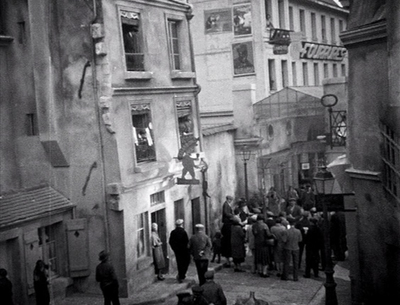Archive for the 'Film technique: Sound' Category
The ten best films of … 1931
M (1931)
Kristin here:
Our regular readers know that this annual series began as a simple salute to 1917, the year in which the basic norms of the classical Hollywood cinema definitively gelled. Starting in 2008, it became the “The 10 best films of …” list. It has stood in for the year-end ten-best lists which critics and reviewers feel obligated to concoct but which we avoid.
1931, I think, was a slight improvement on the rather lackluster 1930. A small handful of filmmakers mastered the “talkies” and made movies that look and sound as if they could have been made years later. These are the first four films below. It was a little harder to fill in the list beyond them. It’s is full of familiar classics, with a film or two that will probably unknown to many. I always try to include at least one worthy out-of-the-way title.
Previous entries can be found here: 1917, 1918, 1919, 1920, 1921, 1922, 1923, 1924, 1925, 1926, 1927, 1928, 1929, and 1930
M
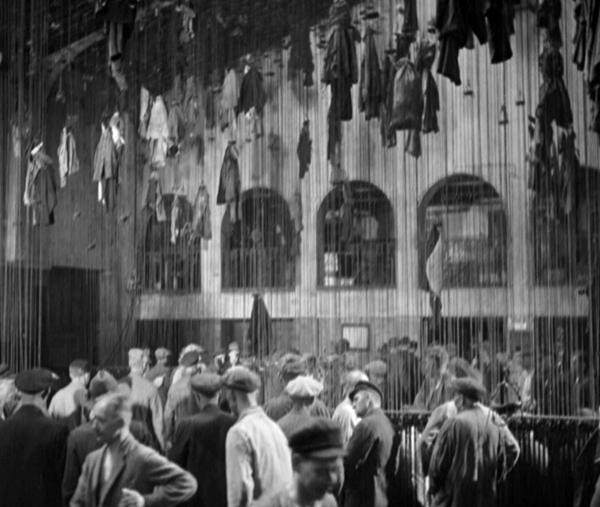
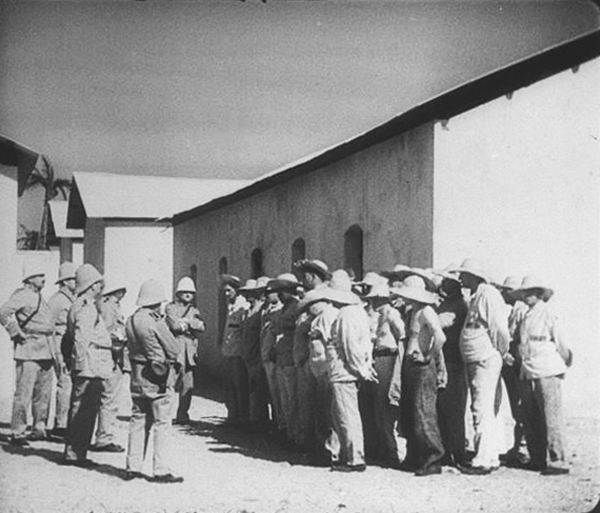
I remember seeing M as a grad student, or maybe even an undergraduate, and being horribly disappointed. This was a masterpiece? Actually it was only a semblance of one. In the 1970s a poor, incomplete 16mm print with as sparse a set of subtitles as I think I’ve ever seen was in circulation. The wit and brilliance of Fritz Lang’s sound links and voiceovers were largely lost, as were the sharp images now evident in the restored version. Even restored, as the introductory titles tell us, it is missing 212 meters. Fortunately that’s only .4% of the total, and the narrative progression is so smooth and absorbing that it’s hard to imagine that anything could be missing.
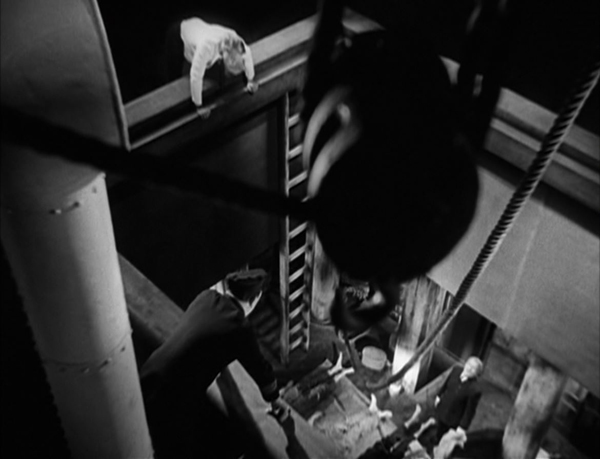
The story concerns a child-murderer terrorizing a city and the parallel searches for him by the police and by the organized underworld, the activities of which are being hindered by constant police searches and raids. At one point Lang famously intercuts a meeting of city officials with one of a group of gangsters. Parallels are created by matched gestures between space but also by one line being started by a character at one meeting and picked up by one at the other. Lang races through exposition by having the voiceover of a phone conversation between officials continuing over shots of the investigation in various spaces.
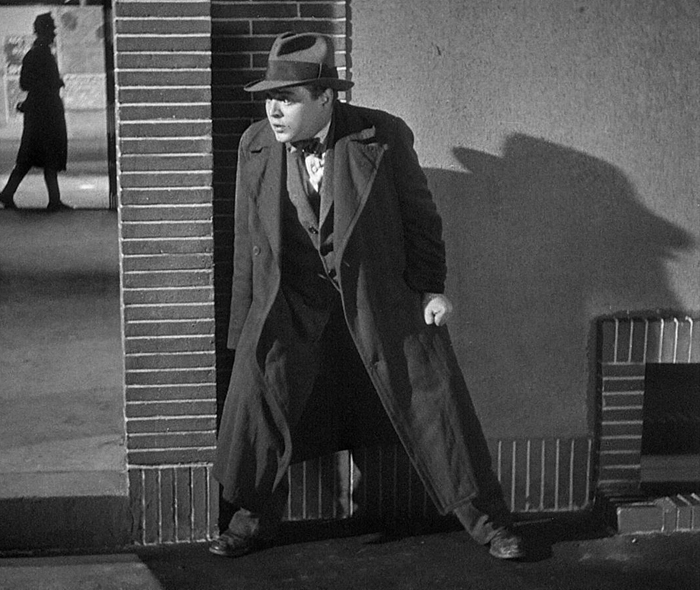
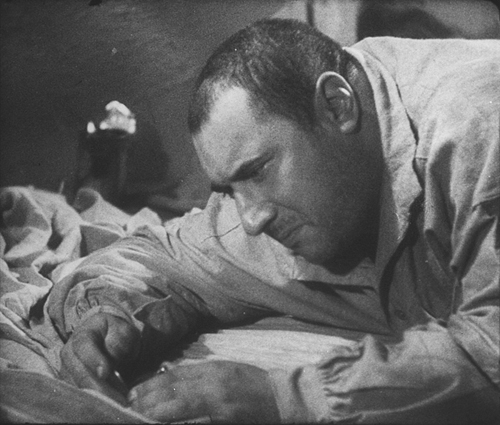
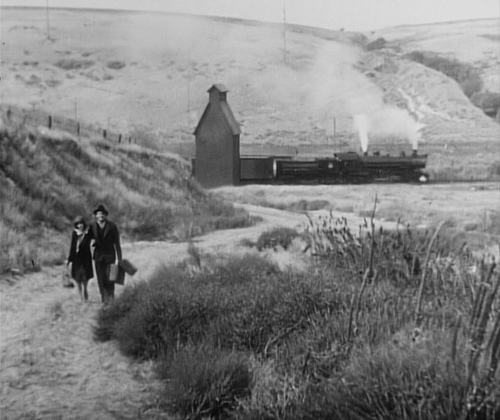
He uses sonic motifs as well. The killer compulsively whistled a Grieg tune as he lures his victims, but whistles come back time and again. Police whistles signal the raid on a basement tavern, and the beggars who tail their suspect signal each other with whistles–heard by the killer, who flees into an empty office building and ends up trapped there (top).
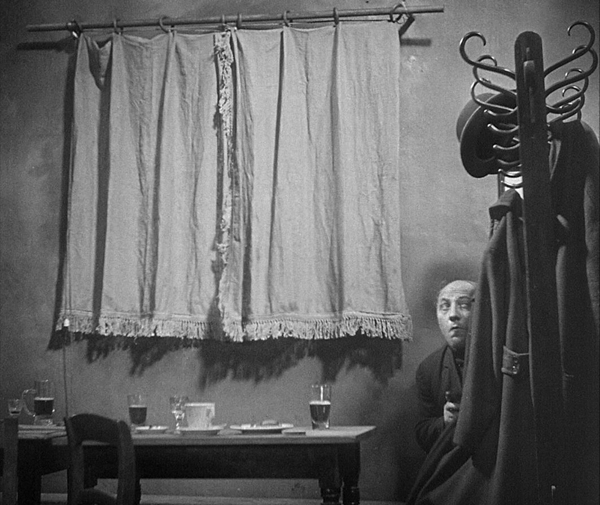
There’s a lot of offscreen sound in this film. The raid on the tavern cuts around to various parts of the space, as when we briefly follow a crook who tries to sneak out (above) while the protests of the crowd and the whistles and shouts of the police are heard off. One might think that all this is to avoid having to lip-sync the sound with the characters speaking–but when he does show the speaker, the sync is perfect. It’s another instance, I think, of Lang using sound to cram a lot of action or information into a short stretch of time. The thwarted crook is just a bit of comic relief, something Lang injects at intervals into this grim narrative.
Back in 2012, when I participated in Sight & Sound‘s poll of critics and academics for the ten best films of all time, I put M on the list. Counting 2021, it is the third film from that list that I have included in this one: The General in 2016, The Passion of Joan of Arc in 2018, and now M. The next one won’t show up for eight years (hint: Renoir made it in 1939), assuming I’m still doing this list at that point.
If you’ve never seen M, make sure you don’t watch an older print! The restored version is on Blu-ray from The Criterion Collection in the US and Eureka! in the UK.
Le Million
René Clair made two film classics in 1931, À nous la liberté and Le Million. I find the latter a better film in that it’s more complex and lively. À nous la liberté, which focuses on only two characters who spend a stretch of the film apart, has a rather thin narrative. Le Million, on the other hand, involves a large cast of amusing characters and constantly bubbles with dances, chases, and farcical situations. Indeed, early on it cites the chase scenes of early cinema when police pursue the kindly thief, Père Tulip, over the rooftops.
The sets were created by the great French film designer, Lazare Meerson (who also did the more austere sets of À nous la liberté). The interiors often have soft, hazy backgrounds (top of this section) apparently done partly by painting and partly with real objects behind scrims. These give a stylized quality appropriate to a classic farce situation: the debt-ridden artist protagonist Michel frantically searches for a jacket holding a winning lottery ticket as the jacket goes from hand to hand. At one point crossing hallways permit two chases–the police after Tulip, the creditors after Michel–to pass through each other.
David and I taught Le Million in an introductory film class back in the 1970s. I hadn’t seen it since, but it lived up to my fond memories of it. As cheerful a film as one could find for what promises to be another year short on cheerfulness.
Le Million is available on DVD from The Criterion Collection. The description says that the lyrics are all translated here for the first time.
Arrowsmith
Early as it is, Arrowsmith is surely one of Fords’s great films of the 1930s. It’s an adaptation of Sinclair Lewis’ 1925 novel of the same name. (Lewis won a Pulitzer for it but refused to accept the award.) The plot centers around Martin Arrowsmith (Ronald Colman), who starts as a medical student eager to establish a reputation and help discover cures for various plagues. He marries a charmingly impertinent nurse Leora (Helen Hayes), who supports him in his efforts.
The style of the film is distinctly flashy in its lighting, depth shots, and set design. It looks like what we tend to think of as Wellesian–though many of these techniques could instead by dubbed Fordian.
There are dramatic chiaroscuro effects as when Arrowsmith arrives home one evening, discouraged, and Leora sympathizes with him. The figures are side-lit with illumination coming from the kitchen, and Arrowsmith becomes a silhouette once he sits down.
The depth shots are equally impressive. A spectacular high angle (top of this section) shows three levels of a ship’s interior, with Sondelius, a medical expert, shouting up to the captain that he has discovered bubonic plague onboard. A less flashy but highly intense shot shows Leora’s death from bubonic plague. The long take is filmed with what David terms “aperture framing,” with Leora placed far off-center and relatively far from the camera, framed in the arms of the foreground rocking chair. It’s the same chair in which she sat when she smoked a cigarette contaminated with one of her husband’s plague samples. It’s a brilliant way to emphasize that she dies alone, with the bright open door at the center of converging lines of the set stressing that her husband does not suddenly appear, as we might expect, to comfort her.
Other more casual uses of depth with prominent foregrounds include a shot of Arrowsmith exiting his laboratory with beakers, bottles, and other equipment dwarfing him (below right).
Note also the prominent ceiling on the sets in the image on the left above. The notion that Citizen Kane was the first Hollywood film to use ceilings on sets has long been discredited, and here’s a good example of why. In general, Richard Day’s art direction combines with the cinematography to create powerful images, as in the hallway of the McGurk Institute, where Arrowsmith gains a research post.
