a fist or an image of a smooth stone on a woman’s palm?
Several scenes of the dead include photos of the person in life. Early on, these are given force through simple cutaways.
Once he’s trained us to watch for these photos, Takita can let us compare death and life through more discreet revelations, as when a slight movement of Daigo’s head allows us to see a photo that remains out of focus.
Or take the moment when Daigo comes home after preparing the decomposed body. He gags when he sees that Mika is preparing raw chopped chicken, but then he frantically embraces her. The gestures begin in panic but end in desire. At this point Takita cuts to a new angle, a long shot showing the couple, the table, and the dish that triggered it all.
It’s always sound practice to tactfully recall earlier moments in a film, but the composition also completes the scene’s arc from disgust at death to ardent vitality.
The whole film’s craftsmanship is as warm and fastidious as the job practiced by the send-off experts. At the end, Daigo’s respectful handiwork, with all its dispassionate concern, turns into caresses, the intimate gestures of a son rediscovering a parent through physical contact. Modulation of movement, mood, and attitude; slight variations that become subtly expressive; the prosaic detail that cuts right through you: In this domain the Japanese cinema has no superior. Departures shows that this tradition lives on.
The Omnivoyeur’s dilemma
Otouto.
DB here:
Any major film festival is really many festivals. You meet someone who tells you about all the films they’ve been seeing, and the overlap with your dance card is virtually nil. You’ve both been in the same town, and probably hit the same venues, but you’ve been to different festivals.
Then there are certain syndromes. You convince yourself you need to see 3-5 films a day. Otherwise, what’s the point of traveling all this way? Soon you realize, horribly, that after a couple of days of this regimen, you can’t recall what you’ve seen. Some early afternoon, Festival Amnesia will set in, and you can’t remember what you saw that morning. Was it that ambitious but ultimately unsatisfying little romance from the Bosporus? Or the Chinese movie about moping teenagers trying to leave their dingy village? What were the names of those movies, anyhow?
My own symptoms are getting acute. Twice in recent years, I have found myself in front of a film suddenly realizing that I had seen it at another festival. I had forgotten the title. At least I caught my mistake with the first shots, but I expect that in time I will obliviously sit through the whole movie twice—probably liking it on the first pass and declaring it disappointing on the second.
Then there’s Viewer’s Remorse. Watching 3-5 titles a day, you inevitably encounter some stinkers. You take this philosophically until you meet someone else, who rhapsodizes about the string of masterpieces they’ve seen. Suddenly you realize that you have backed losers. Your friend has had a transformative festival experience, and you might as well have been flossing. Worse, your carefully picked mediocrities swell in your mind, blotting out the good films you managed to catch by dumb luck. Panicked, you thumb through the schedule to see if the great things you’ve missed are playing a second time.
They aren’t.
So film festivals aren’t by any means the sweet deal they may at first seem. Even putting aside queueing, officious door staff, racing between venues, and projection problems, there are plenty of features to make people like me more neurotic than we already are.
But I can’t complain about my latest visit to Hong Kong. True, breathing problems put me out of commission some days and eventually forced me to return home early. My biggest regrets were missing the Zanussi films and the two Angelopolous films, The Weeping Meadow and The Dust of Time. (Watch: Somebody will tell me they are all masterpieces.) Still, I managed to see a fair amount in two mini-festivals I carved out of Filmart and the festival proper.
Turning Japanese, yet again
Golden Slumber.
Parade, from director Isao Yukisada, is an ensemble picture about Tokyo twentysomethings sharing a flat. Their love affairs and marathon viewings of soap operas are disrupted when Satoru, a male prostitute, crashes there one night and winds up hanging around with them. With his blank passivity and ambisexual good looks he arouses their curiosity and, as usual in such movies, winds up changing everyone’s lives. The film was pretty good at portraying the way the kids keep life intriguing by conjuring up mysteries about their neighbors. (Is the man next door running a brothel?) The plot ran out of steam, I thought, but I enjoyed seeing a movie in that sober style that apparently only the Japanese can now pull off: only about 400 shots in nearly two hours, with an unassertive fixed camera that gave the characters room to breathe.
