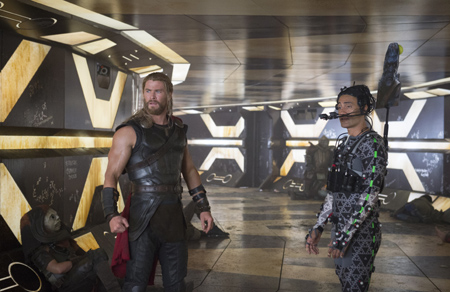Archive for the 'Global film industry' Category
Taika Waititi: The very model of a modern movie-maker
Thor: Ragnarock (2017).
Kristin here:
Not every independent filmmaker secretly longs to direct a big Hollywood blockbuster. Jim Jarmusch made a name for himself 33 years ago with Stranger than Paradise (1984) and won well-deserved praise for Paterson last year. Like other independent directors, Hal Harley turned from filmmaking to streaming television, directing episodes of Red Oaks (2015-2017) for Amazon.
Still, in recent decades the big studios have picked young directors of independent films or low-budget genre ones to leap right into big-budget blockbusters, and those directors have taken the plunge. Doug Liman’s Go (1999) was one of the quintessential indie films of its decade, but his next feature was The Bourne Identity (2002). Colin Trevorrow’s modest first feature Safety Not Guaranteed (2012, FilmDistrict) led straight to Jurassic World (2015, Universal); Gareth Edwards’ low-budget Monsters (2010, Magnolia) was directly followed by Godzilla (2014, Sony/Columbia) and Rogue One (2016, Buena Vista); and Josh Trank went from a $12 million budget for Chronicle (2012, Fox) to ten times that for the $120 million Fantastic Four (2015, Fox).
Something similar happens occasionally with foreign directors. Tomas Alfredson went from the original Swedish version of Let the Right One In (2008, Magnolia) to Tinker Tailor Soldier Spy (2011), and the Norwegian team Joachim Ronning and Espen Sandberg, after making Bandidas (2006, a French import released by Fox) and Kon-Tiki (2012, a Norwegian import released by The Weinstein Company) were hired to do Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Men Tell No Tales (2017, Walt Disney Pictures) and the upcoming Maleficent 2.
Recently women have followed this pattern as well: Patty Jenkins, going from Monster (2003, Newmarket Films) via a long stint in television to Wonder Woman (2017, Warner Bros.), and Ava DuVernay, from two early indie features and Selma (2014, Paramount), again via television, to A Wrinkle in Time (forthcoming 2018, Walt Disney Pictures).
Some of these directors have made the transition smoothly and successfully and some have not. Perhaps the most spectacular success has been that of Christopher Nolan, who went from Memento (2000) via Insomnia (2002) to Batman Begins (2005) and far beyond. But more about him later.
Why have indie filmmakers been able to make this move into the mainstream, often quite abruptly? What about their work appeals to the studios? Of course, there are a variety of reasons, depending on the project and the producers involved. It might be worth following one filmmaker’s career up to the transition to see if there are any clues.
A recent example of this trend is the box-office hit Thor: Ragnarok (released November 3), in the Marvel universe, owned by Walt Disney Studios. Its director, New Zealander Taika Waititi, had directed a handful of modestly budgeted films in his native country. The most successful of those, Boy (2010) made $8.6 million worldwide. After a month in release, Thor will cross $800 million this coming weekend, if not before, and will ultimately gross more than 100 times as much as Boy.
Every filmmaker takes his or her own path before making this leap into blockbuster projects. Waititi did not set out with the ambition to direct a superhero movie with an absurdly high budget. But his career was so full of luck early on that it hardly could have gone better if he had planned it. If you sought a model path to blockbuster fame, you could do no better than to imitate him.
Start by getting nominated for an Oscar
Waititi was actually preparing for a career as a painter, but he was also doing a lot of performing: stand-comedy and film and television acting, perhaps most notably as one of the young flatmates in Roger Sarkies’ 1999 classic, Scarfies. His first brush with superhero movies came with a small role in Green Lantern, 2011. He also, however, made some short amateur films for the 48-Hour film project in Wellington. (Possibly I saw one of them, since I attended the program of shorts during my first visit to Wellington in 2003.) That led to his first professional film, the 11-minute Two Cars, One Night (above).
Virtually all indies made in New Zealand are funded by the New Zealand Film Commission, and in this case the NZFC’s Short Film Fund financed Two Cars. In January, 2004 it premiered at the Sundance Film Festival, with which Waititi soon became closely linked. It’s available on YouTube, but be prepared to pay close attention if you hope to understand the thick, rural Kiwi dialect of the charming non-professional child actors. (Waititi’s Wikipedia entry has a good rundown of his television and other work as well as his films.)
The film got nominated for a best live-action short Oscar, and although it didn’t win that, it picked up prizes from the Berlin, AFI, Hamburg, Oberhausen, and other festivals, as well as the New Zealand Film and TV Awards. In fact, the short effectively drove Waititi into filmmaking, as he described in a 2007 interview.
I spent years doing visual arts, doing painting and photography, and throughout that whole time I was acting quite a lot in theater and New Zealand film and television. But for that whole time I wasn’t really sure which one of those artforms I wanted to concentrate on, and eventually just started tinkering around with writing little short films. I made one short film which ended up doing really well, and then suddenly I was propelled into this job as a filmmaker. But actually I didn’t want to be a filmmaker, I just wanted to make short films to try it out! I still don’t really think I’m a filmmaker.
Perhaps not then, but the idea must be quite plausible to him by now.
Get support from the Sundance Institute ASAP
The short and its Oscar nomination launched Waititi’s move into feature filmmaking. In 2005 it was announced that Waititi had been accepted into the Sundance Directors and Screenwriters labs to develop A Little Like Love, which later became his first feature, Eagle vs. Shark.
It was really good for getting my feature made, because I kinda got fast-tracked in the funding process. In New Zealand, the only way of getting a movie done is through the Film Commission, the government agency that funds everything. So I got nominated for the Oscar in March 2005, I wrote the screenplay for Eagle vs Shark in May, then we went to the Sundance Lab in June, got funding from the Film Commission in August, and we were shooting in October.
In January, 2007, Eagle vs. Shark premiered at Sundance. It got a small release in the USA. Having followed filmmaking in New Zealand during work on my book The Frodo Franchise, I saw it here in Madison in a nearly empty theater.
Asked in the same interview about his experiences in the Sundance Directors and Screenwriters labs, Waititi replied:
It was just totally amazing, totally amazing! I think the biggest thing I took away from the lab was finding the tone for the film. In the marketing, it’s going to be presented as a comedy, and I think that’s where a lot of the problems will lie. Even in the criticism of the film, people don’t get that it’s not pure comedy.
The power of the Sundance Institute in supporting first feature films and in others ways promoting independent production worldwide is surprisingly little known. Most obviously the labs have aided the development of American indies like Miranda July’s Me and You and Everyone We Know (2005), as well as supporting Damien Chazelle’s Whiplash (2014) through the Sundance Institute Feature Film Program. The Institute’s impact goes beyond the USA. The first film made in Saudi Arabia, Haifaa Al Mansour’s Wadjda (2012), also was aided by the Sundance Institute Feature Film Program. Sundance’s website emphasizes that the grants and participation in labs is not just for a single film:
With more than 9,000 playwrights, composers, digital media artists, and filmmakers served through Institute programs over the last 35 years, the Sundance community of independent creators is more far-reaching and vibrant than ever before.
If you have been selected for any Institute lab program or festival, you are a member of this community. Sundance alumni receive support throughout their careers, including access to tools, resources and advice as well as artist gatherings and more. Alumni are also encouraged to actively contribute to the Institute’s creative community and to our mission to discover and develop work from new artists.
Waititi’s second feature, Boy, which premiered in January, 2010, carries the credit, “Developed With The Assistance Of Sundance Institute Feature Film Program.” What We Do in the Shadows, co-directed with comedy partner Jemaine Clement, premiered there in January, 2014, though without a credit to Sundance, but his most recent independent feature, Hunt for the Wilderpeople (January, 2016) gave “Special Thanks” to the Sundance Institute.
Asked about Sundance in 2016, when Hunt for the Wilderpeople had just premiered, he declared,
I’ve got a good relationship with them, I love coming here, and I do think that this festival suits my films rather than most of the festivals I’ve been to. I’m not going to Cannes, you know.