We know that Welles was influenced by Ford’s work, but he primarily stresses Stagecoach as a film he watched repeatedly before making Citizen Kane. Arrowsmith, however, actually looks more like Kane than Stagecoach does. Did Welles and/or Gregg Toland see it? Very likely at least one of them did. There seems to be no record of Welles having said he saw it, but in 1938 he wrote and performed the title role in a radio version of Arrowsmith that had Hayes repeating her role as Leora.
Moreover, Arrowsmith was produced by Samuel Goldwyn. In the late 1920s and early 1930s, Toland was making films there, including Eddie Cantor comedies (Whoopee!, 1930) and two crime dramas starring Colman (Bulldog Drummond, 1929, and Raffles, 1930). It seems implausible that he would not have seen Arrowsmith.
All this is not to say that Arrowsmith was the first film to play with depth and chiaroscuro. As David pointed out in a 2010 blog entry, such ideas were developing in Hollywood during the 1920s, and William Cameron Menzies in particular experimented with them. There David wrote, “The flashy depth compositions of the 1920s and 1930s were typically one-off effects, used to heighten a particular moment.” True enough, but I think Arrowsmith uses them more consistently.
So far Arrowsmith has not been released on Blu-ray, but the MGM DVD has surprisingly good visual quality for a film from this period. (Amazingly enough, you can still buy new VHS copies on Amazon.)
Kameradschaft
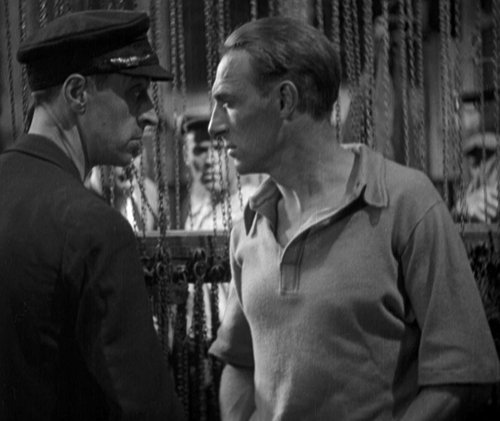
Like Clair, G. W. Pabst directed two classic films in 1931, Kameradschaft (“Comradeship”) and The Threepenny Opera. The former is a network narrative, cutting among several characters or small groups of characters as they react to a mine disaster.
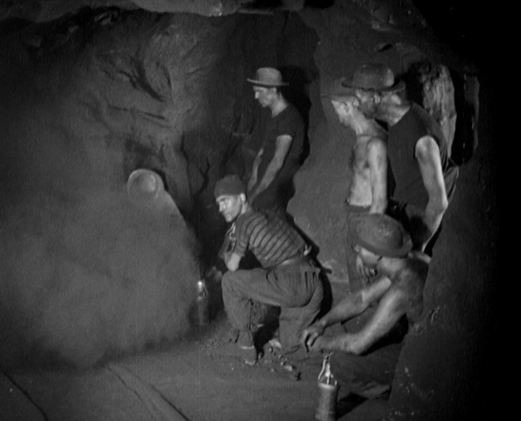
The story is set in two villages on either side of a French-German border. Each is a mining town, exploiting what is actually the same rambling mine that has walls and bars in multiple tunnels marking the end of the German portion and the beginning of the French one. When escaping gas triggers a fire and ceiling collapses on the French side, two truckloads of German miners volunteer to go and help the rescue teams.
As the title suggests, the film stresses the theme of solidarity among the miners, though Pabst doesn’t paint an entirely rosy picture of this. The German miners coming off their shift argue about whether they should assist their French counterparts, and many declare that it’s none of their business. Pabst stages the debate in a visually interesting locale, the changing room where the mining outfits of the men are stored on ropes or wires up by the ceiling (above and below, left). The leader of the group which goes to help with the rescue is played by Ernst Busch, a well-known Communist actor-singer who was also in the original stage version of The Threepenny Opera and Pabst’s adaptation, as well as Slatan Dudow’s Kuhle Wampe (1932), from Brecht’s script. His presence as one of the main characters in the network plot–and the one who spurs others to volunteer as rescuers–helps give Kameradschaft a distinctly leftist tone.
As with many other films set in coal mines, the mine itself was an elaborate and convincing studio set (above right). One collapsing area of a mine looks much like another, but Pabst found ways to vary the action from scene to scene. Variety is added through a contrast in the main characters being followed. An old ex-miner sneaks into the mine to search for his grandson. Three German miners who didn’t go in the trucks to the French side decide to make a rescue effort on their own, breaking through the barred underground border to do so. They end up alongside the old miner and his grandson, trapped in the underground stable, where the presence of a placid but doomed horse adds a poignancy to the scene. At intervals the drama going on among the mothers, wives, and sweethearts of the French miners clustered at the gates is shown.
The weaving together of the various threads of action creates a strong sense of suspense. No one character can be singled out as the protagonist, the one who might be expected to survive. Some miners and rescuers escape, but there are many who die or suffer serious injuries.
Despite the emphasis on the comradeship of miner of both nationalities, the Germans definitely come off better. Their rescue team is well-equipped and efficient, while the French workers deal with problems like an elevator being out of commission. It probably would never have occurred to Pabst and the others involved to make a film where French miners help rescue German ones–and it probably would not have been greenlit by the production company if they had. On the level of the individual miners’ actions, however, the notion of working-class solidarity comes across.
Kameradschaft is available on DVD and Blu-ray from The Criterion Collection.
Tabu: A Story of the South Seas
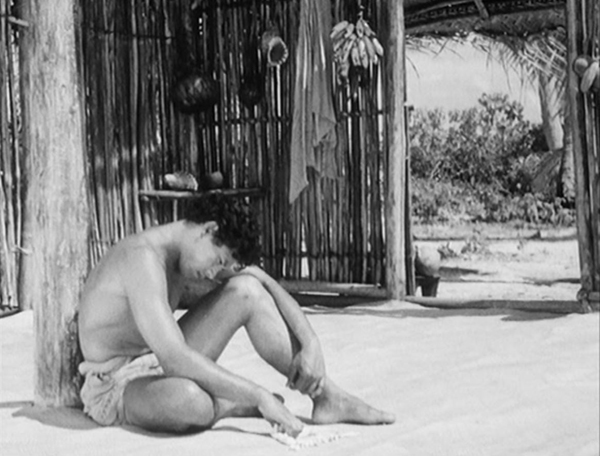
Tabu was Murnau’s final film. (The opening scene of the hero fishing with his friends was shot by intended co-director Robert Flaherty, who soon quit due to disagreements with Murnau.) It deals with Matahi and Reri, who live a joyful life on unspoiled Bora Bora until an elderly man from a nearby island arrives and announces that the “Virgin sacred to our gods” has died, and Reri is to be her successor. Matahi rescues her, and the two flee to another island which has been colonized by the French. They have established a pearl fishery and hire local men to dive for pearls. Matahi proves expert at this, but not understanding what money is, he soon gets himself deep into debt by signing IOUs.
Rather than using Hollywood stars, Murnau cast local unprofessionals. As the credits announce, “only native-born South Sea islanders appear in this picture with a few half-castes and Chinese.”
The two leads are appealing characters, and the images take advantage of the unspoiled scenery of Bora Bora (below left). Floyd Crosby earned an Oscar for Tabu‘s cinematography.
Tabu is a far cry from Murnau’s German films, but Nosfertu‘s famous shot of the vampire’s ship sailing eerily into the frame from offscreen is echoed as a motif here (below right).
The original version released by Paramount was released on DVD by Milestone. A restoration of the original cut of the film is available on DVD and Blu-ray from Kino Classics in the US and Eureka! in the UK, both with numerous supplements. A helpful comparison of these versions is available here.
La Chienne
I think it is safe to say that most critics and historians consider La Chienne the film where Renoir’s distinctive traits as a director began to emerge. I have seen most of the early Renoirs, but long enough ago that I can’t make a comparison. It does seem to me, though, that it is quite different from his previous work.
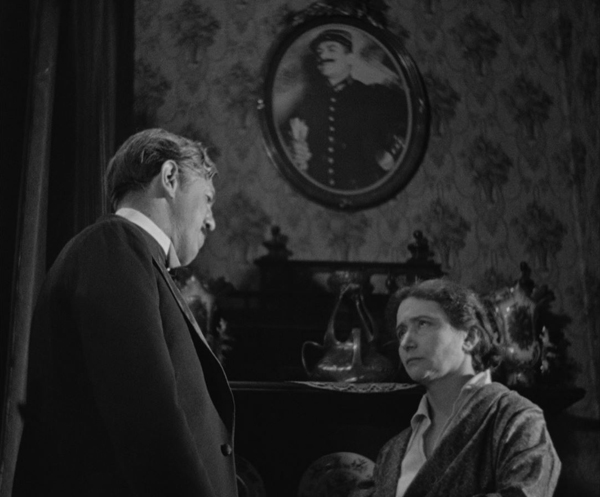
Maurice Legrand, the protagonist played by Michel Simon, is the most Renoirian character. He is a mild-mannered accountant married to a termagant who nags him constantly and forces him to remove from their apartment the paintings and the equipment he uses for his hobby. This sets off the events which follow, as Legrand hangs the paintings in the apartment of a prostitute, Lulu, with whom he has fallen in love. Her pimp Dédé concocts a scheme to sell the paintings, which he passes off to a dealer as the product of an American painter named Clara Wood. Even when Lulu explains what happened to the paintings, Legrand is so besotted that he raises no objections.
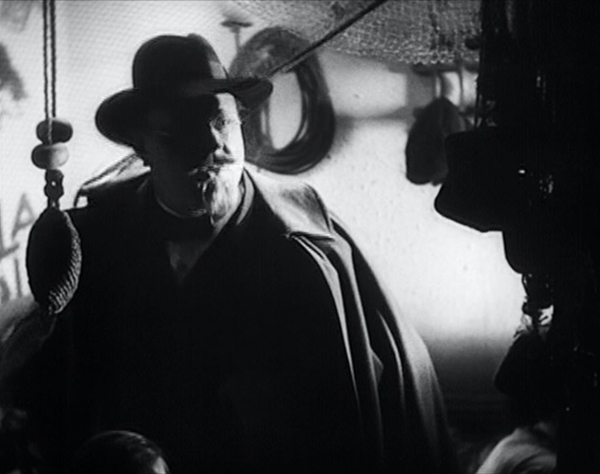
Although “la chienne” of the title is clearly Lulu, it might refer to Adèle Legrand as well. “Chienne” is more-or-less the equivalent of the English “bitch,” meaning both a female dog and an obnoxious woman, which Adèle certainly is. In their first scene together, she berates Legrand at length, comparing him unfavorably with her first husband, whose portrait in military uniform looms over them (above). Legrand does not rebel but answers in quiet sarcastic comments and ultimately obeys her order about the paintings.
In French, “la chienne” has the additional meaning of a prostitute, clearly referring to Lulu. Legrand is trapped between a constantly angry wife and a prostitute skilled in behaving in a docile fashion, pretending, as she finally admits, to love him solely in order to maintain the flow of money from the paintings. This admission finally drives him to fight back, killing Lulu. He ends up as a jovial tramp, foreshadowing Simon’s later role as Boudu in what is arguably Renoir’s first true masterpiece.
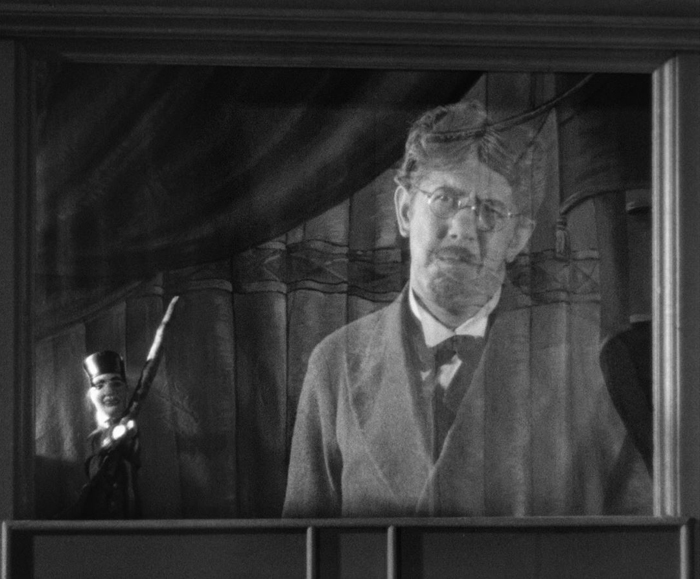
Stylistically the film does not strongly resemble Renoir’s major films of the mid- to late 1930s. Still, the scene in which Dédé and his friend approach an art dealer in their first attempt to sell one of Legrand’s paintings consists of a longish take of nearly two minutes, with staging in depth (below) when the dealer returns from a search and a track-in to a closer framing for the negotiations. Also, the film starts as a puppet show, with puppets introducing the main characters, whose images are superimposed over the little stage (bottom). This looks far forward to his final film, The Little Theatre of Jean Renoir (1970).
La Chienne is available on Blu-ray and DVD from The Criterion Collection.
Tokyo Chorus
Last year Yasujiro Ozu made his first appearance on this list for That Night’s Wife. This year it’s Tokyo Chorus (or Chorus of Tokyo). With sound barely established in Japan, Ozu made this and several subsequent films silent.