Also about a young cohort, but more action-driven, was Golden Slumber, by Nakamura Yoshihiro. He directed Fish Story (2008), a favorite of mine from last year’s festival. This one is about a hapless young man pulled into a plot to assassinate the prime minister. Threaded with glimpses of his college days, when he and his pals worked in a fireworks shop and became connoisseurs of fast food, the plot follows his efforts to avoid arrest and find how he was framed. Like a lot of contemporary Asian films, Golden Slumber sounds a note of nostalgia not only for long-lost innocence but also for kids’ self-consciously retro tastes in popular culture—in this case, the Beatles song “Golden Slumbers” (“Once there was a way to get back home . . . .”). Less zany than Fish Story, whose story pivoted around how an obscure album prepared for the end of the world, this seemed to me finally quite agreeable, thanks to its likably awkward hero and its lovelorn ending.
Longtime readers of this blog won’t be surprised that one favorite of my personal Japanese mini-fest was Yamada Yoji’s tear-jerker Otouto (aka Ototo, “Younger Brother”), a remake of a 1960 Ichikawa film. A widow who ekes out a living as a pharmacist is about to marry off her beautiful daughter. But during the wedding dinner her ne’er-do-well brother pops up and turns the ceremony into a catastrophe. Japanese movies are very good at evoking social embarrassment, and the disruption caused by Tetsuro makes you wriggle in your seat. He could have been simply a lovable loser, but he’s not that likable, let alone lovable, and his waywardness brings misfortunes on his sister’s family. In this movie about how you must love your relations no matter what, Yamada shows the classic resignation to family ties that has characterized the films from the Shochiku studio since the 1920s.
As usual with Yamada, the direction is crystalline in a way you hardly ever see now: calm framings, unhurried pacing, longish takes (about 12 seconds on average), and lighting and composition that etch every object in relief. When Ginko the mother peels an apple, the skin curls off in a long ribbon, and it’s as fascinating as a car chase in any other movie. In a film in which the camera seldom moves, a handheld shot regains some of its original power. Maybe I’m what Groucho called a sentimental old fluff, but like Kabei–Our Mother, Otouto shows that some cinematic traditions are still worth something.
For the real Shochiku flavor, experts will tell you, you need to return to the 1930s, and the festival did so with its small retrospective of Shimazu Yasujiro. A prolific director of comedies and dramas (he made over a hundred silent films), Shimazu built a reputation in the 1920s with family dramas like Father (1923). Most of his films are lost, and he died in 1945, so he didn’t benefit from the postwar revival of the industry and its growing renown in the West. His most famous work is probably the ingratiating Our Neighbor Mis Yae (1934), which features in the retrospective.
The remaining Shimazu films don’t seem to me to reveal the stylistic consistency we find in Ozu or Mizoguchi or Shimizu. There are flamboyant pictorial touches in First Steps Ashore (1932), a drama of sailors and prostitutes with stark lighting and cluttered sets influenced by The Docks of New York.
A fight scene is rendered in a long-lens shot that looks very modern, though the technique had already been seen in Japanese swordplay films.
Perhaps most original are the variants Shimazu works on a picturesque divider in a waterfront bar, which becomes a fascinating grid that sorts out faces.
Having been trained by this cheese-grater divider, we are given the tougher task of spotting the seaman peering from the distance at our stoker hero and the taxi dancer he rescues. (Not so easy to see in my still: He’s watching from the square and circle aligned horizontally behind the hero’s lips and chin.)
This “game of vision,” where we must strain to see action that’s blocked by bits of setting or furnishing, is characteristic of Japanese film then and since.
Okoto and Sasuke (1935) and Lights of Asakusa (1937), the two Shimazus I caught during my stay, aren’t as visually tricky as First Steps Ashore, but they display Shimazu’s characteristic interest in marginal characters (a blind woman in Okoto, stage performers in Asakusa). Both films close with a self-sacrificing retreat from the world. Later films, including the wonderful Brother and His Younger Sister (1939), would give this retreat a positive ideological spin. Disgusted by office politics, a young man takes his sister and mother to Manchuria to start anew, and the finale shows a clump of earth clinging to the plane wheels, as if a bit of Japan’s very soil would sanctify the empire’s new outpost.
Fei Mu, Film Poet
Nightmares in Spring Chamber.