Waititi has taken his membership in this exclusive group seriously. In 2015, Sundance created the Native Filmmakers Lab, aimed at supporting Native American and other Indigenous filmmakers. Such support had been a policy in choosing filmmakers to participate in labs up to that point, and Waititi is mentioned as one of past participants. He also is listed as the only individual among a list of major institutions contributing to the Sundance Institute Native American and Indigenous Program:
The Sundance Institute Native American and Indigenous Program is supported by the W. K. Kellogg Foundation, Surdna Foundation, Time Warner Foundation, Ford Foundation, Native Arts and Cultures Foundation, SAGindie, Comcast-NBCUniversal, the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation, Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences, the Embassy of Australia, Indigenous Media Initiatives, Taika Waititi, and Pacific Islanders in Communications.
Taika Waititi’s father was a member of the Te Whānau-ā-Apanui group of the Mãori people, and his mother was a Russian Jew. Waititi used the name Taika Cohen in his early years as an actor.
Live in Wellington, New Zealand
Part of Waititi’s luck consisted of starting his filmmaking career just as Peter Jackson and his team had transformed filmmaking in New Zealand by building up the state-of-the-art production and post-production facilities needed to made The Lord of the Rings (2001-2003). Peter Jackson, Richard Taylor, and Jamie Selkirk, the co-owners of The Stone Street Studios, Weta Workshop, and Weta Digital, offered services by these firms at cost to New Zealand filmmakers; Peter Jackson and Fran Walsh did the same with The Film Unit (later Park Road Post), a lab with sound-mixing and editing facilities. Indeed, it was the only lab for developing film in New Zealand.
From the start, Waititi could take advantage of this large support system. The credits for Two Cars, One Night (above) include Weta Digital for the special effects and The Film Unit for post-production. The credits of the 2005 short version of What We Do in the Shadows thanked Selkirk and Park Road Post, as well as Peter Jackson, who offered undisclosed further support. Beasts of the Southern Wild credits three companies for its special effects, including Weta Digital for the wild-pig episode and Park Road Post for sound-mixing, along with “Very Special Thanks” to the Sundance Institute.”
Having toured those companies in 2003 and 2004, I can state that few indie filmmakers have had access to such sophisticated facilities.
Make some good, eccentric films
Waititi’s first film to capture wide attention was Boy, based loosely on his experiences growing up in a village on the upper east coast of New Zealand’s north island. The director played the young protagonist’s irresponsible father, a comically incompetent gang leader who had deserted his family and returns home to dig up some stolen money he and his pals have buried in an enormous field–without marking where it is. He strives to be a good father, mostly by showing off, as when he tries to casually leap into his car through the window and ends up in a struggle that embarrasses Boy in front of his young friends (above).
It’s a film that brought the blend of poignancy and offbeat humor that Waititi had established in Eagle vs. Shark to maturity.
He followed it with a very different film, What We Do in the Shadows (2014), a mockumentary about three vampire flatmates living in Wellington. (The reference in Thor: Ragnarok to a three-pronged spear for killing multiple vampires is to the main characters of Shadows.) Here the poignancy is gone and the humor pushed to extremes in a fashion that recalls the Monty Python team. In fact, it’s similar to the silly humor of Thor.
Finally, Hunt for the Wilderpeople, a tale of a rebellious foster child going on the lam with his foster “uncle” in the wilds of New Zealand, ultimately made somewhat less money internationally than the other two but had an enthusiastic critical response in the US. There was some Oscar buzz surrounding it, though no nominations resulted. It was, however, a huge success at home, becoming the highest-grossing New Zealand film ever, taking that title away from Boy, which had taken it from the classic Once Were Warriors (1994). It also won best film, director, actor, supporting actress, and supporting actor at the New Zealand Film and TV Awards. Sam Neill’s participation in this film led to his cameo in Thor: Ragnarock.
Coming into the mid 2010s, Waititi had built a solid career as an independent maker of likable, entertaining, skillfully made–and funny– films.
Get tapped for a blockbuster
How and why did Marvel choose Waititi? One might suspect that it was because he already had a Disney connection. When Moana was in pre-production, they brought in many people native to Polynesia to help with planning and design. (Little-known fact: New Zealand is part of Polynesia.) Waititi was brought aboard and wrote a first draft of the script, most of which was altered in later drafts.
When asked if the Moana work had anything to do with the Marvel invitation, however, Waititi responded,
Well, they had not heard of the Disney thing so I know that wasn’t part of it. They have a record making out there and exciting choices and I think what they said to me was, “We want it to be funny and try a whole new tack. We love your work and do you think you can fit in with this?”
Waititi got the call from Marvel in 2015, when he was editing Hunt for the Wilderpeople. USA Today interviewed him in early 2016, when the film premiered.
“They were looking for comedy directors,” he says. “They had seen What We Do in the Shadows and Boy. They especially liked Boy.”
The result was exactly what the Marvel people were after, since the largely positive reviews have invariably cited the humorous, even self-parodic tone of the film. In interviews, Waititi has often spoken of the scene in which Thor and the Hulk have a fight and then sit down to talk about their feelings (top). He wanted to add it because it was the sort of thing that never happens in superhero movies. The Marvel people seem to have liked it. An excerpt provided the tag ending for the first official trailer.
Upstage your actors
I would wager that fans know more about what Taika Waititi looks like than they do about most of the other blockbuster directors mentioned above. He already enjoyed something of a fan base from his earlier films, largely the cult following of What We Do in the Shadows. He remains an actor, playing a major role in some of his own films (Boy, What We Do in the Shadows) and a minor one in others. He’s been a stand-up comic, so he can keep the patter going in interviews and fan-convention panels.
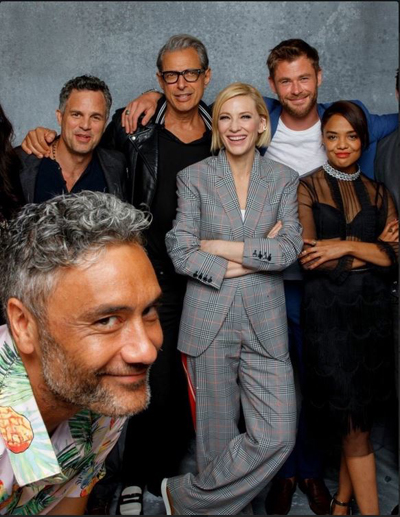
In July, he stole the Thor: Ragnarok Hall H panel at Comic-Con, cracking up the big stars on the panel and getting more laughs from the audience than all of them put together. Waititi’s public persona makes him resemble a character in one of his own films.
Indeed, he again played a supporting character in Thor: Ragnarok, though not exactly in persona proper: Korg, the fighter made of stone. Waititi did both the motion capture and the voice for Korg, and I found the first scene between him and Thor to be the funniest in the whole film.
Even before the release of the film, Waititi quickly gained a reputation for his eccentric clothing preferences. He wore a matching pineapple-print shirt and shorts to the Comic-Con panel (seen in two of the above images). Ava DuVernay was widely quoted as calling Waititi the “best-dressed helmer” in the entertainment world, including in The Hollywood Reporter‘s story on how the director has become a “fashion superhero.” Maybe Waititi is not yet as recognizable to the public as the stars in his film are, but that may not last long. On the day Thor: Ragnarok was released, GQ profiled him, with several photos in different outfits, declaring that he “drips with cool.”
Waititi does cool things that appeal to fans. To raise the money to release Boy in the North American market, he started a Kickstarter campaign with a goal of $90,000 and raised $110,796. He directed one of the popular series of comic Air New Zealand safety announcements based on The Lord of the Rings and The Hobbit, “The Most Epic Safety Video Ever Made,” with himself playing the Gandalf-like wizard (see bottom). He has 262 thousand followers on twitter and tweets frequently. (This does not count the many unofficial pages like TaikaWaititi Fashion, with 978 followers.)
One-for-them, one-for-me respectability
Once admired indie directors start making blockbusters, they often stress that it is a way of getting smaller budgets for more personal projects of the sort that made them admired to begin with. The generation of movie brats, such as Francis Ford Coppola, established this notion of trade-offs with the big studios.
Perhaps as successfully as anyone in Hollywood, Christopher Nolan has shown quite clearly that such trade-offs can work. Once Memento (2000) made his reputation, he followed it with one mid-budget film, Insomnia (2002) and reached the heights of superhero-dom with Batman Begins. The pattern of alternating personal and one-for-them films is evident from the budgets and worldwide grosses of his subsequent films–although he has become so popular that most studios would happily settle for his “one-for-me” grosses:
Memento (2000, reported budget $9 milion; worldwide about $40 million), Insomnia (2002, reported budget $46 million; worldwide $113 million), Batman Begins (2005, reported budget $150 million; worldwide $375 million), The Prestige (2006, reported budget $40 million; worldwide $110 million), The Dark Knight (2008, reported budget $185 million; worldwide, $1. 005 billion), Inception (2010, reported budget $160 million; worldwide $825 million), The Dark Knight Rises (2012, reported budget $250 million; worldwide $1.085 billion), Interstellar (2014, reported budget $165 million; worldwide $675 million), and Dunkirk (2017, reported budget $100 million, worldwide $525 million, with an Oscar-season re-release announced).