As the Criterion Collection liner notes explain, Tokyo Chorus combines the three genres Ozu had worked in before: the student comedy, the salaryman film, and the domestic drama. The student comedy subject gets disposed of early on, with the first scene showing the a comically strict teacher scrutinizing his class, lined up military-style; the protagonist, Shinji, tries some mild defiance by being late and showing off (below left).
Soon he has graduated, though, and is working in an office where the employees are awaiting their year-end bonuses. Just as quickly, Shinji is fired for protesting when an elderly colleague is fired just before his retirement and pension payments.
The rest of the film seems like a practice piece for I Was Born, But … (1932) and other Ozu films involving bratty kids who make demands on their parents. In this case Shinji’s son insists that his father buy him a bicycle and pesters him until he finally gets it (above right). As in the later film, Shinji is humiliated by having to take a job helping his old teacher to publicize his curry cafe.
Ozu’s growing mastery of editing for comedy is shown off in the early scene when the office employees try to find out how big a bonus their colleagues have received. Shinji sneaks away to the restroom to open his envelope, pretending he has gone to use a urinal. A low-height shot shows another man coming in, with the swinging doors of the urinal area showing him only from the waist down. Shinji, just about to open his envelope, glances off and sees him. A reverse shot shows the colleague stopping and staring, clearly more interested in Shinji’s bonus than in using the urinals. Shinji gives up, pretends he is just there to relieve himself, and a final shot shows him departing still not knowing how big his bonus is.
By this point, Ozu has mastered balancing comedy and pathos, a mixture of tones that will reappear in many of his future masterpieces.
Tokyo Chorus is has been released on DVD, appropriately enough along with two of those future masterpieces, I Was Born, But … and Passing Fancy (1933), by The Criterion Collection.
City Lights
I must admit that I do not admire City Lights as much as The Gold Rush and The Circus, which featured in my ten-best lists of 1925 and 1928. I think it has some narrative problems.
For one thing, the blind flower seller as a love interest is pretty passive and doesn’t allow many opportunities for generating humor. In The Gold Rush, Chaplin had the inspiration to introduce a dream sequence about the dance-hall girls, including his beloved Georgia, coming to dinner with him. He then inserted his classic gag, the dance of the rolls. Much of the action in The Circus involves the heroine, as with the magic act into which the Tramp stumbles. The flower seller mainly generates pathos, right up to the ambiguous ending. (I have seen commentators take the ending as a clear indication of a budding romance between the pair, but I think we get no clear indication that her gratitude for the help the Tramp has provided will blossom into love.)
Chaplin needed to fill out the film with action beyond the few scenes involving the flower seller. Much of the action involves the Tramp’s on-again, off-again friendship with the eccentric millionaire, which is a weak premise to carry so much of the narrative. This character treats the Tramp as his closest buddy when drunk but then fails to recognize him when sober. This happens three separate times and gets a bit repetitious in a way not seen in other Chaplin films. The main contributions of the millionaire to the plot are to give the flower seller the impression that the Tramp who buys her flowers is a wealthy man and to give the Tramp the money for the flower seller’s eye-restoring treatment. The character of the millionaire does create some humorous bits, as when the pair eat spaghetti and the Tramp gets a curly streamer mixed in with his and keeps on eating it. I can’t help contrasting the millionaire with the Mack Swain character in The Gold Rush, whose interactions with the Tramp generate so many hilarious gags.
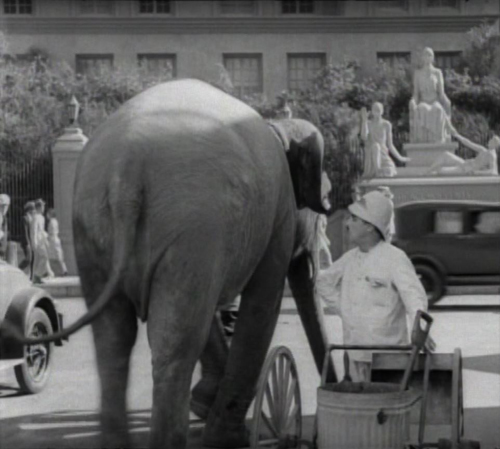
There are admittedly other funny scenes, especially early on, when the Tramp is discovered asleep on the lap of a statue being unveiled before a crowd or when he becomes a street cleaner to earn money for the flower seller and is immediately confronted with a group of horses and, as a topper, an elephant passes.
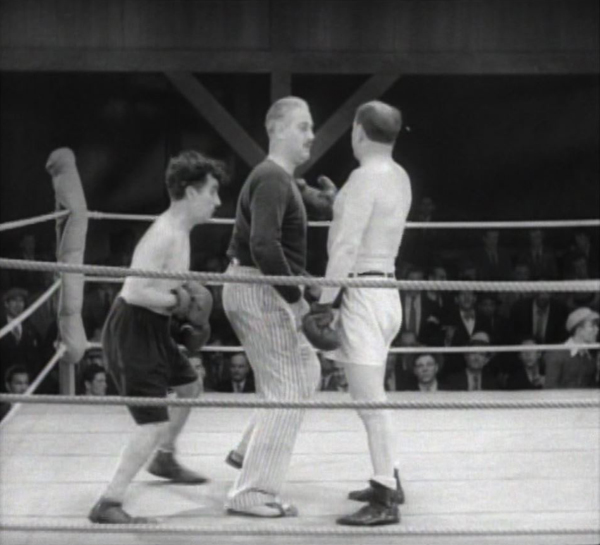
Later on in the film, though, the plot premise of earning money to help the flower seller have an operation to restore her sight generates one of the funniest scenes in all of Chaplin’s work. He agrees to participate in a fixed boxing match, with his opponent going easy on him and the two splitting the purse. The opponent is replaced by a tough guy who clearly has no intention of playing nice. The Tramp’s tactics to avoid being beaten up involve dancing around directly behind the referee at first (top of this section) and then, in a dazzling bit of choreography, the three figures move around the ring, changing places repeatedly so that the Tramp is sometimes behind the referee, sometimes behind his opponent, and so on. It is reminiscent of the scenes in the hall of mirrors as the Tramp is chased by a pickpocket and then by a policeman in The Circus, with the characters and their reflections dodging in and out of view.
Chaplin famously refused to allow spoken dialogue in his film, despite the fact that the transition to sound was well established in the USA by 1931. He restricted the track to music and sound effects, a tactic he carried over to Modern Times as late as 1936, though there the Tramp’s voice is heard for the first and last time singing a nonsense song. Chaplin retired his long-time character thereafter.
City Lights is available on DVD and Blu-ray from The Criterion Collection.
Odna (Alone)
When I was in graduate school, the only film by Grigori Kozintsev and Leonid Trauberg widely known outside the Soviet Union was their 1926 adaptation of The Cloak, which appeared in my best-ten list for that year. Then people discovered, to some extent, The New Babylon, which appeared in the entry for 1929. I suspect that few people have seen, or even heard of, their marvelous first sound film, Odna.
It was planned as a silent film, but delays permitted the use of sound technology to add a track to it. The main element of the track is Dimitri Shostakovich’s musical accompaniment. (He had also composed the musical accompaniment for The New Babylon.) The music comments on the action, often in a mocking way. Occasionally there are sound effects, and very occasionally, brief lines of dialogue, recorded and added after the filming.
The plot centers around a young teacher fresh out of school, Yelena Kuzmina (played by Yelena Kuzmina, who also played the protagonist of The New Babylon).
The first section of the film is played with an absurdly jolly exuberance. Yelena is engaged to a handsome young man, and a lively montage of shots shows her visions of the ideal life she plans to lead with him in Moscow, including window-shopping for expensive sets of dinner crockery, playing a musical duet at a cafe (below left), and teaching attentive children seated in neat rows in a well-equipped classroom (top of section). Shostakovich’s music is ridiculously cheerful, and a song about how beautiful life will be plays over a shot of Kuzmina’s fatuous grin (below right).
The tone switches abruptly as Kuzmina receives an assignment to a teaching post in a remote, mountainous primitive district of Siberia.
Devastated, she lodges a complaint, which seems likely to succeed. An elderly man in the office tells her that she’s right to try to change her assignment (below left). She erupts, “I’m going anyway!” This is one of the few post-dubbed lines.
Upon arrival in the Siberian district, she encounters a dead horse’s skin on display (below right); this returns as a motif to emphasize how primitive and in need of education the area is. At first the villagers react with indifference or antagonism, seeing no point in having their children go to school. Oddly enough, the local Soviet official is lazy and also indifferent, leaving her alone with no aid in convincing the villagers to accept her. (This negative depiction of the Soviet official later got the film banned, despite its considerable popularity upon its initial release.)
Apart from encouraging teachers to accept whatever school they were assigned to, the film has the anti-Kulak theme that was common in Soviet films about the countryside. (See the discussion of Eisenstein’s The General Line in the 1929 entry.) A wealthy local landowner has secretly sold off the sheep that technically belong in common to the villagers, whose main source of income is the wool. Kuzmina exposes the theft and helps the local people resist it, thus finally gaining their trust.
The next-to-last reel of the film, in which the landowner tries to kill Kuzmina, is missing. A restored version of the film accompanied by a reconstruction of the Shostakovich score was released on Dutch and German DVDs in 2007. (The frames here are from the Dutch DVD.) It includes a long series of intertitles describing action in the missing reel, drawn-out so as to match the length of the music, which does survive. As far as I can tell, these DVDs are no longer available. I am reluctant to recommend a version on YouTube, derived from the German DVD and superimposing English subtitles on German ones, on top of Russian intertitles. It does seem to be the only widely available way to see the film at this point, so for those who can put up with the clutter and the poor quality of the online version, it is here. A complete recording of the charming music is still available.
La Petite Lise (1930)
My tenth film is a holdover from last year. I consider Jean Grémillon’s La petite Lise a film worthy of the top-ten list, but when compiling last year’s list I somehow misremembered it as being from 1931. It just goes to show that one should double-check on such things.
Decades ago, I first saw La petite Lise in a 35mm print on an editing table at the Cinémathèque Royale de Belgique (now the Cinematek). I finally saw it on the big screen in 2015, when our UW Cinematheque ran a few Grémillon films in 35mm. Then-graduate student Jonah Horwitz provided the program notes.
Grémillon is best known outside France for the trio of films he made during World War II: Remorques (1941), Lumière d’été (1943), and La ciel est à vous (1944). Criterion has released a box set of all three as Jean Grémillon During the Occupation. Some of his other films are available on disc, as a search of the director’s name on Amazon.com or amazon.fr reveals (including some with English subtitles).
The simple plot involves Berthier, who is serving a long sentence in a prison in Cayenne for having killed his wife in a fit of jealousy. Heroic behavior on his part during a recent fire has led to an early release, and he expresses his desire to see his daughter, Lise, now grown up. All this sets us up to be sympathetic toward him, despite the fact that he is played by by Pierre Alcover, a large, rather sinister looking actor. (Best known to modern audiences, I suppose, as the corrupt banker in L’Herbier’s L’Argent.) Unbeknown to him, Lise has been working as a prostitute but has now ended that in anticipation of marrying André. The pair are in desperate need of obtaining 3,000 F within 48 hours to buy a small house.
Berthier’s reunion with Lise is joyful, and he manages to find a job with his old boss, who gives him a generous advance on his salary. Knowing nothing of this, Lise and André visit a Jewish pawnbroker who André believes has cheated him in the past. When he threatens the pawnbroker, a fight breaks out, and Lise accidentally kills the man. Berthier learns of her past and of the killing, and his great love for her leads him to turn himself in as the killer.
The story is quite touching, in large part because Alcover and Nadia Sibirskaïa (who played the younger girl in Menilmontant) convey the deep love between the pair.
Grémillon adds some unconventional touches which have little direct relation to the plot and are largely dependent on sound. These give the simple plot some variety.
The opening, for example, takes place in the Cayenne prison, with Berthier learning of his pardon from the warden. In the crowded dorm, he reveals to two fellow convicts that his good fortune makes it impossible for him to participate in a planned escape. He shows them a photograph of Lise as a child. Most of the extended dorm scene, however, consists of fairly tight shots of other men’s activities, all packed into the crowded room. The soundtrack, rather than catching scraps of dialogue, remains a loud babble of many men talking at once. These shots tell us us next to nothing about the narrative, beyond suggesting the grim conditions to which Berthier faces returning to at the end. It does, however, create an effective atmosphere of the prison as a backdrop to occasional shots of Berthier gazing at the photo of Lise.
Another example is a scene late in the film, when, having learned of the killing, Berthier goes looking for André. He tries to enter a nightclub, but it is too crowded. He stands watching with several others through the window as a Black dancer performs a lively number for a mixed Black and white audience. For a brief interval, the scene becomes a musical number, extending to the point where couples start dancing, with Berthier becoming quite peripheral to the action. The performer and dancers add nothing to the story, but the scene is delightful in itself.
These and other moments draw us away from the linear progression of the story and make La petite Lise one of those small, simple films that transcend their apparently modest nature–like those of Jean Epstein and Dimitri Kirsanoff.
La petite Lise remains difficult to see. It has never, as far as I know, been available on home video. Grémillon’s film is not on YouTube, but there are several clips from key scenes. (All are pretty poor in quality, and I haven’t seen a good print of it. If elements survive in archive, it seems a major candidate for restoration.) An excerpt from the scene in the prisoners’ dorm near the beginning gives a good sense of the babble of voices. The Black dancer’s number as Berthier searches for André is shown nearly in its entirety. Both of these were put up at the time of the Cinematheque screening in Madison. There are some other brief scenes: the visit to the pawnbroker leading up to the murder, the scene of Berthier applying to his former boss for a job (which includes a sound bridge from the previous scene of Lise at home), and the scene in a restaurant which Lise and André visit in the hope of establishing an alibi. Otherwise, keep an eye open for it if you live near at archive that has public screenings.
