Do not forget to return your 3D glasses
Wednesday | July 27, 2011 open printable version
open printable version
(Yours for $11 in theaters equipped with RealD systems, but you don’t get the pouch they came in at the opening midnight screenings)
Kristin here:
As 3D really took hold in the wake of the release of Avatar in December 2009, we got used to hearing that roughly 60% of a blockbuster’s income came from 3D. This summer the figure has hovered around 40%. Both figures are highly misleading. How much does 3D really bring in?
Yes, 40% of the total amount for almost all big 3D films this summer was for tickets sold for 3D screenings. But looked at another, more realistic way, 3D films as such made far less than that for their makers and the theaters that showed them.
That’s because a lot of the people buying tickets to see a film in 3D probably would have gone to see it if it had been strictly 2D. That, is, 3D itself is probably not luring in many new viewers. If every person buying a 3D ticket would refuse to see the film in 2D, then, yes, the figure would be 40%. I’m sure a small percentage of people are lured to see a given title only because it is in 3D. There’s no way to know how many, however, so let’s stick to the facts we do know.
The basic fact is that the money brought in by a film made in 3D only amounts to the supplement paid by the spectator beyond what he or she would have paid if the film were in 2D. Let’s assume that the supplement is $3 and that a 3D admission costs $12 and a 2D one $9. Let’s also assume for the sake of argument that everyone who saw the film in 3D for $12 would pay $9 to see the same film if it were only available in 2D. (In reality, there’s also evidence that 3D keeps some people away from a film altogether if they don’t have access to 2D screenings. I’ll assume these two groups, the 3D enthusiasts and the 2D hold-outs, cancel each other out.) Removing the $3 supplement takes away 25% of the ticket price. So what the 3D process as such really adds to the box-office total is 10% (that’s 25% of 40%). To put it another way, $9 of the $12 for the ticket is just for the film qua film, the rest is for its being in 3D.
In addition, the costs for the glasses and any extra labor they entail have to come out of that $3. I don’t know what such costs are, so I’ll leave those expenses out of the calculations.
Consider the opening weekend of Captain America, which grossed $65.7 million, 40% of which came from theaters equipped with 3D. But it’s really 10% by my reasoning, so it’s not $26.3 million that 3D generated, but $6.57 million. Assuming further that it costs about $30 million to make a film in 3D or convert it to 3D in post-production, Captain America would have to run in the U.S. market for around four weeks with no decline in attendance to break even on 3D. But most films decline on their second weekend, unless they open in more theaters or have terrific word of mouth. Even The Lord of the Rings: The Fellowship of the Ring, which had lots of repeat business, declined 19% on its second weekend.
Of course, the popularity of 3D films is holding up better abroad than in the domestic market–so far. Still, we have to remember that only about half of the worldwide box-office receipts make their way back to the studios. That seems to imply that a film would have to gross $600 million internationally to break even on the addition of costs for 3D. ($300 million going to the studios, roughly 10% of which is paid for by 3D supplements=$30 million.) Some films do gross that much. Pirates of the Caribbean: On Stranger Tides, Transformers: Dark of the Moon, the final Harry Potter installment have passed that mark this year. It’s not common, though.
Naturally if a film takes in as much as 60% of its box-office from 3D screens, as Transformers: Dark of the Moon did, 15% of the costs of 3D will be paid for by the process.
How consistent is the trend?
Let’s look at the major 3D films out so far this year in terms of percentages of gross vs. percentages of theaters:
Film: Release Date (% of BO from 3D / % of locations showing 3D)
Green Hornet: January 14 (69% / 75%)
Gnomeo and Juliet: February 11 (58% / 60%)
Rio: April 15 ( 58% / 68%)
Thor: May 6 (60% / 69%)
Pirates of the Caribbean: 4: May 20 (46% / 66%)
Kung Fu Panda: 2 May 26 (45% / 69%)
Green Lantern: June 17 (45% / 71%)
Cars 2: June 24 (37% / 61%)
Transformers: Dark of the Moon: 3 July (60% / 70%)
Captain America: July 22 (40% / 68%)
Opening weekend only : Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows: Part 2: July 15 (68% / 71%)
[Added July 31: The opening weekend for The Smurfs followed a similar pattern. The July 29 release made 45% of its gross from 3D engagements; 60% of its venues showed 3D. As Box Office Mojo points out, on the same weekend in 2009, G-Force made 56% of its opening-weekend gross in 3D, which showed in only 43% of theaters.]