Waititi has invoked this notion of returning to his indie roots at intervals. In 2015 We’re Wolves, a sequel to What We Do in the Shadows, was announced, again to be co-directed by Jemaine Clement. Presumably, however, that project was put on hold, but not abandoned, for Thor. He has other scripts in the drawer and in one interview says, “I’m excited to go back and do those, and then I’d like to come back and do something else here. You know, a one-for-them, one-for-you kind of scenario.”
He has specifically said he would be up for another Thor film:
“I would like to come back and work with Marvel any time, because I think they’re a fantastic studio, and we had a great time working together,” Waititi told RadioTimes.com. “And they were very supportive of me, and my vision.
“They kind of gave me a lot of free reign [sic], but also had a lot of ideas as well. A very collaborative company.”
Specifically, he went on, “I’d love to do another Thor film, because I feel like I’ve established a really great thing with these guys, and friendship.
“And I don’t really like any of the other characters.”
The question is, will Hollywood let him go, at least for now?
Waititi’s first decade or so of filmmaking suggests some reasons why he was approached to make a $180 million epic. The Marvel producers were specifically looking for comedy. Comedies are supposedly harder to sell abroad, but put funny material into a big sci-fi film, and it can do just fine overseas. Many of the other indie filmmakers who made this transition started with genre films–low budget crime or sci-fi films.
Moreover, the Marvel producers who approached him were also willing to give him a free rein, so they were presumably trusting and open to someone whose work they admired. Not all producers would be so lenient. It no doubt helped that in this case, the studio was specifically looking for something original and funny–in short, different from the stolid reputation that the Thor films had gained among critics and viewers alike.
The Most Epic Safety Video Ever Made (c. 2014)
Thrill me!
Based on a True Story (Polanski, 2017).
DB here:
Three examples, journalists say, and you’ve got a trend. Well, I have more than three, and probably the trend has been evident to you for some time. Still, I want to analyze it a bit more than I’ve seen done elsewhere.
That trend is the high-end thriller movie. This genre, or mega-genre, seems to have been all over Cannes this year.
A great many deals were announced for thrillers starting, shooting, or completed. Coming up is Paul Schrader’s First Reformed, “centering on members of a church who are troubled by the loss of their loved ones.” There’s Sarah Daggar-Nickson’s A Vigilante, with Olivia Wilde as a woman avenging victims of domestic abuse. There’s Ridley Scott’s All the Money in the World, about the kidnapping of J. Paul Getty III. There’s Lars von Trier’s serial-killer exercise The House that Jack Built. There’s as well 24 Hours to Live, Escape from Praetoria, Close, In Love and Hate, and Extremely Wicked, Shockingly Evil and Vile, featuring Zac Efron as Ted Bundy. Claire Denis, who has made two thrillers, is planning another. Not of all these may see completion, but there’s a trend here.
Then there were the movies actually screened: Based on a True Story (Assayas/ Polanski), Good Time (the Safdie brothers), L’Amant Double (Ozon), The Killing of a Sacred Deer (Lanthimos), The Merciless (Byun), You Were Never Really Here (Ramsay), and Wind River (Sheridan), among others. There was an alien-invasion thriller (Kiyoshi Kurosawa’s Before We Vanish), a political thriller (The Summit), and even an “agricultural thriller” (Bloody Milk). The creative writing class assembled in Cantet’s The Workshop is evidently defined through diversity debates, but what is the group collectively writing? A thriller.
Thrillers seldom come up high in any year’s global box-office grosses. Yet they’re a central part of international film culture and the business it’s attached to. Few other genres are as pervasive and prestigious. What’s going on here?
A prestigious mega-genre
Vertigo (Hitchcock, 1958).
Thriller has been an ambiguous term throughout the twentieth century. For British readers and writers around World War I, the label covered both detective stories and stories of action and adventure, usually centered on spies and criminal masterminds.
By the mid-1930s the term became even more expansive, coming to include as well stories of crime or impending menace centered on home life (the “domestic thriller”) or a maladjusted loner (the “psychological thriller”). The prototypes were the British novel Before the Fact (1932) and the play Gas Light (aka Gaslight and Angel Street, 1938).
While the detective story organizes its plot around an investigation, and aims to whet the reader’s curiosity about a solution to the puzzle, in the domestic or psychological thriller, suspense outranks curiosity. We’re no longer wondering whodunit; often, we know. We ask: Who will escape, and how will the menace be stopped? Accordingly, unlike the detective story or the tale of the lone adventurer, the thriller might put us in the mind of the miscreant or the potential victim.
In the 1940s, the prototypical film thrillers were directed by Hitchcock. I’ve argued elsewhere that he mapped out several possibilities with Foreign Correspondent and Saboteur (spy thrillers) Rebecca and Suspicion (domestic suspense), and Shadow of a Doubt (domestic suspense plus psychological probing). Today, I suppose core-candidates of this strain of thrillers, on both page and screen, would be The Ghost Writer, Gone Girl, and The Girl on the Train.
In the 1940s, as psychological and domestic thrillers became more common, critics and practitioners started to distinguish detective stories from thrillers. In thinking about suspense, people noticed that the distinctive emotional responses depend on different ranges of knowledge about the narrative factors at play. With the classic detective story, Holmesian or hard-boiled, we’re limited to what the detective and sidekicks know. By contrast, a classic thriller may limit us to the threatened characters or to the perpetrator. If a thriller plot does emphasize the investigation we’re likely to get an alternating attachment to cop and crook, as in M, Silence of the Lambs, and Heat.
Today, I think, most people have reverted to a catchall conception of the thriller, including detective stories in the mix. That’s partly because pure detective plotting, fictional or factual, remains surprisingly popular in books, TV, and podcasts like S-Town. The police procedural, fitted out with cops who have their own problems, is virtually the default for many mysteries. So when Cannes coverage refers to thrillers, investigation tales like Campion’s Top of the Lake are included.
In addition, “impure” detective plotting can exploit thriller values. Films primarily focused on an investigation, but emphasizing suspense and danger, can achieve the ominous tension of thrillers, as Se7en and The Girl with the Dragon Tattoo do. More generally, any film involving crime, such as a heist or a political cover-up, could, if it’s structured for suspense and plot twists, be counted as part of the genre.
Yet tales of police detection aren’t currently very central to film, I think. Their role, Jeff Smith suggests, has been somewhat filled by the reporter-as-detective, in Spotlight, Kill the Messenger, and others. Straight-up suspense plots are even more common, as in the classic victim-in-danger plots of The Shallows, Don’t Breathe, and Get Out. Tales of psychological and domestic suspense coalesced as a major trend in Hollywood during the 1940s. It became so important that I devoted a chapter to it in my upcoming book, Reinventing Hollywood: How 1940s Filmmakers Changed Movie Storytelling. (You can get an earlier version of that argument here.)
By referring to “high-tone” thrillers, I simply want to indicate that major directors, writers, and stars have long worked in this broad genre. In the old days we had Lang, Preminger, Siodmak, Minnelli, Cukor, John Sturges, Delmer Daves, Cavalcanti, and many others. Today, as then, there are plenty of mid-range or low-end thrillers (though not as many as there are horror films), but a great many prestigious filmmakers have tried their hand: Soderbergh (Haywire, Side Effects), Scorsese (Cape Fear, Shutter Island), Ridley Scott (Hannibal), Tony Scott (Enemy of the State, Déja vu), Coppola (The Conversation), Bigelow (Blue Steel, Strange Days), Singer (The Usual Suspects), the Coen brothers (Blood Simple, No Country for Old Men et al.), Shyamalan (The Sixth Sense, Split), Nolan (Memento et al.), Lee (Son of Sam, Clockers, Inside Man), Spielberg (Jaws, Minority Report), Lumet (Before the Devil Knows You’re Dead), Cronenberg (A History of Violence, Eastern Promises), Tarantino (Reservoir Dogs, Pulp Fiction, Jackie Brown), Kubrick (Eyes Wide Shut), and even Woody Allen (Match Point, Crimes and Misdemeanors). Brian De Palma and David Fincher work almost exclusively in the genre.
And that list is just American. You can add Almodóvar, Assayas, Besson, Denis, Polanski, Figgis, Frears, Mendes, Refn, Villeneuve, Cuarón, Haneke, Cantet, Tarr, Gareth Jones, and a host of Asians like Kurosawa Kiyoshi, Park Chan-wook, Bong Joon-ho, and Johnnie To. I can’t think of another genre that has attracted more excellent directors. The more high-end talents who tackle the genre, the more attractive it becomes to other filmmakers.