For a look at Ford’s flashy style in his earliest features, see here. For a defense of How Green Was My Valley‘s Oscar win over Citizen Kane for best picture, see here.
My video essay, “Mastering a New Medium: Sound in M“ is number 11 in the series “Observations on Film Art” on The Criterion Channel.
La Chienne (1931)
Oscar’s Siren Song (A Slight Return): Best Original Song
One Night in Miami (2020).
Jeff Smith here:
On Monday, I offered an overview of the five nominees for Best Original Score as well as a prediction regarding the winner. Today, I do the same for the Best Original Song nominees.
The usual caveats apply for those readers interested in the online betting markets. My picks are for “entertainment purposes only.”
As we’ll see, the race in the Best Original Song category is extremely competitive. Indeed, I almost flipped a coin to make my final decision. I didn’t. But the very fact that I thought about it indicates the low level of certainty I have about my prediction.
I should add that there are a few SPOILERS AHEAD. If you don’t want to know some of the key plot twists in Eurovision Song Contest: The Story of Fire Saga or a small but important plot point of The Life Ahead, you can skip to the last section.
Best Original Song: The Underdog
One striking detail about this year’s nominees is the fact that four of the five function as “needle drops” introduced as the film’s closing credits start to roll. Perhaps a steady diet of television episodes streamed during the pandemic has accustomed viewers to expect that this is the way songs now function in movies. Several shows, both old and new, have used these needle drops quite creatively. (I’m thinking here of Mad Men, The Marvelous Mrs. Maysles, and WandaVision. I’m sure you all have your own favorites.)
Set off from the narrative flow of the episode, music supervisors found they could use a song as a curtain closer to highlight elements of theme, tone, or mood without worrying about things like time period or the musical tastes of the show’s characters. Such transmedial influences eventually might establish this as the primary function of popular songs in films. If this year’s nominees are any indication, the trend is already well on its way.
The one exception is “Husavik (My Hometown)” from Eurovision Song Contest: The Story of Fire Saga. The film, of course, is a vehicle for star Will Ferrell. He plays an Icelandic version of his usual man-child persona. It adds, though, a musical competition element borrowed from other comedies, like Pitch Perfect, and from popular music shows, like American Idol.
Ferrell plays Lars Ericksong, a humble “meter maid” whose lifelong dream is to compete in the Eurovision Song Contest. Eurovision, of course, is an annual event in real-life. It remains the longest running internationally televised music competition. The contest played an instrumental role in launching the careers of artists like ABBA, Céline Dion, and Julio Iglesias.
Lars hopes to follow in their footsteps, but his ambitions are mocked by the other residents in his small town.
Lars’ only defender is Sigrit, his childhood friend and his partner in the musical duo Fire Saga. Fire Saga plays a vital role in the town’s musical culture, performing regularly at a local bar. Yet their audience mostly rejects their musical offerings. Instead, they prefer “Ja Ja Ding Dong,” a sexually suggestive nonsense song that is the antithesis of past Eurovision winners.
Sigrit, played winningly by Rachel McAdams, is steeped in Icelandic folklore. She makes offerings to a small den of elves that she hopes will prompt Lars to return her considerable affections for him. She also believes in the “speorg note,” a mystic tone that Sigrit’s mother tells her represents the truest expression of the self.
Fire Saga enters the national competition hoping to earn the honor of representing Iceland. During an Icelandic Public Television meeting, their song is picked at random simply to meet Eurovision’s requirements for a country’s eligibility. At Reykjavik, Lars and Sigrit nervously wait backstage for their performance. Sigrit wishes that she could sing in their native language since it would calm her down. Lars, though, warns against it noting that a song in Icelandic would never win Eurovision.
Fire Saga loses to a talented competitor named Katiana, played by Demi Lovato in a nice cameo. Embittered, Lars refuses to attend a party celebrating the winner and Sigrit joins him in solidarity. When the boat hosting the party explodes, killing everyone aboard, Fire Saga becomes the Icelandic entry as the only surviving runner-up.
Once in Edinburgh, the site of the 2020 competition, Lars and Sigrit clash regarding the best way to present their music. (In reality, the 2020 Eurovision contest was to be held in Rotterdam but was cancelled due to the pandemic.) Lars wants to wow the audience with elaborate costumes and stagecraft. He also hires a K-Pop producer to remix their recording, giving it a hip new arrangement. Sigrit would rather just let the music speak for itself.
During the semi-finals, Fire Saga’s performance of “Double Trouble” seems to be going well. But Lars’ desire for showmanship backfires when the absurdly long scarf he has given Sigrit gets caught in the gears of his giant hamster wheel.
Sigrit is able to free herself before she suffers the fate of Isadora Duncan. But the hamster wheel breaks free and crashes into the audience. Although Lars and Sigrit recover just in time to finish the song, they are initially met with stunned silence. This is followed by some snickers scattered amongst the crowd. Lars and Sigrit leave the stage dejected, smarting from their humiliation.
Crestfallen, Lars returns to Húsavik, reconciled to life as a fisherman rather than a musician. Sigrit stays behind to continue her dalliance with Alexander Lemtov, a rival contestant from Russia. Sigrit is gobsmacked when she learns that Fire Saga has been voted through to the finals, a plot twist perhaps inspired by the real-life hate-watching that produced surprisingly long runs by American Idol contestants like Sanjaya Malakar.
Lars makes a mad dash back to Edinburgh, both to participate in the finals and to declare his love for Sigrit. Looking like the Gorton Fish guy, Lars sneaks onstage just as Sigrit has begun “Double Trouble.” He stops her mid-phrase and persuades her to sing a new song even though he knows the change will result in Fire Saga’s disqualification. Sigrit begins tentatively but soon grows in confidence as she reaches the chorus, sung in Icelandic much to the delight of those watching in Húsavik. The song builds to its climactic final note, a high C# that is held for several seconds, leaving both the audience and Lars rapt in awe. This time Fire Saga’s performance is met with thunderous applause. In an aside just for the viewer, Lars exclaims, “The speorg note!”
There’s a lot wrong with Eurovision. Some of the film’s gags misfire badly. The race to get Lars from the airport to the auditorium features the kind of crazy stunt work that’s grown stale from overuse. (Think spinning car and reaction shots of screaming passengers!) And at 126 minutes, Eurovision has two or even three subplots too many.
Yet the filmmakers definitely stick the landing with Fire Saga’s triumphant performance of “Husavik (My Hometown).” Seeing Lars cede the spotlight to Sigrit and her rise to the moment brings a lump to the throat, just as it does in other show-biz success stories like 42nd Street (1932) and A Star is Born (2017). (It’s an old formula but a potent one.)
Moreover, the sequence pays off several dangling causes (the reference to Icelandic lyrics in the scene backstage, the rekindled romance of Lars’ father and Sigrit’s mother, the speorg note). Even Fire Saga’s disqualification strikes the right tone by making the duo the musical equivalent of Rocky. They win by losing, content in the knowledge they were worthy contenders and in the realization of what they truly value. Watching the folks back in Húsavik swell with community and nationalist pride is just the cherry on top of a very satisfying sundae.
Any one of Eurovision’s Europop pastiches would have been worthy of nomination. For example, the faintly ridiculous quality of Lemtov’s “Lion of Love” makes it a perfect surrogate for the character’s ostentation and vanity. But only “Husavik (My Hometown)” both tickles the fancy and tugs the heartstrings.
Still, despite its appositeness for Eurovision’s story, I think it is a long shot when it comes to claiming the trophy. You have to go back to The Muppets in 2011 to find an Oscar-winning song in a live action comedy. And that was a strange year in which there were only two nominees. Before that, you have to reach all the way back to 1984’s The Woman in Red. That year, the winner was “I Just Called to Say I Love You,” written and performed by the great Stevie Wonder. Despite its considerable craft, “Husavik (My Hometown)” seems unlikely to alter a trend that rewards songs in dramas rather than comedies.
The Bridesmaid (as in “Always the…”)
This past February, Diane Warren received her twelfth Academy Award nomination for “Io Sì (Seen),” featured in the Italian film, La Vita davanti a sé. Warren has won an Emmy, a Grammy, and two Golden Globe awards, but has yet to claim an Oscar. This puts Warren in some pretty good company. Her colleague, composer Thomas Newman, has been nominated fifteen times without winning. Composer Victor Young received 21 nominations before finally breaking through with Around the World in 80 Days (1956). Sadly, Victor Young didn’t live long enough to actually receive the award. He died at age 57 just months before the ceremony.
Warren’s latest effort, “Io Sì (Seen),” is the type of soaring power ballad she has spent much of her professional life perfecting. The song starts with a modest piano figure that accompanies Laura Pausini’s indomitable voice at a moderate tempo. The lyrics offer a simple but powerful declaration of emotional support regarding the need to be “seen.” Pausini’s voice rises in the chorus as she vows in Italian, “But if you want, if you want me, I’m here.” The addition of a string orchestra and tasteful percussion accents provides additional emotional heft.
The modest arrangement allows the song’s simple beauty to shine through. Its mood and Pausini’s vocal delivery seem miles away from the bombast that made Aerosmith’s “I Don’t Want to Miss a Thing,” one of Warren’s earlier nominees, a chart-topping single.
For me, though, that is all to the good. La Vita davanti a sé is itself an unassuming coming-of-age tale that depicts the unlikely friendship that develops between Madam Rosa, an elderly Holocaust survivor, and Momo, a 12-year-old orphan from Senegal.
Buoyed by Sophia Loren’s valedictory performance, the song reflects the strong filial bonds that form when Momo becomes Rosa’s ward. The lyrics’ reassurance that “I’m here” capture the ways in which Momo and Rosa have learned to care for one another. Placed just after the funeral ceremony that closes the film, “Io Sì (Seen)” sustains the scene’s bittersweet, melancholy tone and carries it into the credits. The song also reiterates the story’s central themes regarding the need for unconditional acceptance and love’s ability to overcome differences in gender, race, and age.
La Vita davanti a sé has become an unlikely hit for Netflix. At the peak of its popularity, it reached the streaming service giant’s top ten in 37 different countries. Perhaps that sleeper success will bolster Warren’s chances among Academy voters. She is eminently deserving of the award as a sort of career honor.
Could this be Warren’s year? Perhaps. Still, the fact that more famous songs by Warren, like “Because You Loved Me” and “How Do I Live,” also suffered defeat raises some doubts.
Panthers and Boxers and Yippies (Oh My!)
The three remaining nominees are all songs featured in films that look back at the legacy of sixties political activism. Unlike Eurovision Song Contest and La Vita davanti a sé, Judas and the Black Messiah, One Night in Miami, and The Trial of the Chicago 7 all received multiple nominations. Often the halo effect created by that reflected glow can make a difference in very competitive races. Moreover, the two titles receiving Best Picture nominations – Judas and Chicago – also benefit from the massive “For Your Consideration” ad campaigns that appear in trade publications like Variety. All of this suggests that, if you are looking for this year’s winner, you might look here.
Let’s start with “Fight for You,” the groovin’ track by H.E.R. that closes Shaka King’s Judas and the Black Messiah. The song self-consciously evokes music from the period depicted in the film. As H.E.R. told Variety, she wanted the music to have a hopeful vibe, but lyrics that connected to the Black Panthers’ historic fight against injustice. She drew upon the classic soul music of Marvin Gaye, Nina Simone, and Sly and the Family Stone, artists who made records that were both popular and politically astute.
The final product is a remarkable synthesis of these different elements. The syncopated brass and organ chords recall vintage Sly and the Family Stone tunes like “Stand.” The spare but funky bass line and the supple guitar melody wouldn’t be out of place on Gaye’s classic, “Let’s Get it On” while the doubling of H.E.R.’s voice, sometimes in octaves and sometimes in thirds, conjures up his masterful What’s Going On album. The string arrangements and choral melody also bring to mind Curtis Mayfield’s classic score for Superfly (1972) for good measure. Only one of the five nominees will make you want to get up dance, and this is it. With its Funk Brothers arrangement and uplifting social message, “Fight for You” educes a bit of folk wisdom from P-Funk guru George Clinton: “free your mind… and your ass will follow.”
Celeste and Daniel Pemberton’s “Hear My Voice” from The Trial of the Chicago 7 also evokes sixties soul, albeit with more of pop flavor and even a dash of Northern soul. Celeste grew up around Brighton on England’s southern coast. Her interest in music was nurtured by her early exposure to American jazz vocalists like Ella Fitzgerald and Billie Holiday. Those influences can be heard in Celeste’s elegant phrasing on “Hear My Voice.” (Beware ads.) But her vocal style has also drawn comparisons to more contemporary British soul singers like Amy Winehouse and Adele.
The end result doesn’t slavishly duplicate any of those other singers, emerging as something else entirely. In fact, although Celeste’s voice has a timbre all her own, to my ears, the slightly retro vibe of “Hear My Voice” evokes sixties pop and blue-eyed soul artists like Dionne Warwick and Dusty Springfield. The song itself is a mid-tempo ballad with a loping, syncopated beat and an arching upward melody furnishing the tune’s main hook. Pemberton’s arrangement heightens the pop elements in the recording by emphasizing the piano and strings climbing steadily upward.