(Granted, there is a problem with such figures. The percentage of locations showing 3D is based on theaters, not screens. Any multiplex showing 3D counts as 1, even though it may have 3 screens showing 3D and 2 showing 2D. Whether those two 2D screens would be credited to the venues showing 3D or 2D is not stated. Unfortunately, the way box-office figures are reported, there is no way to calculate by numbers of screens. We’ll do what we can with what we’ve got. In addition, venues without 3D tend to be one- or two-screen theaters in small towns. That 2D now brings in more than half the gross income for most 3D films is all the more impressive.)
Now for the list of films. There are interesting patterns here. First, the drop in 3D percentages came at about the time when the summer-movie season began, and with one exception is has proven surprisingly consistent, hovering in the 40-45% range. Second, the greater the gap between the percentage of income and the percentage of theaters, the less well 3D would presumably be performing for each release. Thus although Transformers: Dark of the Moon brought in a higher percentage of 3D income, it performed proportionately no better than, say, Rio. Third, as long as the percentage of income is less than the percentage of theaters, it should be the case that the average per theater for 2D showings should be higher than those for 3D—which is true for every film.
More theaters, fewer tickets
The decline in 3D’s contribution to film grosses has come despite the fact that the number of screens in the U.S. equipped to show 3D has gone up roughly six-fold since the beginning of 2009: from under 2,000 to over 12,000. Take a look at this graph from The Economist (derived from information supplied by BTIG Research and Screen Digest). The point where the lines cross is May, 2011:
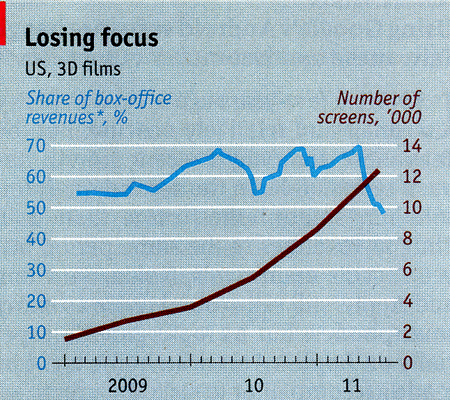 Kvetching about 3D as a process and as a method of purse-gouging has declined somewhat, or at least that’s my impression. It’s not gone, though. Take a look at Mark Harris’ smart piece, “Honk If You’re Sick of 3-D!” in the June 24 Entertainment Weekly. Justin Chang’s Variety review of Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows: Part 2, while generally very favorable, concludes: “D[irector of].p.[hotography] Eduardo Serra’s brooding, beautiful work gains little, however, from the underwhelming stereoscopic conversion; this is the first Potter film to be released entirely in 3D as well as 2D, and on this count, at least, one can be grateful that it will be the last.” “The “entirely in 3D” phrase refers to earlier episodes which have had a few scenes in 3D.)
Kvetching about 3D as a process and as a method of purse-gouging has declined somewhat, or at least that’s my impression. It’s not gone, though. Take a look at Mark Harris’ smart piece, “Honk If You’re Sick of 3-D!” in the June 24 Entertainment Weekly. Justin Chang’s Variety review of Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows: Part 2, while generally very favorable, concludes: “D[irector of].p.[hotography] Eduardo Serra’s brooding, beautiful work gains little, however, from the underwhelming stereoscopic conversion; this is the first Potter film to be released entirely in 3D as well as 2D, and on this count, at least, one can be grateful that it will be the last.” “The “entirely in 3D” phrase refers to earlier episodes which have had a few scenes in 3D.)
There was also the controversy back in late May over whether 3D lenses, which notoriously cast dim images of 3D films, were being left on movie projectors for 2D screenings, thereby dimming the light getting to the screen for them as well. I don’t have the space to trace that discussion, but you can read about it in the original Boston Globe article, Roger Ebert’s indignant follow-up, and an expert projectionist’s assessment of the situation. Here the problems were being discussed largely in relation to 2D screenings.
