Archive for the 'Awards' Category
Women, Oscars, and power (a repost)
Kathleen Kennedy on the 1 January 2013 cover.
Kristin here:
David’s health situation has made it difficult for our household to maintain this blog. We don’t want it to fade away, though, so we’ve decided to select previous entries from our backlist to republish. These are items that chime with current developments or that we think might languish undiscovered among our 1000+ entries over now 17 years (!). We hope that we will introduce new readers to our efforts and remind loyal readers of entries they may have once enjoyed. The run-up to the Oscars seemed a good time to revisit this one.
Ever since the Oscar nominations were announced on Tuesday, January 23, social media and mainstream news outlets have been full of posts and articles about the “snubs” of female directors, notably Greta Gerwig and Celine Song. Even Hilary Clinton weighed in with some Barbie-love. Of course the failure to nominate many other people, male and female, also insired similar indignant tirades by fans. How could Alexander Payne be left out when virtually everyone who sees The Holdovers adores it? What about Leonardo DiCaprio? Or Greta Lee? Or fill in the blank?
This sort of kvetching goes on every year, when inevitably a large number of worthies fail to be nominated. This year was perhaps bound to produce more of these also-rans, since as many have pointed out, this year saw an unusual number of excellent films. Christopher Nolan, Wes Anderson, and Alexander Payne released films that are arguably among their best. Aki Kaurismäki, after a gap of six years, returned with the quietly excellent Fallen Leaves. Hayao Miyazaki came out of retirement with The Boy and the Heron. Outside the Oscar nominees, major veteran filmmakers contributed Close Your Eyes (Víctor Erice) and R.M.N. (Cristian Mungui). The list could go on.
Returning to the issue of female directors and actors being snubbed by Academy voters, a few people point out that Margot Robbie is nominated for “Best Picture,” having been one of the producers of Barbie. Emma Stone is in the same position with Poor Things (though she, of course, did get nominated for Best Actress). On the whole, however, being a woman nominated for producing a Best Picture gets little or no attention, even if it is arguably as prestigious, if not more so.
This strange imbalance has gone on for a long time. On October 23, 2017, I posted a blog entry on the topic. It was inspired by a Variety cover story on Kathleen Kennedy (above). I discussed the reasons why female producers are ignored by the public and by journalists. As I say below, that happens partly because there is no “best producer” category, and in the past, the names of the producers who would claim the statuette if their films won, were not listed. I see that this year, the Academy’s website does list all the names of the producers of the Best Picture nominees. Did they read my post? I’ll never know. I note that the suggestion made in my final paragraph has not been followed by the press.
The old post does give a rundown of female producers who were nominated and in some cases won, from the first in 1973 up to 2016, by which point women were commonly being nominated in this category. For 2023, eight of the 30 producers of Best Picture nominees are women.
The original entry
We are now well into the season when award speculation begins. Well, actually Oscar speculation knows no season these days, but it snowballs between now and the announcement of the winners on March 4–at which point the speculation concerning the 2018 Oscar race revs up.
Among the issues that will inevitably come up is the question of whether more women directors will get nominated, especially following the critical and box-office success of Patty Jenkins’ Wonder Woman. It would be great to see more female nominees for Best Director, but the real problem is achieving more equity in the number of women being able to direct films at all. Unless more women direct more films, their odds of getting nominated will be low. Maybe the occasional Kathryn Bigelow will emerge, but overall the directors making theatrical features remain largely male.
Variety recently ran a story about initiatives to boost women’s chances in Hollywood. It stressed the low percentage of women in various key filmmaking roles:
The Center for the Study of Women in Television and Film at San Diego State University found that in 2014, women made up just 7% of the directors behind Hollywood’s top 250 films. Overall, of the 700 films the center studied in 2014, 85% had no female directors, 80% had no female writers, 33% had no female producers, 78% had no female editors and 92% had no female cinematographers.
Discouraging, except that there’s one figure that doesn’t support the lack of women. If 33% of films were without female producers, that means 67% had female producers–which is a lot better than in those other categories.