Signing on to a tradition
Creepy (Kurosawa, 2016).
If you’re a writer or a director, and you’re not making a superhero film or a franchise entry, you really have only a few choices nowadays: drama, comedy, thriller. The thriller is a tempting option on several grounds.
For one thing, there’s what Patrick Anderson’s book title announces: The Triumph of the Thriller. Anderson’s book is problematic in some of its historical claims, but there’s no denying the great presence of crime, mystery, and suspense fiction on bestseller lists since the 1970s. Anderson points out that the fat bestsellers of the 1950s, the Michener and Alan Drury sagas, were replaced by bulky crime novels like Gorky Park and Red Dragon. As I write this, nine of the top fifteen books on the Times hardcover-fiction list are either detective stories or suspense stories. A thriller movie has a decent chance to be popular.
This process really started in the Forties. Then there emerged bestselling works laying out the options still dominant today. Erle Stanley Gardner provided the legal mystery before Grisham; Ellery Queen gave us the classic puzzle; Mickey Spillane provided hard-boiled investigation; and Mary Roberts Rinehart, Mignon G. Eberhart, and Daphne du Maurier ruled over the woman-in-peril thriller. Alongside them, there flourished psychological and domestic thrillers—not as hugely popular but strong and critically favored. Much suspense writing was by women, notably Dorothy B. Hughes, Margaret Millar, and Patricia Highsmith, but Cornell Woolrich and John Franklin Bardin contributed too.
I’d argue that mystery-mongering won further prestige in the Forties thanks to Hollywood films. Detective movies gained respectability with The Maltese Falcon, Laura, Crossfire, and other films. Well-made items like Double Indemnity, Mildred Pierce, The Ministry of Fear, The Stranger, The Spiral Staircase, The Window, The Reckless Moment, The Asphalt Jungle, and the work of Hitchcock showed still wider possibilities. Many of these films helped make people think better of the literary genre too. Since then, the suspense thriller has never left Hollywood, with outstanding examples being Hitchcock’s 1950s-1970s films, as well as The Manchurian Candidate (1962), Seconds (1966), Wait Until Dark (1967), Rosemary’s Baby (1968), The Parallax View (1974), Chinatown (1974), and Three Days of the Condor (1975), and onward.
Which is to say there’s an impressive tradition. That’s a second factor pushing current directors to thrillers. It does no harm to have your film compared to the biggest name of all. Google the phrase “this Hitchcockian thriller” and you’ll get over three thousand results. Science fiction and fantasy don’t yet, I think, have quite this level of prestige, though those genres’ premises can be deployed in thriller plotting, as in Source Code, Inception, and Ex Machina.
Since psychological thrillers in particular depend on intricate plotting and moderately complex characters, those elements can infuse the project with a sense of classical gravitas. Side Effects allowed Soderbergh to display a crisp economy that had been kept out of both gonzo projects like Schizopolis and slicker ones like Erin Brockovich.
Ben Hecht noted that mystery stories are ingenious because they have to be. You get points for cleverness in a way other genres don’t permit. Because the thriller is all about misdirection, the filmmaker can explore unusual stratagems of narration that might be out of keeping in other genres. In the Forties, mystery-driven plots encouraged writers to try replay flashbacks that clarified obscure situations. Mildred Pierce is probably the most elaborate example. Up to the present, a thriller lets filmmakers test their skill handling twists and reveals. Since most such films are a kind of game with the viewer, the audience becomes aware of the filmmakers’ skill to an unusual degree.
Thrillers also tend to be stylistic exercises to a greater extent than other genres do. You can display restraint, as Kurosawa Kiyoshi does with his fastidious long-take long shots, or you can go wild., as with De Palma’s split-screens and diopter compositions. Hitchcock was, again, a model with his high-impact montage sequences and florid moments like the retreating shot down the staircase during one murder in Frenzy.
Would any other genre tolerate the showoffish track through a coffeepot’s handle that Fincher throws in our face in Panic Room? It would be distracting in a drama and wouldn’t be goofy enough for a comedy.
Yet in a thriller, the shot not only goes Hitchcock one better but becomes a flamboyant riff in a movie about punishing the rich with a dose of forced confinement. More recently, the German one-take film Victoria exemplifies the look-ma-no-hands treatment of thriller conventions. Would that movie be as buzzworthy if it had been shot and cut in the orthodox way?
Fairly cheap thrills
Non-Stop (Collet-Serra, 2014). Production budget: $50 million. Worldwide gross: $222 million.
The triumph of the movie thriller benefits from an enormous amount of good source material. The Europeans have long recognized the enduring appeal of English and American novels; recall that Visconti turned a James M. Cain novel into Ossessione. After the 40s rise of the thriller, Highsmith became a particular favorite (Clément, Chabrol, Wenders). Ruth Rendell has been mined too, by Chabrol (two times), Ozon, Almodóvar, and Claude Miller. Chabrol, who grew up reading série noire novels, adapted 40s works by Ellery Queen and Charlotte Armstrong, as well as books by Ed McBain and Stanley Ellin. Truffaut tried Woolrich twice and Charles Williams once. Costa-Gavras offered his version of Westlake’s The Ax, while Tavernier and Corneau picked up Jim Thompson. At Cannes, Ozon’s L’Amant double derives from a Joyce Carol Oates thriller the author calls “a prose movie.”
Of course the French have looked closer to home as well, with many versions of Simenon novels by Renoir, Duvivier, Carné, Chabrol (inevitably), Leconte, and others. The trend continues with this year’s Assayas/Polanski adaptation of the French psychological thriller Based on a True Story.
In all such cases, writers and directors get a twofer: a well-crafted plot from a master or mistress of the genre, and praise for having the good taste to disseminate the downmarket genre most favored by intellectuals.
Another advantage of the thriller is economy. There are big-budget thrillers like Inception, Spectre, and the Mission: Impossible franchise. But the thriller can also flourish in the realm of the American mid-budget picture. Recently The Accountant, The Girl on the Train, and The Maze Runner all had budgets under $50 million. Putting aside marketing costs, which are seldom divulged, consider estimated production costs versus worldwide grosses of these top-20 thrillers of the last seven years. The figures come from Box Office Mojo.
Taken 2 $45 million $376 million
Gone Girl $61 million $369 million
Now You See Me $75 million $351 million
Lucy $40 million $463 million
Kingsman: The Secret Service $81 million $414 million
Then there are the low-budget bonanzas.
The Shallows $17 million $119 million
Don’t Breathe $9.9 million $157 million
The Purge: Election Year $10 million $118 million
Split $9 million $276 million
Get Out $4.5 million $241 million
Of course budgets of foreign thrillers are more constrained, and I don’t have figures for typical examples. Still, overseas filmmakers tackling the genre have an advantage over their peers in other genres. Thrillers are exportable to the lucrative American market, twice over.
First, a thriller can be an art-house breakout. Volver, The Lives of Others, and The Girl with the Dragon Tattoo (2009) all scored over $10 million at the US box office, a very high number for a foreign-language film. Asian titles that get into the market have done reasonably well, and enjoy long lives on video and streaming. The Handmaiden and Train to Busan, both from South Korea, doubled the theatrical take of non-thrillers Toni Erdmann and Julieta, as well as that of American indies like Certain Women and The Hollers. Elsewhere, thrillers comprised two of the three big arthouse hits in the UK during the first four months of this year: The Handmaiden, a con-artist movie in its essence, and Elle, a lacquered woman-in-peril shocker.
Second, a solid import can be remade with prominent actors, as Wages of Fear and The Secret in Their Eyes were. Probably the most high-profile recent example was The Departed, a redo of Hong Kong’s Infernal Affairs. Sometimes the director of the original is allowed to shoot the remake, as happened with The Vanishing, Loft, and Hitchcock’s The Man Who Knew Too Much.
Even if the remake doesn’t get produced, just the purchase of remake rights is a big plus. I remember one European writer-director telling me that he earned more from selling the remake rights to his breakout film than he did from the original. He was also offered to direct the remake, but he declined, explaining: “If someone else does it, and it’s good, that’s good for the original. If it’s bad, people will praise the original as better.” And by making a specialty hit, the screenwriter or director gets on the Hollywood radar. If you can direct an effective thriller, American opportunities can open up, as Asian directors have discovered.