But for quite some time now the larger 3D-equals-dim-images notion got wide coverage, and the topic had featured in many articles and postings critical of 3D. All that must have had some impact. In June Variety announced that for Transformers: Dark of the Moon Paramount would take “the unprecedented step of releasing a special digital print aimed at delivering almost twice the brightness of standard 3D projection.” These special prints, however, only went to about 2,000 theaters, those with RealD systems. But would prospective ticket purchasers know which cinemas had these prints? As Variety pointed out, “Exhibs may want to avoid planting the notion that some 3D screens are better than others when there’s no price distinction between the screens.” Given that it’s almost impossible these days to call a movie theater and ask a question, I doubt whether many moviegoers who attended Transformers knew which version they saw. Paramount’s move was obviously a desirable one, but it can’t account for the relatively high percentage of the film’s 3D income. (The New York Times also covered Michael Bay’s and Paramount’s efforts to promote screen brightness for the film.)
All in all, evidence seems to show that many theater owners are losing business by showing 3D films. Of Captain America’s total gross income, 40% came from the theaters showing 3D, which amounted to 68% of all venues (2511 locations out of 3715). Flip the figures, and the 32% of the theaters showing the film in 2D brought in 60% of the gross. On average, if you were an exhibitor playing the film, you made more money if you showed it in 2D. A lot more. Even not being able to charge $3 extra.
Box Office Mojo’s report on Captain America‘s first weekend confirmed that attendance was not dropping for the film as a whole, but that a greater proportion of people were opting for 2D: “While the gross difference was a sliver, Captain had eight percent greater estimated attendance than Thor, which received more bolstering from 3D (and had IMAX): Captain‘s 3D share was 40 percent at 2,511 3D locations, compared to Thor‘s 60 percent at 2,737.
Industry spokespeople are putting a good face on all this. Rob Moore, vice-chairman of Paramount, seized upon Transformers: Dark of the Moon’s 60% 3D opening-weekend share to boost the format to Variety: “‘There are so many 3D releases, audiences now are going to pick and choose which films to see in 3D,’ Moore said, before adding that the format has become a tool more for event filmmaking. ‘If the 3D is good, audiences are going to pay for it.'” But of course, most theater-goers don’t know whether the 3D is good until they have already paid for it. They go for other reasons, whether star, director, or genre. Or maybe it’s what their date or friends or family want to see. If it has those factors and it’s in 3D, it might seem worth the extra $3.
The opening weekend for Deathly Hallows might tend to confirm Moore’s claim, but the 3D share of the gross was still slightly below the percentage of 3D theaters, if not by much, and included an unusually large number of Imax locations (274)–which charge an even larger fee for 3D. Given the fans’ frenzy to see Deathly Hallows on its first weekend, they probably bought tickets for whichever screening they could, not much swayed by whether they would be seeing it in 3D or 2D.
Another point before I move on. Consider The Hangover Part II: $80 million dollars announced budget, $562.9 million worldwide gross and still in distribution. No 3D.
Anti-3D sentiment
Some people just don’t like 3D, supplement or no supplement. I went to some of the early releases to keep up with developments in the industry. It’s part of my job, after all. But after I got a sense of what it was like, I gave it up. I think the last 3D film I saw, apart from Werner Herzog’s wonderful Cave of Forgotten Dreams in February, was Avatar in December, 2009, and the one before that Up, in the summer of that year. I just saw Cars 2 the other day, 2D and on 35mm film, a treat that we must savor before release prints on film disappear over the next few years. By the way, Cave of Forgotten Dreams is the only exception to my new avoid-3D rule, and it also happens, proportionate to its budget, to be the most successful 3D film so far this year.
I’ve seen the two Pixar films made since Up only in 2D, and I don’t miss the 3D at all—despite the fact that Pixar’s films are probably the best that have been made during the latest vogue for 3D. Cars 2 naturally had quite a few shots with depth in the set design and staging. It occurred to me when I saw them that I actually might be getting a stronger sense of depth watching them in 2D than in 3D. The human mind has all sorts of ways of reading depth cues in a flat image. 3D tends to exploit only one of them, binocularity, which I suspect minimizes the others. I have no scientific evidence for that, just my own impression formed while watching the film.
I’m far from alone in avoiding 3D. The other day I participated in an online exchange on the subject. Sean Axmaker, contributor to the Parallax View website, wrote on his Facebook page that he had just seen Deathly Hallows 2 on film, in 2D and added, “I’d see “Captain America” here too, but it’s only in 3D and I just don’t see the need to see it with an extra pair of glasses on.”