The Trial of the Chicago 7’s title is fairly self-explanatory, dramatizing the prosecution of activists from the Black Panthers, the Yippies, and Students for a Democratic Society after protesters violently clashed with police at the 1968 Democratic Convention. David’s blog on Aaron Sorkin shows, among other things, how the screenwriter/director drew upon the “drama of ideas,” a tradition associated with “turn of the century” playwrights like Henrik Ibsen and George Bernard Shaw. In a slight break from that tradition, though, Sorkin sought to end the film on a note of optimism and hope that would yield a sense of empowerment.
According to Pemberton, the director’s first choice for an end-title song to reflect that tone was the Beatles’ classic from Abbey Road, “Here Comes the Sun.” The composer, though, gently persuaded Sorkin to try something fresh, a new song unburdened by the enormity of the Beatles’ legacy. He also reminded Sorkin of the huge licensing fees that any Beatles song would inevitably command. Pemberton and Celeste’s much-deserved Oscar nomination vindicates the composer’s instincts. Had Sorkin used “Here Comes the Sun,” viewers would have soaked in its upbeat vibe. But The Trial of the Chicago 7 would have gotten only five nominations rather than the six it ultimately received.
Last, but certainly not least, we have Leslie Odom Jr. and Sam Ashworth’s “Speak Now,” featured in Regina King’s directorial debut, One Night in Miami. The film offers a fictionalized account of a fabled meeting of four icons of the 1960s: Malcolm X, Jim Brown, Muhammad Ali, and Sam Cooke.
The group assembles in a room at the Hampton Hotel to celebrate Ali’s victory over then heavyweight champion Sonny Liston. Yet, with only some vanilla ice cream and a flask of booze as party favors, the good-natured banter soon devolves into a debate about the best ways to achieve social change on the path toward racial equality.
Both musically and lyrically, “Speak Now” seems keyed to an important scene in the film where Malcolm chides Cooke for recording trifling love songs rather than music that speaks to the ongoing struggle for civil rights. He pulls out a copy of The Freewheelin’ Bob Dylan and plays “Blowin’ in the Wind.” Malcolm then asks Sam why it is that a white boy from Minnesota makes music that seems so perfectly attuned to the historical moment. Isn’t “Blowin’ in the Wind” the type of song Cooke should write? Malcolm’s criticism becomes a dangling cause that is picked up in the film’s epilogue. As a guest on The Tonight Show, Sam performs “A Change is Gonna Come” for the first time, showing how he embraced Malcolm’s challenge to him.
Beginning with a syncopated acoustic guitar riff, “Speak Now” not only recalls several moments of the film where Cooke pulls out his own guitar, but also evokes the type of folk music that was Dylan’s stock in trade during the early sixties. The guitar is soon joined by a swirling Hammond B-3 organ. The instrument’s timbre evokes both the gospel music that inspired Cooke throughout his career and Al Kooper’s distinctive organ stylings on two Dylan masterpieces recorded after he went electric: Highway 61 Revisited and Blonde on Blonde. Floating above both is Odom’s plaintive voice, urging the film’s viewer to “Listen, listen, listen.” Providing the link between past and present, the lyrics entreat the audience hear to the “echoes of martyrs” and the “whispers of ghosts.” Odom’s soaring falsetto suggests both vulnerability and hope. The song gradually builds, adding strings and percussion, until it reaches a rousing climax.
With its simple arrangement and its mixture of styles, “Speak Now” sounds like the musical child that Bob Dylan and Sam Cooke never had the opportunity to conceive. It provides a fitting end to One Night in Miami by reminding us that the struggle for civil rights continues, especially at a historic juncture where America is challenged to confront the structural and institutional foundations of white privilege and white supremacy.
Prediction
On Oscar night, I will be watching with bated breath to see if…..
…singer Molly Sandén hits the “speorg note” during the performance of “Husavik.” If she does, it will bring down the house (or at least break a few champagne glasses).
But the winner? Your guess is as good as mine. This is among this year’s most competitive races. In Variety, Jon Burlingame notes that Diane Warren’s past nominations made her the early favorite, but adds, “You can’t count out anyone, however, in this year’s level playing field.”
If the vote reflects the song that is most clearly integrated into the film’s story, it’s “Husavik.” It is also rumored to be making a late charge, aided by late campaigns by Netflix and the tiny town of the title.
If, on the other hand, the vote reflects the song that I’d want next in my iTunes queue, it’s “Fight For You.” It’s got a funky groove that just keeps on keepin’ on.
That being said, I don’t think either of those two songs will carry the day. Ever since the nominations were announced, it’s generally felt like a two-horse race: Diane Warren vs. Leslie Odom Jr. The voting could split between those who desire to finally recognize Warren after so many nominations and those who find Odom deserving of the award for Best Supporting Actor but who still voted for Daniel Kaluuya instead.
The fact that Odom is a double nominee would seem to help his chances. But his song’s social significance also gives it a slight edge. In 2015, Common and John Legend took home the prize for “Glory,” their inspirational song from Selma. Like “Speak Now,” the lyrics of “Glory” captured the zeitgeist surrounding the Black Lives Matter movement, particularly the protests in Ferguson, Missouri. The message of “Speak Now” is just as relevant and just as timely. It is possible that voters will want to acknowledge it for that very reason.
Still my gut tells me this is Diane Warren’s year. Thirty-three years ago, Warren sat in the venerable Shrine Auditorium as a first-time nominee. She came in with a fighter’s chance. Her song, Starship’s “Nothing’s Gonna Stop Us Now,” had a fighter’s chance having hit the top of the charts in five different countries, eventually earning gold or platinum record status in four of them. But it was aced out by an even more popular song, “(I’ve Had) The Time of My Life” from Dirty Dancing. It had gone to #1 in six countries and earned gold or platinum status in seven different markets.
Warren’s been waiting ever since for a chance to pop the cork in a champagne bottle at an Oscars afterparty. I think the bubbly finally flows for her this Sunday.
Once again, a shoutout to Jon Burlingame for his coverage in Variety of the Academy Awards’ music categories. His analysis of the Best Original Song nominees can be found here, here, and here.
To find short interviews with all of the songwriting teams, check out these items from The Hollywood Reporter and Billboard.
A podcast with H.E.R. discussing her collaboration with Tiara Thomas and D’Mile on “Fight For You” can be heard here.
A very long interview with Daniel Pemberton describing his work on The Trial of the Chicago 7 can be found here.
Leslie Odom Jr. talks about writing “Speak Now” here and here.
Finally, Diane Warren performs a medley of all twelve of her Oscar-nominated songs here.
Eurovision Song Contest: The Story of Fire Saga (2020).
Oscar’s Siren Song (A Slight Return): Original Score
Soul (2020).
Jeff Smith here:
After a short hiatus, I’m back with a preview of this year’s Oscar nominees for Best Achievement in Music Written for Motion Pictures. As with everything else in the COVID pandemic, this year’s nominees represent a slight departure from previous years. With the massive shuffling of release schedules, some films like No Time to Die, Dune, and In the Heights that would have been strong contenders in these categories will have to wait until next year. At the same time, the closure of theaters, and the attendant changes regarding Oscar eligibility, meant that some smaller films’ fortunes were boosted by their availability on top streaming services like Netflix and Amazon Prime.
Here I survey the five scores that received nominations and offer a prediction regarding the eventual winner. Later this week, I’ll do the same for the Best Original Song nominees.
The usual caveats apply for those readers interested in the online betting markets. My picks are for “entertainment purposes only.”
Moreover, I admit that my track record hasn’t exactly been stellar. If memory serves, I’ve gone five for eight in my previous predictions. That’s about a 62% accuracy rate. Better than chance but hardly anything to brag about.
Consequently, I advise readers to treat both predictions as the equivalent of a handicapper’s pick for a daily double. It feels really good if you are right. But truth be told, odds are against it.
Let’s turn now to the nominees for Best Original Score. At first blush, it would be hard to imagine a more disparate group of nominated films. It includes a Western, an adventure film, a family drama, a retro-styled biopic, and a metaphysical comedy in cartoon form.
Composers Trent Reznor and Atticus Ross are heavy favorites going into Sunday as double nominees. They were recognized both for their jazz-flavored orchestral score for Mank and, along with fellow nominee Jon Batiste, for their electronic atmospherics in Soul. As previous winners for The Social Network (2010), they stand a good chance of adding more little gold men to their mantles.
The long shot
The Oscar betting markets have Terence Blanchard’s score Da 5 Bloods as the nominee with the longest odds. That is a shame insofar as Blanchard remains one of the most underrated composers writing for films. Using a 90-piece orchestra, Blanchard provides an epic sound for Spike Lee’s clever take on The Treasure of the Sierra Madre. I wouldn’t say Blanchard and Lee’s collaboration on Da 5 Bloods is a career best. For me, their peak is represented by the magisterial score in 25th Hour (2003), one of the best films of the 2000s. Still, Blanchard’s music for Da 5 Bloods is awfully, awfully good.
Besides the resources of a conventional orchestra, Blanchard also engaged the services of Pedro Eustache to play the duduk, an Armenian double reed instrument that adds an unusual tone color to some of the score’s melodies. The duduk adds a touch of exoticism as a reminder that the protagonist Paul and his crew of Vietnam vets are strangers in a strange land. Yet the score wisely avoids the kinds of Orientalizing musical gestures that are common in many Hollywood films with South Asian settings. The duduk is heard in a handful of cues that underscore Otis’ relationship with Tien, his old Vietnamese girlfriend.
In contrast, strings and brass are key to several cues pitched in an elegiac register. As Todd Decker notes in his book, Hymns for the Fallen: Combat Movie Music and Sound after Vietnam, this style of music became especially common in Hollywood war films after Samuel Barber’s famous Adagio for Strings was used so memorably in Oliver Stone’s Platoon (1986). A good example is “MLK Assassinated” where the squad reacts to Hanoi Hannah’s announcement of the civil rights leader’s death.
Blanchard, too, mines this vein in cues accompanying scenes where the crew recalls the death of their squad commander Stormin’ Norman Earl Holloway.
Da 5 Bloods is a film of greed and grief, rage and remorse. Blanchard’s score not only captures the frustrations occasioned by America’s racial reckoning, but also reveals the deep sadness beneath, paying tribute to the sacrifices Black soldiers made while serving in Vietnam.
The Newbie
Our second nominee is Minari, which features the music of composer Emile Mosseri. Mosseri studied film scoring at the prestigious Berklee College of Music in Boston. But he also is a member of an indie rock band, The Dig, which has released three albums and four EPs since their debut in 2010. Mosseri got his first major film assignment in 2019 when he wrote the score for Joe Talbot’s acclaimed debut, The Last Black Man in San Francisco. Mosseri soon established himself as an up-and-comer in the world of American Indie cinema. In 2020, Mosseri not only wrote the music for Minari, but also scored Miranda July’s Kajillionaire.
Minari tells the autobiographical story of a Korean-American family’s move to Arkansas in the 1980s. When Mosseri offered to help with the film’s music, director Lee Isaac Chung gave the composer only one directive. He told him not to do something Korean. Instead, Chung and Mosseri discussed the work of Maurice Ravel and Erik Satie, seeing their impressionistic, delicate tone as an idiom more fitting for the story. Mosseri took the unusual step of writing some sketches before production began. This assured that the tone of the score was “baked in” to the film throughout post-production. It also allowed Chung and his film editor to adjust the duration of shots and select takes to better fit Mosseri’s already existing music.
Given Ravel’s and Satie’s influence on the score, it is not surprising that Mosseri’s melodies and orchestrations emphasize piano and strings. Mosseri, though, varies the tonal palette by occasionally adding voices, winds, and vintage LFO synthesizers, instruments whose timbre helps to suggest the feeling of a “dream-memory” soundscape. Many of the cues unfold as patterns of slowly shifting harmonies. This is evident in “Outro” which can be heard below.
Mosseri notes that the real challenge in the film was to communicate Minari’s warm and gentle tone without being saccharine. The score’s modesty makes it appear to be the polar opposite of Blanchard’s epic style in Da 5 Bloods. Whereas Blanchard goes for emotional sweep and impassioned sorrow, Mosseri strives for reserve and subtlety. Moreover, although Blanchard writes for a 90-piece orchestra, Mosseri’s ensemble is less than half that size. Lastly, whereas Da 5 Bloods contains a lot of music — not just Blanchard’s score, but also another ten period-appropriate songs — Minari has a little over thirty minutes of underscore, heard for less than a third of the film’s 115-minute running time.
Still, Minari and Da 5 Bloods have one thing in common. A film composer’s first job is to serve the story, tailoring their music to the specific needs of each scene. Blanchard and Mosseri have done that as well as anyone this past year. I would be happy to hear either one of their names called out as the winner come Sunday night.
The Oater
The third film nominated for Best Original Score is the Paul Greengrass Western, News of the World. Unlike Mosseri, who is a first-time nominee, this is composer James Newton Howard’s ninth nomination. During a career in Hollywood that spans more than 35 years, Howard has enjoyed close collaborations with directors like M. Night Shyamalan and Francis Lawrence. His music has also been a vital component of popular franchises like The Hunger Games and the Harry Potter spinoff, Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them.
On a personal note, Howard played a key role in my own musical biography. Earlier in his career, Howard did string arrangements and played keyboards on Elton John’s Blue Moves (1976), an album that was among the first dozen or so I bought as a teenager. I also listened repeatedly to its biggest hit, “Sorry Seems to Be the Hardest Word,” trying to slavishly duplicate both Elton’s piano part and Howard’s nifty keyboard solo. Elton won last year for Rocketman in the category of Best Original Song. It somehow seems fitting that Howard could take home an Oscar this year for Best Original Score.