Thrillers attract performers. Actors want to do offbeat things, and between their big-paycheck parts they may find the conflicted, often duplicitous characters of psychological thrillers challenging roles. For Side Effects Soderbergh rounded up name performers Jude Law, Rooney Mara, Catherine Zeta-Jones, and Channing Tatum. The Coens are skillful at working with stars like Brad Pitt (Burn after Reading). The rise of the thriller has given actors good Academy Award chances too. Here are some I noticed:
Jane Fonda (Klute), Jodie Foster (Silence of the Lambs), Frances McDormand (Fargo), Natalie Portman (Black Swan), Brie Larson (Room), Anjelica Huston (Prizzi’s Honor), Kim Basinger (L.A. Confidential), Rachel Weisz (The Constant Gardener), Jeremy Irons (Reversal of Fortune), Denzel Washington (Training Day), Sean Penn (Mystic River), Sean Connery (The Untouchables), Tommy Lee Jones (The Fugitive), Kevin Spacey (The Usual Suspects), Benicio Del Toro (Traffic), Tim Robbins (Mystic River), Javier Bardem (No Country for Old Men), Mark Rylance (Bridge of Spies).
Finally, there’s deniability. Because of the genre’s literary prestige, because of the tony talent behind and before the camera, and because of the genre’s ability to cross cultures, the thriller can be….more than a thriller. Just as critics hail every good mystery or spy novel as not just a thriller but literature, so we cinephiles have no problem considering Hitchcock films and Coen films and their ilk as potential masterpieces. On the most influential list of the fifty best films we find The Godfather and Godfather II, Mulholland Dr., Taxi Driver, and Psycho. At the very top is Vertigo, not only a superb thriller but purportedly the greatest film ever made.
I worried that perhaps this whole argument was an exercise in confirmation bias–finding what favors your hunch and ignoring counterexamples. Looking through lists of top releases, I was obliged to recognize that thrillers aren’t as highly rewarded in film culture as serious dramas (Manchester by the Sea, Moonlight, Paterson, Jackie, The Fits). But I also kept finding recent films I’d forgotten to mention (Hell or High Water, The Green Room) or didn’t know of (Karyn Kusama’s The Invitation, Mike Flanigan’s Hush). They supported the minimal intuition that thrillers play an important role in both independent and mainstream moviemaking.
And not just on the fringes or the second tier. Perhaps because film is such an accessible art, all movies are fair game for the canon. As a fan of thrillers in all variants, from genteel cozies and had-I-but-known tales to hard-boiled noir and warped psychodramas, I’m glad that we cinephiles have no problem ranking members of this mega-genre up there with the official classics of Bergman, Fellini, and Antonioni (who built three movies around thriller premises). Of course other genres yield outstanding films as well. But we should be proud that cinema can offer works that aren’t merely “good of their kind” but good of any kind. For that reason alone, ambitious filmmakers are likely to persist in thrill-seeking.
Thanks to Kristin, Jeff Smith, and David Koepp for comments that helped me in this entry. Ben Hecht’s remark comes from Philip K. Scheuer, “A Town Called Hollywood,” Los Angeles Times (30 June 1940), C3.
You can get a fair sense of what the Brits thought a thriller was from a book by Basil Hogarth (great name), Writing Thrillers for Profit: A Practical Guide (London: Black, 1936). A very good survey of the mega-genre is Martin Rubin’s Thrillers (Cambridge University Press, 1999). David Koepp, screenwriter of Panic Room, has thoughts on the thriller film elsewhere on this blog.
Having just finished Delphine de Vigan’s Based on a True Story, I can see what attracted Assayas and Polanski. The film (which I haven’t yet seen) could be a nifty intersection of thriller conventions and the art-cinema aesthetic. As a gynocentric suspenser, though, the book doesn’t seem to me up to, say, Laura Lippman’s Life Sentences, a more densely constructed tale of a memoirist’s mind. And de Vigan’s central gimmick goes back quite a ways; to mention its predecessors would constitute a spoiler. For more on women’s suspense fiction, see “Deadlier than the male (novelist).” For more on Truffaut’s debt to the Hitchcock thriller, try this.
The Workshop (Cantet, 2017).
The end of Theatoriums, too
Moving Picture World (February 1908), 135.
DB here:
Vis-à-vis the last post, all of three hours ago, Alert Reader and arthouse impresario Martin McCaffery sends the above.
Actually, it’s much in the spirit of current jeremiads: Movies and their theatoriums better shape up, or they’ll be finished–like bicycles and Ping-Pong.
History is so cool. Full text here and below. There’s also a 1908 rebuttal, in the spirit of movies-are-doing-just-fine-thanks, here. Both courtesy the prodigious Lantern.
Pandora’s digital box: End times
35mm projection booth at Market Square Cinema, Madison, Wisconsin; 10 May 2013.
DB here:
When exactly did film end? According to the mass-market press, here are some terminal dates.
July 2011: Technicolor closes its Los Angeles laboratory.
October 2011: Panavision, Aaton, and Arri all announce that they will stop manufacturing film cameras.
November 2011: Twentieth Century Fox sends out a letter asserting that it will cease supplying theatres with 35mm prints “within the next year or two.”
January 2012: Eastman Kodak files for bankruptcy protection.
March 2013: Fuji stops selling negative and positive film stock for 35mm photography.
Each of these events looked like turning points, but now they seem merely phases within a gradual shift. After all, the digital conversion of cinema has been in the works for about fifteen years. The key events–the formation of a studio consortium to set standards, the cooperation of technical agencies and professional associations, the lobbying for 3D by top-money directors–didn’t get as much coverage. Because so many maneuvers took place behind the scenes and unfolded slowly, digital cinema seemed very distant to me. To understand the whole process, I had to do some research. Only in hindsight did the quiet buildups and sudden jolts form a pattern.
On the production end, it seems likely that filmmakers will continue to migrate to digital formats at a moderate pace. Proponents of 35mm are fond of pointing out that six of 2012’s Oscar-nominated pictures were shot wholly or partly on film. (To which you might well respond, Who cares about Oscar nominations? I would agree with you.) Yet even 35mm adherent Wally Pfister, DP for Christopher Nolan, admits that within ten years he will probably be shooting digital.
What about the other wings of the film industry, distribution and exhibition? Put aside distribution for a moment. Digital exhibition was the central focus of the blog series that became my e-book Pandora’s Digital Box. There I try to trace the historical process that led up to the big changes of 2009-early 2012.
Today, a year after Pandora’s publication, everybody knows that 35mm exhibition of recent releases is almost completely finished. But let’s explore things in a little more detail, including poking at some nuts and bolts. As we go, I’ll link to the original blog entries.
Top of the world!
35mm print of Warm Bodies about to be shipped out from Market Square Cinemas, Madison, Wisconsin; 10 May 2013.
The overall situation couldn’t be plainer. At the end of 2012, reports David Hancock of IHS Screen Digest, there were nearly 130,000 screens in the world. Of these, over two-thirds were digital, and a little over half of those were 3D-capable.
Northern European countries have committed heavily to the new format. The Netherlands, Denmark, and Norway are fully digital, while the UK is at 93% saturation and France is at 92%. Both national and EU funds have helped fund the switchover. Hancock reports that in Asia, Japanese screens are 88% digital, and South Korean ones are 100%. China is the growth engine. Rising living standards and swelling attendance have triggered a building frenzy. Over 85%, or 21,407 screens are already digital, and on average, each day adds at least eight new screens.
In the US and Canada, there were at end 2012 still over 6400 commercial analog screens, or about 15% of the nearly 43,000 total. My home town, Madison, Wisconsin, has a surprising number of these anachronisms. One multiplex retains at least two first-run 35mm screens. Five second-run screens at our Market Square multiplex have no digital equipment. That venue ran excellent 2D prints of Life of Pi (held over for seven weeks) and The Hobbit: An Unexpected Journey. It’s currently screening many recent releases, including the incessantly and mysteriously popular Argo. In addition, our campus has several active 35mm venues (Cinematheque, Chazen Museum, Marquee). Our department shows a fair amount of 35mm for our courses as well; the last screening I dropped in on was The Quiet Man in the very nice UCLA restoration.
Unquestionably, however, 35mm is doomed as a commercial format. Formerly, a tentpole release might have required 3000-5000 film prints; now a few hundred are shipped. Our Market Square house sometimes gets prints bearing single-digit ID numbers. Jack Foley of Focus Features estimates that only about 5 % of the copies of a wide US release will be in 35mm. A narrower release might go somewhat higher, since art houses have been slower to transition to digital. Focus Features’ The Place Beyond the Pines was released on 1442 screens, only 105 (7%) of which employed 35mm.
In light of the rapid takeup of digital projection, Foley expects that most studios will stop supplying 35mm copies by the end of this year. David Hancock has suggested that by the end of 2015, there won’t be any new theatrical releases on 35mm.
Correspondingly, projectionists are vanishing. In Madison, Hal Theisen, my guide to digital operation in Chapter 4 of Pandora, has been dismissed. The films in that theatre are now set up by an assistant manager. Hal was the last full-time projectionist in town.