The issue of studios and theaters switching entirely from 35mm release prints to digital projection would require a whole additional entry. But in late May Variety ran a long story, “Studios must revisit d-cinema,” with people from within the industry recounting dismal experience viewing both 3D and 2D films with digital projection. One 3D system cuts fully half the light from the projector. Cinematographer Roger Bailey is quoted: “It’s unbelievable that in an age when we think we have unbelievable technology, and the studios are talking about eliminating 35mm film prints in the next 18 months, that they haven’t begun to sort out the problems that have been caused by digital projection.”
The Economist ended its recent article, the one that contained the above graph, on a sour note:
Richard Gelfond, the boss of IMAX, reckons customers have become picky. “People used to see something just because it was in 3D,” he says. Now they ask how much pleasure the glasses will add. The explosive “Transformers 3” did well in 3D; perhaps the 2D version was not sufficiently headache-inducing. The key to three-dimensional projects, then, is to put out hugely popular films with extraordinary special effects. Easy.
Speaking of headaches, a small study conducted at the University of California-Berkeley seems to indicate that 3D glasses can cause eyestrain and discomfort. For those who want the full scientific text, it’s here. For a brief summary, go here. The main point is that the eyes naturally try to focus on the screen (the focal distance). The vergence point is where the imaginary lines going out from the 2 slightly separated 3D lenses come together. If it’s in front of or “behind” the screen, eyestrain can occur, since one is trying to focus on two different planes in depth simultaneously. The problem turns out to be worse the further you sit from the screen.
I myself have not noticed eyestrain or headaches caused by watching 3D movies with the current generation of glasses. I could imagine that since eyestrain is cumulative, those who watch large doses of television or spend hours at a 3D gaming console would have greater problems with the glasses.
Whether we want it or not
Business types seem to think people want 3D inserted into their lives. Note the 3D Webcam, pictured at the bottom. The accompanying text says, “The Minoru 3D Dual lens web camera is still at proof of concept stage atm but it can create stereoscopic 3D video which needs those cool blue and red 3D glasses to view.” (Note: “atm” means “at the moment,” not “go withdraw some money to buy one.”) I also ran across the 3D drawing pad pictured below left. It is available from the Perpetual Kid website, which explains: “Each page is a stereographic background for your writing or drawing. Put on these ultra cool (come on…you know you look good in them!) 3D specs and see your lines float above the page!” Why do people promoting such things seem to think that we can be convinced these glasses are cool?
 Right now there’s a big push to sell 3D mobile phones and other handheld gadgets. On July 25, Roger Cheng posted a skeptical article on the subject of the Thrill 4G model, by LG:
Right now there’s a big push to sell 3D mobile phones and other handheld gadgets. On July 25, Roger Cheng posted a skeptical article on the subject of the Thrill 4G model, by LG:
But it’s unclear if consumers are ready to grab hold of it yet.
3D is the latest feature to be crammed in the increasingly Swiss Army-knife-like smartphone. Like with televisions, the feature is getting aggressive marketing support. But despite the marketing campaigns, the feature has been little more than a gimmick. And like 3D televisions, there’s been tepid interest.
“3D is just one of an onslaught of features that end up on a phone even if people don’t ask for it,” said Maribel Lopez, an analyst at Lopez Research.
Sam Biddell over on Gizmodo, did not hold back in commenting on the HTC Evo 3D phone:
The EVO 3D is the first phone to ever literally hurt my face. The 4.3-inch 3D screen’s glasses-free, of course, which means it uses the same auto-stereoscopic method as the Nintendo 3DS. Well, not the same—the 3DS is a joy to use and view, while looking at 3D stuff on the Evo felt like I was having my eyes gouged out, Oedipus-style. It gave me a headache. I wanted to look away. And for what? A 3D effect that just isn’t very good. To pull off a 3D picture of video that has any ‘pop’ whatsoever, you need to use framing so contrived as to render the whole thing pointless.
This, mind you, despite the fact that you don’t need glasses to see a 3D image on phones.
What’s next for theatrical 3d?