A second mini-festival during my Hong Kong stay centered on Chinese film history. I’ve mentioned the Patrick Lung Kong titles in an earlier entry. The other prime figure was Fei Mu, celebrated as one of China’s best filmmakers. His Spring in a Small Town (1948) is often considered the greatest of all Chinese films, and it’s not an unreasonable judgment.
Unfortunately, only about half of Fei’s output survives. The earliest film we have is Song of China (aka Filial Piety, 1935), a paean to Confucian virtues. Parents permit their son to move to the city, but the son falls prey to self-indulgence and a temperamental wife. Even when he holds a banquet to honor his parents it is merely an excuse for what the father calls “revelry and gambling.” Soon the daughter is being seduced by a city slicker and told that “parental consent is a timeworn tradition.” This lesson in traditional morality is filmed quite fluently, with telling use of tracking shots, especially during the banquet, and sudden bursts of angular montage.
On Stage and Backstage (1937), from a Fei Mu script, is a 37-minute comedy. A troublesome diva refuses to come to a performance unless she’s paid, but the manager can’t afford it. So a street performer is brought in to substitute for the star in a performance of Farewell My Concubine. While the production is shot frontally and with little depth, director Zhou Yihua contrasts that area of action with the backstage milieu by means of layered compositions and lateral tracking shots through tangles of ropes and props. I enjoyed this charming film when I saw it during my first trip to Hong Kong, and its appeal held up well for me.
I came home too soon to catch Bloodshed on Wolf Mountain (1936), usually considered a strong work, and the little-seen Children of the World (1940). Other films in the series included The Show Must Go on (1952) from a Fei script and Romance in the Boudoir (1960), from Fei’s brother Louis; I already discussed the latter here. There were also two Chinese Opera films. A Wedding in the Dream (1948), China’s first color film, stars the legendary Mei Lanfang, the Peking Opera performer best known in the west who became friends with Chaplin and Eisenstein.
This image from Wedding in the Dream is a posed production still; the film itself, a straightforward record of Mei’s performance, survives in dreadfully worn condition. I found Murder in the Oratory (1937) more intriguing. A man is urged by his mother to murder his wife, the daughter of the man who killed his father. From the start, when an opera stage dissolves into a fully three-dimensional space, you realize that this will be an experiment in creating something halfway between canned theatre and a “filmic” treatment. So we get all the trappings of an opera performance, including stylized movement and singing, but with the camera weaving among the characters and furnishings, finding unusual angles, and even assuming characters’ optical viewpoints.
Far different is another title I enjoyed on my first visit to Hong Kong in 1995. Nightmares in Spring Chamber (1937) is an episode in the portmanteau film Lianhua Symphony. This 13-minute allegory of Japan’s imperial ambitions shows a maniacal frock-coated Japanese pursuing innocent Chinese girls through a vast bare villa. He cackles over a spinning globe and captures one girl, but she’s rescued by the other, a surrogate for the Chinese soldier we glimpse occasionally. Full of canted angles, hallucinatory visions, under lighting, looming shadows, and other trappings of German Expressionism, and accompanied by snatches of Debussy and the Danse macabre, it’s a far cry from the other items in the series, and it suggests a director of considerable versatility.
Last year the Festival premiered the restoration of the rerelease of Fei’s 1940 Confucius, which I wrote about then. This year a second restoration inserted titles to cover the gaps and put some scrappy scenes into their proper order. In addition, a very informative book, Fei Mu’s Confucius, accompanied the screenings. The essays explicate the film from several angles, including its relation to Confucian doctrine, to classic poetry and painting, and to other Fei Mu works.
Thanks to retrospectives like this one, we can see how much Fei’s official masterwork owes to his earlier efforts. There are touches of lighting and staging in these films that are more subtly developed in Spring in a Small Town, and the stately pacing of Confucius is here put to more mundane subject matter. Still, nothing I saw matches the quiet erotic boldness of this milestone of world cinema, which anticipates so much of what we find in Antonioni and other postwar European filmmakers.
So much to see, and even less time than I’d planned: Film festivals somehow manage to leave you unsatisfied and yet feeling full. A nice dilemma to have.
Spring in a Small Town.