The wholesale conversion was initiated by the studios under the aegis of their Digital Cinema Initiatives corporation (DCI). The plan was helped along, after some negotiation, by the National Association of Theatre Owners. Smaller theatre chains and independent owners had to go along or risk closing down eventually. The Majors pursued the changeover aggressively, combining a stick—go digital or die!—with several carrots: lower shipping costs, higher ticket prices for 3D shows, no need for expensive unionized projectionists, and the prospect of “alternative content.”
The conversion to DCI standards was costly, running up to $100,000 per screen. Many exhibitors took advantage of the Virtual Print Fee, a subsidy from the distributors that paid into a third-party account every time the venue booked a film from the Majors. There were strings attached to the VPF. The deals are still protected by nondisclosure agreements, but terms have included demands that exhibitors remove all 35mm machines from the venue, show a certain number of the Majors’ films, equip some houses for 3D, and/or sign up for Network Operations Centers that would monitor the shows.
The biggest North American chains are Regal, AMC, and Cinemark. They control about 16,500 screens and own fifty-three of the sixty top-grossing US venues. The Big Three benefited considerably from the conversion. By forming the consortium Digital Cinema Solutions, they were able to negotiate Wall Street financing for their chains’ digital upgrade. They also formed National Cinemedia, a company that supplied FirstLook, a preshow assembly of promos for TV shows and music. Under the new name of NCM Network, the parent company now links 19,000 screens for advertising purposes. NCM also supplies alternative content to over 700 screens under the Fathom brand: sports, musical acts, the Metropolitan Opera, London’s National Theatre, and other items that try to perk up multiplex business in the middle of the week.
The digital conversion has coincided with—some would say, led to—a greater consolidation of US theatre chains. Last year the Texas-based Rave circuit was dissolved, and 483 of its screens, all digital, were picked up by Cinemark. More recently, the Regal chain gained over 500 screens by acquiring Hollywood Theatres. The biggest move took place in May 2012 when the AMC circuit was bought for $2.6 billion by Dalian Wanda Group, a Chinese real estate firm. Combined with Wanda’s 750 mainland screens, this acquisition created what may be the biggest cinema chain in the world. Wanda has declared its intent to invest half a billion dollars in upgrading AMC houses.
Meanwhile, vertical integration is emerging. In 2011, Regal and AMC founded Open Road Films, a distribution company. It has handled such high-profile titles as The Grey, Killer Elite, End of Watch, Side Effects, and The Host. Cinedigm, which began life as a third-party aggregator to handle VPFs, has moved into distribution too, billing itself as a company merging theatrical and home release strategies tailored to each project.
It has become evident that the digital revolution in exhibition permits American studio cinema a new level of conquest and control. Distribution, we’ve long known, is the seat of power in nearly all types of cinema. Whatever the virtues of YouTube, Vimeo, and other personal-movie exhibition platforms, film’s long-standing public dimension, the gathering of people who surrender their attention to a shared experience in real time, is still largely governed by what Hollywood studios put into their pipeline.
On the margins and off-center
View of Madagascar from the Sky-Vu Drive-In, 2012. Photo by Duke Goetz.
While the Big Three grew stronger, what became of smaller fry? John Fithian of NATO suggested that any cinema with fewer than ten screens could probably not afford the changeover, and David Hancock suggested that up to 2000 screens might be lost. Recent speculation is that drive-ins will be especially hard hit. Pandora’s Digital Box, as blog and then book, surveyed those most at risk: the small local cinemas and the art houses.
I fretted about the loss of small-town theatres, not least because I grew up with them. Data on such local venues are hard to get, so for the blog and the book I went reportorial and visited two Midwestern towns. The blogs related to them are here and here.
The long-lived Goetz theatres in Monroe, Wisconsin, consist of a downtown triplex and the Sky-Vu drive-in. They’re run by Robert “Duke” Goetz, whose grandfather built the movie house back in 1931. Duke is a confirmed techie and showman. He designs and cuts ads and music videos to fill out his show, and he personally converted all his screens to 7.1 sound. So it’s no surprise that he’s a fan of digital cinema. But back in December his digital upgrade took place during the worst box-office weekend since 2008–a bad omen, if you believe in omens.
Seventeen months later, Duke reports more cheerful news. Everything has gone according to plan and budget. The company that installed the equipment, Bright Star Systems of Minneapolis, has proven reliable and excellent in answering questions. Duke especially likes the fact that digital projection allows him to “play musical chairs with the click of a mouse.”
I can move movies from screen to screen in short order or download from the Theatre Management System to any and all theatres at one time, so when the weather is damn cold, for Monday -Thursday screening I’ll play the shorter movies in the biggest house. . . . I am now able to start the movies from the box office with software that accesses the TMS, so it’s just like being at the projector. It saves my guys time and keeps them where the action is.
Duke programs his offerings to suit the tastes of the town, and for the most part, he can get the films he wants. Attendance at the three-screener has increased, partly, he thinks, because of digital. Even marginal product gets a bit more attention when people find the image appealing. Duke says that Skyfall played so long and robustly partly because it was a strong movie, but also because the presentation was compelling. Thanks to his subwoofer, viewers could feel onscreen shotgun blasts in their backsides. Immersion goes only so far, however. Duke remains leery of 3D: “People are tired of paying the extra charge, and with the economy in my area I’ll still wait.”
Contrary to trends elsewhere, the Sky-Vu has benefited strongly from digital display. Duke’s was the first North American drive-in to sign up for the NEC digital system. People comment on how the bright, sharp image has improved their experience. The drive-in had “a tremendous summer,” with the first Saturday night of Brave, coupled with Avengers, proving to be the best night of the year. Measured by both box office returns and number of admissions, that show did better than Transformers the summer before. Last fall, when the Sky-Vu was the only area drive-in still open, some patrons traveled 2 1/2 hours from Illinois. The only problem with digital under the stars was that Duke couldn’t get a satisfactory VPF deal for an outdoor cinema because he doesn’t run it year-round.
While Duke runs the Goetz theatres as a family business, the JEM Theatre in Harmony, Minnesota is more of a sideline for its owner-operator Michelle Haugerud. A single screen running only at 7:30 on weekend nights, the JEM plays a unifying role in the life of the town. But it’s a small market. Harmony consists of only 1020 people (many of them Amish), and the median household income is about $30,000. Michelle had to finance the conversion through donations and bank assistance. The task was complicated by the unexpected death of her husband Paul, who ran the JEM with her.
Michelle reports that the digital conversion hasn’t increased business. Box office was about the same in 2012 as in 2011, and so far this year ticket sales have been down. It has been a slow winter and spring throughout the industry, and people are hoping the summer blockbusters will lift revenues. But the JEM faces particular problems that the Goetz doesn’t.
Michelle wants to show films in first run, as Duke does. But the distributors typically demand that she play a new movie for three weeks. That’s not feasible in her small town, so Michelle winds up missing out on films she knows would draw well. In addition, she’d be willing to screen two shows a day, the first a kid movie and the second an adult picture, but the companies don’t allow this double-billing. Moreover, she thinks that the shrinking windows–the speed with which films come out on Pay Per View, VOD, and DVD–are eroding her audience. “Many people are willing to wait for these releases since they now realize they will be out shortly after they hit the theatres anyway.”
Michelle and her family run the JEM as much for the community as for themselves. She is hoping for better times.
Converting to digital has made showing movies easier, and I have had no issues with the new equipment. However, it has not helped with ticket sales at all. I am holding on and committed to this year, but if I get to the point where it is costing me personally to stay open, I don’t think I will continue. I love having the movie theatre and would love to keep it going. I do feel if I had a say on what movies I showed and when, I would do so much better.
Kickstarting the arthouse
Robert Redford addresses the Art House Convergence, January 2013.
Several managers and programmers of arthouse cinemas around the country have formed an informal association, the Art House Convergence. It meets once a year just before the Sundance Film Festival, which many members attend. When I visited the conference in 2012, the digital transition was the central topic. It aroused curiosity, bewilderment, frustration, and some annoyance. This year, things were different.
Participants were calmly reconciled to the inevitable, and some looked forward to it. On one of the few panels that took up the subject, moderator Jan Klingelhofer of Pacific Film Resources began by asking: “How many of you are still on the fence about digital?” Just one hand was raised.
On the panel, technology experts from major companies showed how new projection systems could be installed even in offbeat venues. The New Parkway in Oakland was once a garage, and the Mary D. Fisher Theatre in Sedona is a converted bank. Panelists also gave information on choices of technology, from lamps and servers to the best screen materials for 3D. The teeth-gnashing is over, and now art-house leaders are focusing on practicalities: the best strategies suited for their business models.