News of the World tells the story of Captain Jefferson Kyle Kidd, a Civil War veteran who travels across Texas, reading news stories aloud in frontier towns for both entertainment and edification. Early on, Kidd comes across an overturned wagon and discovers a lost child. Abducted by the Kiowa, Johanna was being escorted back to her family by a federal officer when their party was bushwhacked. Kidd learns that Johanna will have to wait several months for the return of the Bureau of Indian Affairs representative. So the Captain decides to deliver Johanna to her surviving family. The rest of the film dramatizes their growing bond as Kidd and Johanna make the 400-mile trek through hostile territory to her aunt and uncle’s homestead.
Adapted from Paulette Jiles’ 2016 novel, News of the World feels a bit like a mashup of The Searchers (1956) and the Coen Brothers’ remake of True Grit (2010). Its kidnapped-child premise seems inspired by the former while the picaresque journey structure and “father-daughter” emotional dynamic derive from the latter.
Several of the film’s plot elements, though, offer comment on contemporary politics. The brusque handling of Johanna by Union Army officials in Texas can’t help but remind us of the Trump administration’s family separation policies. Similarly, when Kidd and Johanna are stopped by brigands from a radical militia, they are taken to a town governed under White Supremacist principles, an episode that serves as a grim reminder of contemporary threats of domestic terrorism.
Like Mosseri’s score for Minari, much of Howard’s music in News of the World strives to capture the intimacy and deepening trust that develops between the central characters. That relationship is reflected in one of Howard’s main musical themes heard here in a cue entitled “Kidd Visits Maria.”
Howard’s cues often feature long languid melodies in the strings, but he also nominally adheres to genre convention by incorporating harmonica, mandolin, banjo, guitar, and scratchy fiddle airs to flavor the score with a folksy, period sound. For a handful of scenes involving shootouts, hazardous travel, and hair’s breadth escapes, Howard furnishes the rhythmic drive and dynamics that give them their emotional punch. But the score is most effective in its quiet and reflective moments. Kidd and Johanna both suffer from a sense of loss and loneliness. As they gradually come to realize how much they need each other, Howard’s music communicates that well of feeling, expressing what the characters themselves are too reticent to admit.
Souls and the Soulless
This brings us to the final two nominees: Mank and Soul. For Mank, Trent Reznor and Atticus Ross sought to create a score that would seem experimental if it were featured in a film made in 1940. To some extent, they succeed. By opting for an orchestral jazz sound, they evoke a style that did not become common until the 1950s when it was popularized by later Hollywood composers like Alex North, Elmer Bernstein, and Henry Mancini. Still, despite that disjuncture, Reznor and Ross’ score still seems period appropriate insofar as it recalls much of the popular music recorded during the 1930s.
In preparing Mank’s score, Reznor and Ross decided to write cues in two different, but related styles. One set of cues involved big-band and foxtrot arrangements that would underscore scenes involving studio politics. An example is the cue “Fool’s Paradise” heard below.
The other set of cues deployed an orchestral palette and speak more to Mank’s emotional journey over the course of the film.
Notably, Reznor also admits that they often referred back to Citizen Kane during the writing process. Not surprisingly, some cues, like “Welcome to Victorville” and “Absolution,” sound a bit “Herrmannesque” in their evocation of Kane’s famous score.
A few, such as “San Simeon Waltz,” are even in the lyric mode Bernard Herrmann used in scores like The Magnificent Ambersons (1942) and The Ghost and Mrs. Muir (1947). The latter, not coincidentally, was directed by Herman Mankiewicz’s younger brother, Joseph.
For the most part, Mank’s music hits all the right notes, as bracing as a warm breeze on a summer day. The score is aptly sweet and tender for the heart-to-heart talks between Mank and Marion Davies, arch and mischievous for moments that display Mank’s acrid wit. In fact, Mank’s score seems most period-appropriate on the rare occasions when it indulges a bit of “Mickey-mousing.” An example of this occurs in the scene where Mank drunkenly stumbles as he exits a car in front of Glendale Station. As Ross notes, the music “gets drunk” as well with muted horn figures that could easily have been pulled from an MGM or Warner Bros. cartoon. All that’s missing is the sound of Mank’s hiccup.
And then there’s Soul. Reznor and Ross’ collaboration with New Orleans musician Jon Batiste is a favorite with good reason. The film’s protagonist is a jazz pianist, an element of the story that makes music integral to the viewer’s experience. Such narrative motivation has certainly helped several previous winners, like La La Land, The Red Violin, and Round Midnight. It also helps that Soul has swept almost all of the year-end critics’ awards for Best Score as well as winning a Golden Globe, a BAFTA, and a Society for Composers and Lyricists Award.
Like the score for Mank, most of the music for Soul consists of two types. On the one hand, there is the earthbound jazz performed by Joe Gardner, the film’s protagonist. These cues provide Jon Batiste an opportunity to shine. Anyone who knows Batiste from his regular gig with Stay Human, the house band on Late Night with Stephen Colbert, are well aware of his enormous talent. For me, even more amazing is Pixar’s skill in animating Joe’s pianistic skills which mimic Batiste’s virtuoso scale runs and arpeggios.
On the other hand, though, we have the music Reznor and Ross wrote for the film’s depiction of the “Great Before,” the way station where counselors prepare unborn souls for their journey to Earth.
And for the zone, a place where souls can experience euphoria upon realizing their life’s passions.
Some reviewers have characterized these cues as spacey New Age music, and that description has a grain of truth to it. Yet, the sounds created by Reznor and Ross seem more like an extension of the electronic experiments they explored in their cutting-edge work on The Social Network, Gone Girl (2014), and Waves (2018).
According to Reznor, to convey the sense of the afterlife as a world both strange and comforting, he and Ross brought in some ideas about microphone placement, vocal textures, and scraping noises they had tried out in their studio. They also processed the sounds from samples and recordings of instruments to give them a slightly off-kilter quality. Such techniques were intended to underline the “imperfections of humanity” in an interesting way. The end product is a “very sublime synthetic score,” in the words of sound designer Ren Klyce. To it, Klyce added the sounds of waving wheat fields and children’s voices to create an environment that felt safe, peaceful, relaxing, and nurturing.
The tranquil score is a perfect fit for director Pete Docter’s vision of the “Great Before.” Yet it also feels a bit uncanny coming from Reznor, a pioneer of industrial music, a style of rock music as cacophonous, abrasive, and propulsive as its name implies. Reznor’s primal howl as the frontman for Nine Inch Nails remains a cultural touchstone of premillennial, post-adolescent angst. Reznor’s contributions to Soul not only show he has mellowed with age, but also that the guy has got extraordinary range.
Prediction
This is the easy one. Barring some groundswell of support that would produce a Minari sweep, Soul will take home the Oscar for Best Original Score. All of its previous awards are very strong indicators. It’s hard to see how the Academy will be any different from any of the 35 other organizations that have recognized Soul’s score as the best of the past year.
As always, my go to source for information about the Academy Awards’ music categories is Jon Burlingame, Variety’s film music specialist. Burlingame’s coverage of these races is always informative and insightful. Some examples of his reportage can be found here, here, and here.
The Hollywood Reporter also has published some useful articles about this year’s nominees, which can be found here.
Besides the interviews mentioned above, one can find many other interviews through the web. An interview with James Newton Howard about his work on News of the World can be found here.
Discussions with Emile Mosseri about the collaboration with Lee Isaac Chung can be found here, here, and here.
Terence Blanchard talks about the music for Da 5 Bloods and his long partnership with Spike Lee here, here, and here.
Trent Reznor and Atticus Ross discuss their approach to Mank here.
The duo are featured in a long video discussing and demonstrating their creative process here.
Lastly, a link to Todd Decker’s Hymns for the Fallen can be found here.
Soul.
The ten best films of … 1930
The Blue Angel (1930)
Kristin here:
The end of this horrendous year is fast approaching, though we are still facing a long struggle to end the pandemic. On a happier note, it is also time for a little distraction in the form of my annual year-end round-up of the ten best films of ninety years ago. 1930 was also a grim year, with the Depression well established and nowhere close to its end. Herbert Hoover decided not to use federal governmental powers to help end the crisis (sound familiar?) and eventually was cashiered into a 32-year retirement, though he continued to oppose Roosevelt’s policies. At least we don’t face that long a stretch of down time with the current “president.”
I discovered that 1930 did not produce many masterpieces. There are some obvious titles on my final list, as always, but some of the films are good but not great. In any other year they would not have made the cut. (The contrast with 1927, for example, is pretty stark.) Presumably one major reason is that filmmakers were still struggling with the introduction of sound. Fritz Lang didn’t release a film that year, though he came roaring back with M in 1931, as assured a treatment of sound cinema as one could find during those early days. (For those of you who subscribe to The Criterion Channel, I contributed a video essay on sound in M to David’s, Jeff Smith’s, and my series, also called “Observations on Film Art.”) Eisenstein was off in Hollywood unsuccessfully trying to make a film for Paramount and about to fall in love with Mexico. With one notable exception, Hollywood’s important auteurs made no films or minor films or films that don’t survive.
This dearth of really great films will be short-lived. From 1932 on, I shall no doubt have the opposite problem. For now, here are my picks. All the films are worth seeing, though good copies or even any copies of some are hard to track down. (The idea that all films are available to stream online is as absurd as when, back in 2007 when I wrote “The Celestial Multiplex.”) Some of my illustrations in this entry are subpar, but 1930 does not seem to be a year that studios and home-video companies are mining for titles to restore. I hope this entry will give them a few ideas.
I try not to include more than one film by the same director in these entries, aiming for variety and coverage. This year’s most prolific great directors were Josef von Sternberg and Yasujiro Ozu, who together could have filled in half the ten slots, but I have stuck to my guideline. (When we reach 1932 and 1933, I may be tempted to make an exception for Ozu.)
Given that sound developed at a different pace in different countries, some of this year’s films are silent.
For previous 90-year-ago lists, see 1917, 1918, 1919, 1920, 1921, 1922, 1923, 1924, 1925, 1926, 1927, 1928 and 1929.
Dovzhenko’s Earth
Some of the films on my top-ten list this year may raise eyebrows, but Earth is probably my least controversial choice. It remains one of the last classics of the Soviet Montage movement.
The policy of merging small farms into collective ones had begun in 1927 as part of the First Five-Year Plan. In 1929-30, the push increased, with the seizure of the assets of the more prosperous peasants who resisted collectivization, termed kulaks. Major films were made with the aim of villainizing the kulaks and emphasizing the backbreaking labor involved in traditional, non-mechanized farming. Eager young peasants were hailed as heroes, and tractors appeared as the means to greatly increase wheat yields–wheat which was often seized and sent to the cities to enable rapid industrialization.
Eisenstein had promoted collectivization with his Old and New in 1929, and Dovzhenko followed a year later with Earth. While Eisenstein’s approach had been sarcastic and comic, Dovzhenko pursued his poetic approach to cinema. The opening celebrates the fecundity of the earth and the cycles of nature. The famous opening juxtaposes a peasant girl’s face with a large sunflower. Semion, an aged peasant, is calmly, even cheerfully awaiting his imminent death, lying on a blanket and surrounded by heaps of apples.
A kulak family is soon introduced, angry at the idea that their possessions will be seized. The head of the family declares that he will kill his animals rather than turn them over, and he tries to attack his horse with an axe.
The arrival of the village’s new government-provided tractor marks a shift to an emphasis on the advantages of collective farming. As it approaches, the kulaks stand watching and mocking the idea of a machine taking over. In one shot, an elderly kulak stands framed against the sky, his wealth indicated by the presence of a hefty cow. The tractor temporarily halts, but it turns out that the radiator is dry. The simple solution is for the collective members to urinate into it.
Earth is a visually beautiful film, but like other Soviet classics I have complained about, there is no decent print of it available. The old Kino disc groups it with Pudovkin’s The End of St. Petersburg (the cropping of which I mentiooned in the 1927 entry) and Chess Fever. The copy of Earth is too dark and indistinct. To get some frames for illustrations, I watched the visually superior copy on YouTube, but there the images are cropped to a widescreen format. Just as bad, there are ads scattered through it, including one in the middle of Vasyl’s twilight dance in the road just before he is shot!
As before, I must end by pointing out that an archival restoration and a Blu-ray release are in order.
Ozu debuts on the list
Although after 1937 there are years when Ozu did not make a film, he will likely feature on these lists as long as I continue to post them. In 1930 he made six features and a short. Only three survive: Walk Cheerfully, I Flunked, But … , and That Night’s Wife. I’ve chosen the last, though Walk Cheerfully is a viable candidate as well. Sound was adopted slowly in Japan, and Ozu held out until 1936 before releasing his first talkie, The Only Son, which will doubtless feature on my list for that year.
The British Film Institute released That Night’s Wife in a boxed set called “The Gangster Films,” along with Walk Cheerfully and Dragnet Girl. Yes, Ozu made gangster films, including the wonderful Dragnet Girl, the film that might lead me to make my exception in the 1933 entry.
That Night’s Wife, though, is not really a gangster film. Shuji, the father of a daughter with a potentially fatal illness, is not a gang member but a decent working man who stages a hold-up to get money for her medicine. Ozu handles this hoary plot premise with his usual unconventional approach.