In my original “Has 3D already failed?” I wrote that it
depends on how one defines success. If you’re Jeffrey Katzenberg and want every theater in the world now showing 35mm films to convert to digital 3-D, then the answer is probably yes. That goal is unlikely to be met within the next few decades, by which time the equipment now being installed will almost certainly have been replaced by something else […] But it also seems possible that the powers that be will decide that 3-D has reached a saturation point, or nearly so. 3-D films are now a regular but very minority product in Hollywood. They justify their existence by bringing in more at the box-office than do 2-D versions of the same films. Maybe the films that wouldn’t really benefit from 3-D, like Julie & Julia, will continue to be made in 2-D. 3-D is an add-on to a digital projector, so theaters can remove it to show 2-D films. Or a multiplex might reserve two or three of its theaters for 3-D and use the rest for traditional screenings.
If for the rest of this year blockbuster films continue to bring in 40% of their gross revenues in 3D-equipped venues and those venues continue to be around 70% of the total locales, then I would think that the saturation point I mentioned has been exceeded. Some theater owners might decide that they could make more money with less hassle by showing 2D. That would drive 3D devotees to the reduced number of 3D houses, making their revenue go up. Which in turn would presumably make some of the exhibitors who had given up 3D go back to it, and the balancing act would continue until the precise saturation point is finally attained. But at this point, adding more 3D screens to a multiplex or converting a mom-and-pop theater in a small town would probably just worsen the problem. I think what I predicted is coming true, that multiplexes will reserve a small number of their screens for 3D and keep the rest flat. Maybe the studios will decide that $30 million is not a great investment.
The more important news is that digital projection will continue to spread. Some theaters have installed it already to save costs. Wanting to play 3D films (which mostly can only be shown digitally) has undoubtedly been a factor in exhibitors’ purchases of digital projectors, but it will probably become less so now. The studios, however, want to give up 35mm release prints, which cost a lot for both lab work and shipping. They’ll pressure the theaters until it finally happens.
Stifel Nicolaus analyst Ben Mogil downgraded box-office projections for the second half of the year and lowered his target for the company’s stock price to $27, from $32. His report came a week after similar predictions were made by Merriman Capital. The stock was trading at $25.33 late Monday.
“We believe that estimates for IMAX for [second half 2011] are too optimistic given that the [fourth quarter 2011] slate has three kids’ films, a genre which this year has seen considerably lower 3D share this year compared to last,” Mogil wrote.
Most, but not all, Imax movies play in 3-D, a technology that has been dropping in popularity among domestic movie audiences.
These downgrades came partly as a result of the fact that IMAX has had three straight quarters where income fell short of its own predictions.
This story was updated later the same day: “Imax Chief Executive Richard Gelfond said, ‘We have a diversified slate based on blockbuster films in 2D and 3D, for families and fanboys. We think it’s way too premature to predict how the slate will perform for the year.'”
As I read this, Gelfond is assuring investors that there are quite a few 2D films mixed in among the 3D films, so that the latter’s decline will not hurt the firm’s overall income.
On July 26, Variety ran a long story with Jeffrey Katzenberg giving an elaborate explanation of how Kung Fu Panda 2 underperformed in the U.S. because it opened the same weekend as The Hangover: Part 2. There’s no indication as to how a raunchy, R-rated film could run roughshod over a kid-oriented animated movie. All those older brothers refusing to take their younger siblings to the movies? Usually it’s called “counter-programming” and often it works.
According to Variety:
Katzenberg is also still high on 3D, at least overseas, where “the marketplace couldn’t be stronger,” he said. “Outside of North America, the performance of 3D continues to be very strong across many different films. We see continued interest in it and appeal for it and growth over these next 12 to 24 months. There’s still a pretty decent way for it to expand meaningfully internationally.”
Domestically, the exec admitted to being partly to blame for some of the extremely optimistic views of 3D’s revenue potential. At the same time, the pessimism of its longevity is also on an extreme level, he said.
For DWA [Dreamworks Animation], at least, 3D remains one of the best returns on investment for the company, after it was able to shave off the costs to produce its pics in the format.
Two years ago, DWA spent $15 million per pic to deliver a 3D version. Today, the cost is half that, Katzenberg said. The studio now has nine 3D films in production.
If executives keep offering rationalizations and suggestions that we look to the future instead of the past, maybe we can conclude that 3D is officially in a slump.
As seen on Gadgettastic.com