A private, for-profit art house faces many of the problems faced by Duke Goetz and Michelle Haugerud, except that the art-house is screening films of narrower appeal. Because the audience is smaller and more select, many art houses have become not-for-profit entities created by community cultural organizations. They are dependent on donations, private or public patronage, and miscellaneous income from many activities, not only screenings but filmmaking classes, special events, and other activities. A good example of the diversity of outreach an arthouse can have is the Bryn Mawr Film Institute, whose director, the estimable Juliet Goodfriend, also coordinates the annual AHC survey. So the coordinators of the not-for-profit theatre must persuade boards of directors and generous patrons that the digital upgrade is necessary.
Small venues, whether private or not-for-profit, can’t benefit much from economies of scale. A multiplex can amortize its costs across many screens, but a big proportion of art houses boasts only one or two. Add to this the fact that multiplexes are encroaching on the art-house turf with crossover films like Moonrise Kingdom and upscale entertainment like opera and plays from Fathom. Even museums are starting to install digital equipment and play arts-related programming.
The chief task, of course, is paying for the upgrade. Last year’s AHC session was often about the money. Small local cinemas like the Goetz could benefit from VPF deals, but for many art houses such deals weren’t a good option. These houses don’t run enough films from the Majors to repay the subsidy. While they’re often eager to take something from Fox Searchlight, Focus Features, and the Weinstein company, they book a lot from IFC, Magnolia, and other independent distributors.
A common solution was to launch fundraising campaigns from the community, much as Michelle did in Harmony. One of the biggest initiatives was that conducted by the boundlessly energetic John Toner and Chris Collier of Renew Theaters in Pennsylvania. Without going for a VPF, they raised $367,000 to pay for converting three screens (one in 3D). John and Chris are vigorous advocates for the new format, and their “This Is Digital Cinema” series treats restorations of classics like Gilda and The Ten Commandments as showcases for the DCP. At AHC 2013, John and Chris provided an entertaining PowerPoint presentation on how they managed the switchover; for a prose version, you can read John’s account here.
Likewise, the Tampa Theatre raised $89,000 from its community. But what if your community can’t sustain such a big campaign? I hadn’t predicted in Pandora how powerful Kickstarter would be in the film domain, and the results are initially encouraging. Donations to the Cable Car Cinema and Cafe of Providence surpassed the goal by six thousand dollars, and the theatre is already preparing for the new equipment. The final 35mm program will be, what else?, The Last Picture Show, complete with pulled-pork sandwiches. The Crescent Theatre of Mobile won nine thousand more than it asked for, and Martin McCaffrey, venerable moving spirit of Montgomery’s Capri Theatre, followed suit and came out ahead by about the same amount.
Currently the Kickstarter site lists dozens of conversion projects, and many have met their goals–with Boston’s Brattle and LA’s Cinefamily hitting over a hundred thousand dollars. The pitches are pretty creative (“The Cinefamily is a non-profit movie theater with awesome programming, but crappy everything else”) and so are the giveaways (the Skyline drive-in of Everett, Washington offers a vintage speaker box that’s “clean and suitable for presentation”).
So maybe predictions were too pessimistic. Will we lose so many theatres to the switchover? Maybe not. But raising money for the initial conversion isn’t the whole story.
Technology: Running in place to keep up?
In the shift to digital projection, some would say the pivotal moment came with the success of Avatar and other 2009 3D releases (Monsters vs. Aliens, Ice Age: Dawn of the Dinosaurs, and Up). In 2009 there were about 7400 digital screens; a year later there were nearly 15,000. Then the acceleration began. Ten thousand screens converted in 2011 and eight thousand more the following year.
But I see 2005 as another major marker. In 2004, there were only 80 digital screens in the US. By the end of 2005, there were over 1500. The early adopters were pushed by the emergence of 3D, heavily touted by several major directors at NATO’s annual convention and the strong 3D releases of The Polar Express (2004) and Chicken Little (2005). So there were two bursts of digital adoption, both driven by 3D.
With 3D as a Trojan horse, digital entered exhibition. The format eventually settled on was the Digital Cinema Package, an ensemble of files gathered on a hard drive. The movie, with subtitles and alternate soundtracks, is wrapped in a thick swath of security files. The studios, petrified of piracy, had delayed the completion of digital cinema for some years until an ironclad system was protecting the movie. The DCP can be opened only with a customized key, delivered to the theatre separately from the hard drive. Typically the key is sent on a flash drive, so that the staff member need not retype the tediously long string of alphanumeric characters that make it up. Copying that key into the theatre’s server, its theatre management system, or the projector’s media block allows the film to be played on a certified projector.
A digital projector suitable for multiplex use relies on one of two available technologies. Sony’s proprietary system works only on its own projectors. Texas Instruments’ Digital Light Processing (DLP) technology was licensed to three manufacturers: Christie, Barco, and NEC. By fall 2010, all four companies had produced high-level, and quite expensive, machines capable of producing 4K displays. The rush to convert led to thousands of units being bought over a few months. This was great for business in the short term, but how could the manufacturers count on selling the product in the years and decades ahead? Michael Karagosian sketches the problem: “The big challenge today for technology companies is the massive downturn in sales that is destined to take place the last half of this decade as the digital installation boom ends.”
One way to expand the market was offered by cheaper machines. In fall of 2012, all the manufacturers introduced DCI-compliant projectors suitable for screens around thirty feet wide. The machines were still quite expensive, but they were marginally more affordable for the smaller or independent exhibitors who had been reluctant to convert or who had missed the deadlines for VPF financing. To maintain a quality difference from high-end machines, the cheaper versions typically lacked some features. They might be capable of only 2K, or they might not permit a wide range of frame rates, or they offered less brilliant illumination.
Another answer to a saturated market was continuous research and development. No sooner had exhibitors installed the “Series 2” projectors introduced in late 2009-early 2010 than speculation began about enhancements. How soon, for instance, might we expect 6K or even 8K resolution? Two other innovations were responding to problems with the dimness of digital 3D images.
One possibility was laser projection, which would be expected to brighten the image considerably. Laser projectors may start appearing in Imax cinemas later this year, but for most venues the current costs are prohibitive, running about half a million dollars per installation.
3D light levels could also be boosted by shooting and showing at higher frame rates than the standard 24. Peter Jackson famously experimented with 48-frame production on The Hobbit: An Unexpected Journey, and some theatres screened it that way. Response was mostly skeptical, with critics complaining of the hypersharp, “soap-opera” effect onscreen. The frame-rate issue has mostly quieted down, but it did trigger academic studies of the perceptual psychology involved in frame rates. In addition, James Cameron has insisted that his sequels to Avatar will be shot at an even higher frame rate. Most projectors require new software in order to increase frame rates.
Alongside developments in the projection market have come new devices for sound. As Jeff Smith pointed out in an earlier entry, innovative sound systems have been enabled by the switchover to digital presentation. 35mm film stock constrained the amount of physical space on the film strip that auditory information could occupy. Now that sound is a matter of digital files, sound designers can add many tracks for greater immersive effects—so-called “3D audio” platforms. Barco’s Auro 11.1 system and Dolby Atmos position several more speakers around the auditorium, including ones high above the audience. Costs of installation for these systems run from $40,000 to $90,000.
Still, projector and sound-system manufacturers can assume that business will continue because of the pressures for change inherent in digital technology. Experienced equipment installers suggest that a digital projector’s life is between five and ten years. Already the Series 1 projectors introduced in 2005 are becoming obsolete. Chapin Cutler, of Boston Light & Sound, notes:
A digital projector is a computer that puts out light. How many computers will you go through in the next ten years?
How many Series 1 projectors are still in use and supported by the manufacturers? Try buying parts for them. I know of one that was purchased four years ago that has been pushed into a corner. It has sat there for about two months so far, with no end in sight. (Thank heavens they still have their 35 mm gear!) It is broken and the manufacturer cannot supply parts; their customer service department doesn’t know about the machines, as they have only had to deal with the newer models; and the parts are not listed in their own internal parts book. Yes, four years old.
When replacement parts are available, they can be exceptionally pricey. A projector’s light engine, central to the image display, can run $22,000. And if an exhibitor buys a brand-new projector some years from now, the studios aren’t likely to launch a new round of VPF financing.
So even if a theatre can afford the expense of conversion today, upgrades and maintenance will demand big commitments of money in the years ahead. John Vanco, Senior VP and manager of New York City’s IFC Center, has put it well:
Many, many small, independent theatres, which are vital to the survival of non-studio films, will end up being fatally hobbled by the transition. They may be able to raise funds to cover the initial conversion, but what will crush many of them in the long term is the ongoing capital resources that will be necessary to continue to have DCI-compliant equipment in the next ten and twenty years. . . .