The opening, with its shots of dark, empty streets through which the police chase Shuji, is film noir ahead of its time. We soon are introduced to his worried wife, Mayumi, tending the little girl. She’s cute but has a distinctly bratty streak so common to Ozu children. This and fairly frequent moments of subtle humor help Ozu avoid a purely melodramatic presentation of the situation.
Once Shuji arrives at home, Mayumi gets him to confess what he has done. He intends to turn himself in after the daughter’s crisis passes, but a gruff detective who has posed as a cabby to find out where he lives, appears. Being told that the daughter will only survive if she lasts through the night, the Detective agrees to stay and settles in to guard his prisoner. Mayumi reveals her inner toughness and determination to defend her husband. At one point the Detective dozes off and she steals his gun and points it and her husband’s pistol at him, urging Shuji to escape (above). That shot, by the way, shows a motif typical of early Ozu films: having posters, often for American movies, visible on the walls behind the characters.
That Night’s Wife doesn’t display the fully mature Ozu style, but no one would mistake it for a film by another director. He has already mastered the perfect match on action, and he uses one in the early scene where Mayumi sits down as the doctor tends the daughter. Ozu cuts in with a move across the axis of action that places us 180 degrees on the other side of her.
Ozu is not using 360-degree space consistently yet, but he’s playing with the idea. Twice he has transitions that move through a series of adjacent spaces, one of his key devices and one that will last throughout his career. Here we move from the worried Mayumi to Shuji, trying to elude the police after the theft.
There’s a lyrical motif mutating from shot to shot: worried wife, interior lamp, interior plant against wood, outdoor light with leaves, stone building with the shadows of leaves, and stone building with the subject of Mayumi’s thoughts, cowering. But causally the four “extra” shots tell us little about where Shuji is in relation to the home he seeks to reach.
I took these frames from the BFI set, but in the US Criterion released the same three films in its Eclipse brand under the more accurate title “Silent Ozu – Three Crime Dramas.” (I Flunked, But … is in the BFI’s four-film set, “The Student Comedies.” Criterion hasn’t released a DVD of it, but it is streaming on the Channel.)
The Germans’ sound advantage
Unlike other countries, Germany developed its own sound system, owned by the Tobis-Klangfilm company. Tobis was initially able to use court injunctions to keep American films out of the German market. In 1930, this pressure led ERPI and RCA, owners of patents on the major US sound-on-film systems, to form a cartel in conjunction with Tobis, which had producing and distribution subsidiaries throughout Europe. Tobis-Klangfilm continued to dominate European sound recording and reproduction until the beginning of World War II.
Partly as a result of this technical advantage, several early 1930s German films became classics, though not all of them are known abroad.
One internationally famous classic is The Blue Angel. I’ve mentioned that von Sternberg was among the most prolific of major directors in 1930. I debated whether to put this or Morocco on the list. If cinematography were the main criterion, Morocco would have been the choice. Not surprisingly, Lee Garmes’s camerawork and lighting is spectacularly good.
I initially saw The Blue Angel decades ago, in grad school. It was the usual hazy 16mm print of the American release version. Watching it again in the German version, remastered from a 35mm negative, was a revelation. Not that it will ever be one of my favorites. It has its problems. The motif of the clown, implied to be Lola’s degraded ex-lover, is heavy-handed. Emil Jannings’ lumbering performance as Prof. Rath is at odds with the casual realism of the other performances. The time-passing montage accomplished via a hair-curler ripping down a series of calendar pages creates a time gap of years passing and the characters–especially Lola–have changed radically. Her change from a kind attitude toward Rath to cruelty and indifference is logical, given his passive decline from professor to clown, but it is presented too abruptly. Still, in my opinion the film’s pluses outweigh its minuses.
The Blue Angel, seen in a good print, is wonderfully photographed as well (see top). It may not have Lee Garmes, but it has Günther Rittau (co-cinematographer with Hans Schneeberger). He had lensed Die Nibelungen, Metropolis, Heimkehr, and Asphalt. He brings a dark look to the film, as in these shots of Rath in dignified professor mode and later onstage in a caricature of his former self.
The camera movements are rare and unobtrusive. A visual motif set up early on shows the bustling classroom that Rath presides over, where despite the students’ dislike of him, they obey his strict commands. Later, in after Rath has visited The Blue Angel and met Lola, his blackboard is covered with caricatures and insults drawn there by the students to mock his obsession with Lola. A slow track back emphasizes the empty classroom as he sits at his desk, his authority over the students gone.
No doubt it’s a matter of taste, but I find Marlene Dietrich’s performance here more attractive than in Morocco–and it is, of course, central to the film’s appeal. Her amused playfulness with Rath, her quietly sarcastic attitude toward her sexuality being The Blue Angel’s main attraction, and her frequent bits of business with props unrelated to the story all differ considerably from her Hollywood performances. She has a natural glamor here that will disappear in her roles for von Sternberg in Hollywood.
After this film, von Sternberg made Dietrich a Hollywood symbol of glamor, but as a result she tends to be less spontaneous and active, with the camera and lighting lingering over her. Basically her glamor became more sultry. The result has its own appeal (and Shanghai Express is a good bet for a place on the 1932 list), but it is revealing to see her performing in a way that she only recaptured occasionally, if at all, in her subsequent films.
The frames were taken from the Kino on Video two-disc set, which has both the German and truncated American versions, as well as some supplements. It was subsequently released on Blu-ray, but I haven’t seen that version.
I always try to call attention to little-known films rather than sticking to the conventional classics for the whole list–and there aren’t a lot of such classics this year anyway. This time it’s a charming, imaginative musical romance, Die Drei von der Tankstelle, or “The Three from the Filling Station,” directed by Wilhelm Thiele and starring Lilian Harvey and Willy Fritsch. It was so popular that it outgrossed The Blue Angel in Germany.
Three carefree young men, who start off driving in a car and singing about friendship, arrive in their lavish shared home to discover that they are bankrupt. Low on gas, they are inspired to start their own filling station. They sing a nonsense song, “Kuckuck” (the German equivalent of “cuckoo”) as their belongings are hauled away, and they give this name to their art-deco filling station.
Lilian (the heroine’s name as well) shows up in search of gas for her roadster, and the three men fall in love with her. The rest of the film involves their competition over her. Naturally she chooses Willy (Fritsch’s character name). The two were often paired in later German films of the 1930s and became the ideal movie couple.
The film maintains its playful, often silly tone until the end. As Lilian and Willy are united before a closed theatrical curtain, she turns front and says, “People! The public!” There is an objection that this is not the way to end an operetta and the curtain opens to reveal the entire cast as well as additional dancers and singers performing a lively and somewhat chaotic grand-finale number.
I originally saw this film at the Cinémathèque Royale de Belgique (now the Cinematek). As it does not circulate in the US on home-video, I have taken these low-quality frames from a homemade DVD, probably originally dubbed from an unsubtitled German VHS copy. It is available on a German DVD, since it is considered a perennial classic there. Unfortunately it has no subtitles. (The German manufacturers do not seem to have cottoned onto what their counterparts in other European nations–notably France–have: that if you include optional English subtitles, you can sell more copies.)
I hope, however, that eventually someone at the DVD/Blu-ray companies will discover this very entertaining film and make it more widely available.
A German director abroad
F. W. Murnau’s City Girl is another of those films I saw in a poor print decades ago and respect a great deal more after seeing it in a good version and knowing more about film than I did then. I wouldn’t put it in the same league as some of his earlier films, but for a 1930 list, it stands out.
Murnau was already on the way out at Fox when he was making the film. After his departure, the film was “finished,” including some dialogue scenes that were inserted. As with several other films of the era, such as Borzage’s Lucky Star and Duvivier’s Au Bonheur des Dames (see below), we are lucky in that only the silent version survives. The restored dialogue scenes in Fejos’s Lonesome show how ghastly these added interludes could be. (My apologies to the restorers. Obviously somebody had to do it.)
The heroine of the title is Kate, a waitress in a busy Chicago diner. Disillusioned by the obnoxious male customers she must cope with and lonely in her sparse apartment (below), she dreams of the apparently peaceful countryside that she sees in pictures. Lem wanders in for a meal, having been sent by his tyrannical father to sell the harvest from their wheat farm in Minnesota. He becomes a regular customer as he stays in Chicago waiting for the price of wheat to rise. His friendly, courteous behavior confirms her idealization of rural life, and they fall in love. Once she arrives at the farm, however, her illusions are shattered by the father’s violent rejection and the loutish behavior of a gang hired to help with the harvest, against neither of whom Lem seems able to defend her.
As in Sunrise, City Girl creates a contrast of city and country, though on the whole the city here comes across as more oppressive than the relatively friendly treatment the couple in Sunrise receive there. Sunrise spends half the film presenting the aftermath to the couple’s reconciliation, while City Girl has a grimmer tone, and the happy ending arrives very suddenly and briefly.
According to Janet Bergstrom’s informative essay accompanying the “Murnau, Borzage and Fox” DVD boxed-set, Murnau initially wanted to film in Grandeur, a widescreen format of the day, but the budget wouldn’t allow it. (I suppose the effect might have worked, as the 70mm version of Days of Heaven demonstrates with a similar locale.) Perhaps it was just as well. Cinematographer Ernest Palmer has handled the landscapes well (top of this section) and given a distinctly documentary look to the harvest scenes.
The restored version of the film in the Fox boxed-set is excellent, but that box is long out of print. British company Eureka! has released City Girl on Blu-ray, which should look even better, available as an import on Amazon.com in the US (where it is listed as Blu-ray but is the same edition as is listed on amazon.co.uk as dual-format Blu-ray/DVD).
The French between silence and sound
René Clair has long been considered one of the directors whose early sound films were among the most imaginative and technically sophisticated. Indeed, that era was perhaps the high point of his career, with Sous les toits de Paris (1930), Le Million (1931), and À nous la liberté (1932) coming out in quick succession. The first two were made for the French subsidiary of Tobis, Films Sonores Tobis, which produced French films in its Epinay Studios. Its prosperity and technical sophistication are evident in the large sets constructed for Sous les toits.
The film centers on Albert, who makes his living selling sheet music to passersby in the street and leading them in sing-alongs. In the opening scene, a small crowd joins in a song called “Sous les toits de Paris” (above). He falls in love with Pola, who is claimed by Fred, one of the many thugs played by Gaston Modot across his career. She moves in with Albert, but when he is framed for a crime committed by Fred’s gang and sent to jail, she takes up with Albert’s best friend.
This light tale gives Clair the opportunity to show off the flexibility and even flashiness of his style. The opening shot is a long crane movement descending from chimneys against the sky to the crowd singing along with Albert. Clair also uses a variety of camera angles, as in the low-angle still above.
There are several carefully lit street scenes, including this one shot in depth with both characters’ backs to the camera as Albert spots Pola outside a bar.
The climactic scene involves a tense conversation between Albert and his pal as Pola looks on. Clair shoots the two men in shot/reverse shot through glass doors, so that we do not hear them but only watch their actions and faces in a deliberate reversion to silent cinema.
Sous les toits de Paris is still in print as a DVD from The Criterion Collection. (An early issue, number 161.)
At least in the US, Julien Duvivier is not as familiar as Clair, being known mainly for Pépé le Moko, but his reputation is rightly growing. David did his part in promoting Duvivier by contributing a video analysis of his 1941 Hollywood romance Lydia on The Criterion Channel.
I don’t know whether Duvivier was inspired by L’Herbier’s L’Argent (which featured on my 1928 list) to make Au Bonheur des Dames, but there are certainly similarities between them. L’Herbier’s film was adapted from the eighteenth novel in Zola’s Rougon-Macquart series, published in 1891, but the film updated the story to the 1920s. Au Bonheur des Dames was adapted from the eleventh novel in the series (1883) and also updated. L’Argent showed the harm done by large banks, while Au Bonheur des Dames deals with the damage wrought on traditional small shops by the rise of huge, corporate-level department stores. Zola had modeled his giant store on Le Bon Marché, while Duvivier was able to shoot interiors for the store “Au Bonheur des Dames” in the Galerie Lafayette–much as L’Herbier had shot in the Paris Bourse over a weekend.
The story concerns Denise (Dita Parlo in her first French film), a naive young woman who comes to Paris expecting to work and live in her uncle’s custom-tailor shop. Instead she finds him on the verge of ruin, since the new department store is located directly across the street. He refuses to sell to Mouret, who runs the department store and wants to expand. But all the shop-owners on the block have given up, and the demolition work removing them gradually drives the tailor mad. In the meantime Denise, fascinated despite herself with the glamor of the department store, gets a job as a model there. She attracts the romantic attention of Mouret and the lecherous attention of a manager and would-be rapist (see respectively in the center and right foreground in the frame above).
Also like L’Argent, Duvivier’s film has strong elements of the Impressionist movement, which was largely over by the late 1920s. The opening portrays Denise’s reaction to the bustle of Paris after she arrives by train by a rapid montage images superimposed around her bewildered face. Later, her uncle’s growing obsession with the demolition of his neighborhood is suggested by many subjective devices, including a prismatic shot of the workers.
There are also many shots staged in depth, including a cut between Denise’s cousin’s fiancé, who has been caught sneaking out to desert her, and a reverse angle (maintaining screen direction) from behind her as he looks guiltily back.
The film was made in both sound and silent versions. Only the latter survives. I watched the Arte Video/Lobster Films version, still in print. (A Facets release in the US is out of print.) The French DVD has English subtitles, as well as a short, informative video introduction by Serge Bromberg in lieu of program notes.