In the same way the current inexorable pattern of planned obsolescence forces consumers to continually repurchase computers, phones, etc., cinemas too are going to find that they have to spend much more for cinema equipment over the next twenty years than they did, say, from 1980 to 2000. . . . So these technological progressions will make it harder for those small theatres to survive.
Dylan Skolnick of Huntington, New York’s Cinema Arts Centre adds to Vanco’s point. “We have great supporters, but I can’t go back to them every five-to-ten years with a ‘Digital Upgrade or Die’ campaign.”
The problem is acute for small and art-house venues, but it isn’t minor for the Big Three either. Unless film attendance jumps spectacularly (it has been more or less flat for several years), exhibitors may need to raise ticket prices and the costs of concessions. This strategy may work in urban areas but won’t be popular elsewhere. Moreover, part of the boom in box-office revenues during recent years has been due to the upcharge for 3D features. But in the US, 3D revenues are currently leveling off at about $1.8 billion, a drop from the format’s 2010 peak of $2.14 billion. In 2012, 3D’s market share slipped as well. It isn’t clear that people would flock to 3D if the images were brighter. And if 3D television takes off, stereoscopic cinema will seem less compelling as a novelty.
Some observers hold out hope for glasses-free 3D technology in theatres, a change that would probably boost business. But the difficulties of creating 3D of this sort for multiplex venues are immense. The glasses-free platforms proposed by Dolby are aimed at small displays, like TVs, smartphones, and tablets. Of course, if 3D without glasses were devised for big screens, it would almost certainly demand yet another projector redesign.
No more silver bricks
When it comes to distribution, digital isn’t there yet. The UPS and Fed Ex corps still bring movies to multiplexes the old-fashioned way. The little briefcases are a lot lighter than hulking metal shipping cases, but we’re still dealing with physical artifacts.
At least for the moment. Festival submissions are already being placed in Cloud-based lockers like Withoutabox in an effort to replace DVD screeners. Online delivery is already being used for many of those operas, ballets, and other forms of “alternative content” flowing onto screens from various suppliers. A Norwegian distributor sent a 100 gigabyte local film, fully encrypted, to forty cinemas in the spring of 2012. This and experiments in other countries employ fiber-based networks, but the Digital Cinema Distribution Coalition, a joint venture among Hollywood studios and the Big Three exhibition chains, is exploring satellite systems.
So much for the impassive silver bricks in their cute pink beds on the cover of Pandora’s Digital Box. They may become as quaint as film reels and changeover cue-marks. For a time, the hard drives may survive as backup systems that will reassure exhibitors, but eventually no physical site may serve as the movie’s home. An exhibitor will download the film to the server, apply a decryption key sensitive to time, venue, and machine, and the movie will be, as they say, “ingested.”
In the Pandora book, I included chapters on other exhibition domains I haven’t revisited here. Take archives. More and more studios refuse to rent prints, will not prepare DCPs of most classic titles, and won’t let theatres screen Blu-ray discs commercially. So repertory cinemas turn to archives, seeking to rent 35mm copies that may be irreplaceable. In addition, archivists, laboring under tight budget constraints, are racing to preserve and restore their material on film, which remains the most stable support medium. At the same time, archives are expected to get involved in preparing high-quality digital versions of popular classics. Henceforth most restorations that you see will be circulated on 2K or 4K, as Metropolis, La Grande Illusion, and Les Enfants du Paradis have been in recent years.
Film festivals, as Mike King, one of our Wisconsin Film Festival programmers observes, are now file festivals. Cameron Bailey reported that of the 362 titles screened at TIFF last year, only fifty-one were on film. Last month, our annual event ran twenty-one new films on film; most were 16mm experimental items. The remaining 132 were on DCP, HDCam, Quicktime files, or DVD/Blu-ray. On the plus side, independent filmmakers are learning to encode their films in the DCI-compliant format, often without layers of security, so at least in this respect technology may not be a severe barrier to entry.
As for me, I’m still in the midst of churn. I watch movies on film, on DCP, on DVD and Blu-ray and VOD, even on laserdisc, and sometimes on my iPad. But my research will miss 16mm and 35mm. Some of the questions I like to ask can be answered only by handling film. Last weekend I sat down at a Steenbeck flatbed and counted frames in passages of Notorious and King Hu’s Dragon Inn. This sort of scrutiny is virtually impossible on DVDs and Blu-rays, which don’t preserve original film frames.
What I’ve lost as a specialist is offset by many gains. Since the arrival of Betamax and VHS, nontheatrical cinema has expanded to limits we couldn’t have imagined in the 1970s. Thanks to consumer digital formats, more people have more access to more movies of all sorts than at any point in history. Although some aspects of film-originated movies are hard to recover on digital playback, we can study cinema craft to an extent that wasn’t possible before. Digitization has allowed sophisticated visual and sonic analysis to bloom on websites around the world. See, among many examples, Jim Emerson’s Scanners and A. D. Jameson’s work on Big Other.
With the rise of nontheatrical consumption, though, what’s most at risk is theatrical cinema: film viewing as a public forum. Exhibition outside film festivals is already starting to narrow to recent releases and a few approved classics. We will be able to watch The Suspended Step of the Stork and Leviathan on our home screens for a long time to come, but very seldom on the scale that benefits them most.
As ever, the problem of technology isn’t only a matter of hardware. Technology develops within institutions. Hollywood has standardized a new technology favoring its goals. The institutions of minority film culture–festivals, art houses, archives, local cinemas, schools–need to be robust and resourceful to maintain all the types of cinema we have known, and the types we might yet discover.
Since Pandora was published, a very comprehensive guide to the mechanics of digital projection has appeared: Torkell Saætervadet’s FIAF Digital Projection Guide, and it’s a must. One rich treatise I didn’t cite in Pandora is Hans Keining’s 2008 report 4K+ Systems: Theory Basics for Motion Picture Imaging. Michael Karagosian’s website is an excellent general source on digital exhibition in the late 2000s.
Screen Daily provides a good overview of the new technology on display at CinemaCon 2013. For general background on industry trends after the changeover, see the Variety article “Filmmakers Lament Extinction of Film Prints.” As for archives, Nicola Mazzanti edited a very useful European Commission study, Challenges of the Digital Era for Film Heritage Institutions (Berlin/ UK, 2012). May Haduong surveys current problems of print access and film archives in “Out of Print: The Changing Landscape of Print Accessibility for Repertory Programming,” The Moving Image (Fall 2012), 148-161. The piece requires online library access, but a summary is here.
Much of the industry information in this entry came from proprietary reports published in IHS Screen Digest. Thanks to David Hancock for his assistance with other data, and to Patrick Corcoran of NATO for updated information on theatre conversion. Thanks as well to Chapin Cutler, Duke Goetz, Michelle Haugerud, and Dylan Skolnick for permission to quote them. I’m also grateful to Jack Foley of Focus Features and Joshua Hittesdorf of Market Square Cinemas. Finally, I want to thank Russ Collins and his colleagues at the Art House Convergence for mounting another splendid event and for inviting me back last January. I continue to learn from the discussions on the AHC listserv, and I’m particularly grateful to John Toner for his reports on independent cinemas’ funding efforts.
Other entries on this site offer material on the digital transition. There’s “It’s good to be the King of the World,” on James Cameron’s push for 3D TV; “ADD = Analog, digital, dreaming,” about the powers of photochemical cinema on display at the Toronto International Film Festival 2012; “Digital projection, there and here,” some notes on the situation in Western Europe; and “Side by side: Quick catchups,” includes notes on sources for studying digital cinema. In “16, still super,” veteran programmers talk about how they continue to rely on this format; in the process they convey their commitment to providing unusual fare.
P. S. 15 May 2013: Rebecca Hall of the extraordinary Northwest Chicago Film Society has posted a continually updated list of theatres that are dedicated to showing films in 16mm and 35mm.
P.P.S. 12 June: David Hancock has just presented a very full report entitled “Digital Cinema Worldwide: 35mm phased out in many countries, though some lag behind.” It is published in the June IHS Screen Digest. One of my remarks above has been corrected in light of some information in the report: I claimed that Belgium has fully converted, but David’s figures indicate 96.5% conversion.
David predicts that by end 2013, 90 % of world screens will be digital. Even India is making the move, as circuits relying on DVD or other low-resolution sources are converting to DCI-compatible equipment. Those regions slowest to convert include Italy, Greece, and Spain (not surprisingly, given recent austerity policies), as well as areas of South America and the Pacific (e.g., Thailand, the Philippines). Thanks to David and his team at IHS Screen Digest for their comprehensive coverage of this process.
Dragon Inn (King Hu, 1967). 35mm frame enlargement, taken on Fujichrome 64.