The lingering legacy of World War I
During World War I, the relatively small number of films about the war naturally supported the combat, demonized the enemy, and in the US, urged people to buy War Bonds.
Given the pointlessness and widespread death and injury caused by the war, a reaction soon occurred in filmmaking within the major countries involved. Abel Gance’s J’Accuse (1919) is the earliest film displaying a bitterness about the needless bloodshed of the war, followed soon by Rex Ingram’s adaptation of Vicente Blasco Ibáñez’s 1918 bestseller, The Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse. The film made it onto my 1921 ten-best list. There the emphasis shifts to family members and friends of different nationalities having to fight each other (a theme that Griffith had used in The Birth of a Nation). Four Horsemen ended with progressively distant views revealing an enormous cemetery of white wooden crosses, a motif also used briefly in J’Accuse that would become common in pacifist films of the period.
The next big film was King Vidor’s The Big Parade (see my 1925 list), one of the great box-office successes of the 1920s. The filmmakers went so far as to end the film with the hero reunited with his French love, but having lost a leg in the combat. From that point, killing off some or all of the major characters became the norm of subsequent significant anti-war films. (The Big Parade does kill off the hero’s two friends-in-arms.)
The 1930s carried on the condemnation of World War I, with two of the major films on opposite sides being released in 1930. They carry on the idea introduced in The Big Parade that the ordinary soldiers fighting on the German and American sides were basically alike and could recognize each other’s humanity.
G. W. Pabst’s Westfront 1918 starts late in the war, when the German soldiers in the trenches have become thoroughly disillusioned and unspeakably weary. The first big attack on their position turns out to be friendly fire from their own artillery. (The trope of incompetent commanding officers as among the true villains in World War I–and in some case other wars–has lingered in films ever since.) One of the four German soldiers who form the group protagonist falls in love with a French barmaid in a village near the front. In the final scene, huge numbers of casualties from the latest French attack are treated at a German war hospital, with French and German patients mixed together–as the dead had been in the battle itself (see the image above).
Pabst, like other filmmakers, uses the visit home on leave as a way to emphasize the war’s impact on the home front. Karl, the most important character of the four main soldiers, returns for the first time in eighteen months only to find his wife in bed with another man. Pabst introduces the home-front section with a long line of people waiting to buy food. Karl’s mother sees him arrive but cannot greet him because after hours of waiting she had reached the front of the line.
The impressive final battle scene ends with the last of the central characters dead, and the carnage drives the lieutenant who commands them into mad raving.
The film makes a powerful statement designed to end all wars, and yet one cannot help wonder if those Germans inclined to resent the results of the Treaty of Versailles might have been inspired to a greater desire for revenge by it.
The American counterpart of Pabst’s film is Lewis Milestone’s adaptation of All Quiet on the Western Front. The 1929 translation of the German novel had become a huge bestseller in the US. Producer Carl Laemmle, who was born in Germany and visited friends and family there regularly, no doubt had a personal as well as a financial incentive to acquire the rights for Universal.
It would be easy to dismiss this big Hollywood production and ultimate Best Picture winner at the Oscars as a slick commercial venture. Certainly it has the glossy, expensive studio look that Westfront 1918 lacks, as in this scene, with its perfect three-point lighting carefully picking out each figure.
Being from a German novel, however, makes this the first significant Hollywood film to treat German soldiers sympathetically and to make them the lead characters. As in Westfront 1918, there is a tight little group of friends, three in this case, with the point-of-view figure being Paul (Lew Ayres). He is the one whom we follow on his visit home while on leave. There he visits his mother, as expected, but he also drops in on his old classroom and is disgusted to find that his teacher is glorifying war and preparing a new generation of young men to go off to become soldiers.
The opening of the film had shown Paul as a student being told of the glories of war and rushing off to sign up. This is the only one of the anti-war films I know of that portrays this sort of social indoctrination as a crucial cause of the horrors of war.
As with the other anti-war films of the 1920s and 1930s, the scenes of are extended and realistic in their depiction of trench warfare. And as in Westfront 1918, all the main characters die. At the end we see them marching off, with vast fields of white crosses superimposed.
The French produced their great anti-war films only slightly behind the Germans and Americans. Raymond Bernard’s masterful but little-known Wooden Crosses (1932), which focuses largely on French troops, is no less powerful in its depiction of trench warfare. Jean Renoir’s Grand Illusion (1938) broke with tradition by downplaying battlefield action and focusing on the senseless loss of life and liberty and the effects of class differences in warfare.
All Quiet on the Western Front has been restored and released on Blu-ray a deluxe edition with DVD and supplements or with the supplements but no DVD.
Experimental cinema in 1930
Surprisingly enough, in a weak year for commercial feature films, there was a considerable number of significant experimental films made. The standard historical accounts when I was a grad student (and probably thereafter) suggested that sound made film production too expensive for the shoestring-budgets of experimental filmmakers. Clearly, though, many of them carried on. Some of the 1930 films are silent, but by no means all. Therefore I’ve decided to devote the tenth slot in my list to a brief summary of several of them. These are in no particular order.
Mechanical Principles was Ralph Steiner’s next film after the better-known H2O (1929). Despite the scientific-sounding name, Mechanical Principles is an abstract film made by shooting close view of moving gears and other devices for moving parts of machines (above). The shapes and movements are engaging in themselves, but there is also, I think, a subtle and amusing progression toward more odd and even absurd-looking mechanisms. I doubt anyone would learn anything about “mechanical principles” from the film. (Included in Flicker Alley’s excellent duel Blu-ray/DVD collection, “Masterworks of American Avant-garde Experimental Film 1920-1970.” The visual quality is distinctly better than the versions on YouTube.)
The wonderful German animator Oskar Fischinger specialized in making abstract animation in time to pieces of music. In 1930 he made Studies No. 2 through 7. YouTube contains only snippets of his films; presumably the rights holder, the Center for Visual Music, has diligently patrolled it.) Studies No. 6 and 7 are the most widely seen. I am particularly fond of Study No. 6, to “Los Verderomes fandango,” by Jacinto Guerrero (below). These shorts use a broad range of musical accompaniment. Study No. 7 is done to Brahms’s “Hungarian Dance No. 5.” I haven’t seen all of the Studies, but I assume they all use the same technique, charcoal drawings on paper. There were VHS videotapes released and a laserdisc in 1996, all long out of print. The Center for Visual Music has brought out two DVDs with selections from his films, digitally remastered and with intriguing-sounding supplements.They are sold through the CVM.
The Bridge is a silent film, adapted from the Ambrose Bierce story “An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge.” Its director, Charles Vidor (né Karoly Vidor in Hungary, no relation to King Vidor), had come to the US in 1924 and worked as a chorus singer. He managed to self-finance The Bridge, which centers on a man condemned to execution as a spy. As he is being hanged by a military escort on a bridge, we see a complex combination of flashbacks to his childhood and fantasies of escape (below). The film was impressive enough to gain Vidor to gain an MGM contract to direct The Mask of Fu Manchu (1932). The high points of his long career are Cover Girl (1944) and Gilda (1946).
The Bridge is included on the fourth disc in the “Unseen Cinema” collection.
Walther Ruttmann’s Weekend (the original title is in English) is not a exactly a film, even though its subtitle is “Ein Hörfilm von Walter [sic] Ruttmann.” That roughly translates as “a radio-film,” and it was produced by the Reichsrundfunk Gesellschaft (national radio). On the DVD it is reproduced as a black screen with sound over, which one could play in projection. The list of sections given at the beginning runs: “Jazz der Arbeit / Feierabend / Fahrt ins Freie / Pastorale / Wiederbeginn der Arbeit / Jazz der Arbeit” (Jazz of Work / Quitting time / Travel in the Open Air / Pastorale / Recommencing Work / Jazz of Work). The “film” is a lively and often amusing montage of sounds, including trains, tools, engines starting, drum beats, brief snatches of dialogue, a cuckoo clock, a siren, a rooster, and so on. Its twelve-minute length is well gauged to avoid having the device wear out its welcome.
I hardly need to write anything about Dziga Vertov’s Enthusiasm: Symphony of the Donbass. For many years Vertov held his high reputation largely on the basis of Man with a Movie Camera, one of last year’s top ten. Enthusiasm was Vertov’s last Ukrainian film and apparently the first Ukrainian sound feature. Although the film’s credits emphasize that it was shot on location, including the interior of a coal mine, clearly nearly all the footage was shot silent and had a “symphony” of sounds woven together and laid over it.
The film has some of the playfulness and experimental cinematography so familiar from Man with a Movie Camera. That film is so engaging in part because it was primarily a lively look at Soviet everyday life, including movie-going. Enthusiasm, however, is far more overtly propagandistic, being largely a celebration of the early achievement of the First Five Year Plan’s coal quota in the Ukraine in four years. This was thanks to the “enthusiasts,” as the film puts it: Stakhanovites, that is, workers who did considerably more than their comrades through hard labor and efficiency. (They were named after Alexei Stakhanov, a coal miner; the movement started in the coal industry.) Some of the Soviet workers and peasants sincerely approached their work in this way, but in reality much of the achievements of the Plan were achieved through forced labor.
The restored film is included on Flicker Alley’s Blu-ray disc, “Dziga Vertov: The Man with the Movie Camera and Other Newly Restored Works.”
One of the finest experimental films of 1930 is Lázló Moholy-Nagy’s Ein Lichtspiel: Schwartz Weiss Grau (“A light play [i.e., a film]: Black White Gray”). It is derived from his constructive sculpture, Lichtrequisit einer elektrischen Bühne (“Light device for an electric stage”), which consists of many metal elements, some of them pierced with rows of holes, through which lights can be shown to create moving shadows. It later came to be known as the Light-Space Modulator. (The original is in the Busch-Reisinger Museum, Harvard.)
Moholy-Nagy made a film of the Modulator in action, with shifting solid shapes and shadows. It is sometimes hard to tell whether the camera or the device itself itself is moving.
Unfortunately no high-quality print seems to be available. Facets offers several of Moholy-Nagy’s films on separate DVDs, including Ein Lichtspiel–which is a little odd, given that it is only six and a half minutes long. (The modern soundtrack makes the object seem like a very elaborate set of wind chimes.) This DVD is probably the source of some of the better versions of the film posted on YouTube. It would be a pity to encounter the film in this way, but given the current situation, this is the best of the copies available there.
Kenneth MacPherson was co-founder of the Swiss-based Pool-Group, along with his wife, Bryher (née Annie Winifred Ellerman) and the poet, HD (Hilda Doolittle). Together they started Close-up, an important journal on international art and experimental cinema (1927-33). MacPherson made a few films, most notably the short silent feature Borderline. MacPherson was influenced by French Impressionism and Soviet Montage, and their stylistic traits are used in Borderline, including subjective camerawork and bursts of very rapid editing to convey violence or psychological stress.
The plot deals with racial and sexual tensions in a small Swiss village when a black couple comes to live there. Pete, in a genial performance by Paul Robeson, takes back his fiancée (or wife?) after she has had an affair with a white man, Thorne. Thorne remains obsessed with her, which gradually drives his neurotic, racist wife, Astrid (HD, credited as Helga Doorn) mad. Although Thorne has rented a room over a tavern owned by people sympathetic to the black couple, the scandal leads the villages to demand that Thorne be evicted, and he leaves town.
Some other experimental films made in 1930 that I didn’t think were as good as these but are still worth watching if one is particularly interested in this genre:
Francis Bruguière’s Light Rhythms (on the third disc of the Unseen Cinema set), a more low-budget attempt at something like Ein Lichtspiel, using paper cut-outs.
Luis Buñuel’s L’Âge d’or. (The BFI Blu-ray/DVD combo is out of print, although amazon.com is still selling it. Kino Lorber put out a DVD, which I haven’t seen.) I know this is considered a wonderful film by many, but I dislike it and much prefer Un chien andalou.
James Sibley Watson’s Tomatos Another Day (on Kino International’s “Avant-garde 3” set) is a pretty dreadful film, a sort of “theater of the absurd” before its time. I suspect it is a parody of a modernist play of the day. If so, and if anyone knows what play it was, please message me on Facebook and I’ll add that information. Suffice it to say that the husband, his wife, and her lover say obvious things out loud and very slowly “You are my lover,” “I am alone,” that sort of thing. Then all three start talking in dreadful puns (“Tomotos’ another day”). One might say it’s so bad, it’s good.
Sergei Eisenstein and Grigory Alexandrov co-directed Romance sentimentale, a quite uncharacteristic imitation of French Impression or city symphonies. Finally getting a chance to see it decades ago was one of the great disappointments of my life. It is available as a supplement on the Kino DVD of the restored Qué viva México.
A succinct account of Tobis-Klangfilm’s business operations can be found in Douglas Gomery’s “Tri-Ergon, Tobis-Klangfilm, and the Coming of Sound,” Cinema Journal 16, 1 (August 1976): 51-61. (Available on JSTOR.)
I have summarized the “wooden crosses” motif that is almost universal in anti-war films of the 1920s and 1930s (and occasional later films as well) in my video essay on Raymond Bernard’s Wooden Crosses on The Criterion Channel, where the film is permanently streaming.
Our friend and colleague Vance Kepley published an excellent study, In the Service of the State: The Films of Alexander Dovzhenko (University of Wisconsin Press, 1986).
January 27, 2021: Thanks to Cindy Keefer of the Center for Visual Music for kindly sending some corrections to my discussion of Oskar Fischinger:
All Quiet on the Western Front (1930)