One thing that has struck me as odd is the lack of attention paid to the distinct rise in the number of female producers being up for Oscars in the recent past. This Variety article, however, is the first one I’ve seen offering numbers to show that women are doing a lot better in the producing field than in other major areas.
The missing names
Kathleen Kennedy, the lady illustrated at the top of this entry has produced seven films nominated as Best Picture, and she is considered one of the most powerful people in Hollywood. How could she not be? She produced Steven Spielberg’s films, alongside others, for many years and since October, 2012, she has been President of Lucasfilm in its incarnation as a subsidiary of Disney. She runs the Star Wars series.
In the Indie realm, producer Dede Gardner is on a roll, having since 2011 had three films nominated for the top prize in addition to wins in 2013 and 2016. Others, such as Megan Ellison and Tracey Seaward, have enjoyed multiple nominations. (I’m using the film’s year of release rather than the year when the award was bestowed.) As we’ll see, female producers are beginning to catch up to their male colleagues in number as well as prestige. Why no fuss about such important strides?
I think the main reason is that there’s no “Best Producer” category. If there were, I suspect our image of women in the industry would be very different. But there’s just a Best Picture one. In most cases neither the industry journals nor the infotainment coverage lists the producers alongside the titles of the Best Picture nominees. So who’s to know that the “Best Picture” race also is, faut de mieux, the “Best Producer” contest.
Another, perhaps less important reason why producers draw less attention is that because a film often has several producers. It’s more complicated to assign responsibility for who did what. Most people have a general idea of what directors do. They’re on set, they make decisions, and they supervise other artists. A female producer, like a male one, may have been included for many reasons. She might have done most of the work in assembling the main cast or crew members or she might have concentrated on gaining financial support. She might instead be termed a producer as a reward for crucial support at one juncture. We can’t know, and that perhaps makes it difficult for the public to get enthusiastic about producers. Of course, if journalists covered them more in the entertainment press, the public might gain more of a sense of what producers do.
Yet whatever their contribution, those producers played some sort of crucial role, and they are the ones who get up and receive the statuettes when that last climactic announcement of the evening is made. (Lately there has been a trend for the every member of the cast and crew and all their relatives present to rush onto the stage for a grand finale, but it’s the producers who give the thank-you speeches.) They can take those statuettes, with their names engraved on them, home and put them on their mantels or to their office to display in a glass case. Yet few have any name recognition outside the industry, the entertainment press, and a few academics.
Despite these producers’ importance, it’s difficult to find out who they have been over the years. Go to almost any website, including the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences’ own, in search of Oscar nominees stretching back through the years, and you will usually find names listed in all the other categories–but only the title of the nominated films in the Best Picture category. I finally found a complete list of Best Picture nominees’ producers compiled by an industrious contributor to Wikipedia. Going through and doing some counting and cross-checking, I have created and annotated my own list. With it I’ve tried to show the fairly steady progress that women have made in this category. I call them “nominees” below. Somewhat paradoxically, they win the Oscars, though technically the film is the official nominee.
To keep this list from becoming even longer, I’ve listed only nominated films which had one or more women among their group of producers. Up to 2008 there were five films each year. Starting in 2009 the number could be anywhere between five and ten, though it’s usually eight or nine. I give the number of nominated films starting in 2009. Assume any films not listed were produced by men. If you’re curious about who those men were, click on the link in the previous paragraph.
Here’s how things developed, including only years when female producers were “nominated.” (My comments in red.) Be patient. It gets off to a slow start, but things pick up.
And the nominees are …
1973 The Sting (WINNER) Tony Bill, Michael Phillips, and Julia Phillips.
Julia Phillips becomes the first female producer nominated since the Oscars began in 1927 and the first to win.
1982 E.T. Steven Spielberg and Kathleen Kennedy.
The second female producer nominated.
1984 Places in the Heart. Arlene Donovon.
The third nominated female producer.
1987 Fatal Attraction. Stanley R. Jaffe and Sherry Lansing.
The fourth nominated female producer.
1989 Driving Miss Daisy. (WINNER) Richard D. Zanuck and Lili Fini Zanuck.
Lili Fini Zanuck is the second female producer to win.
1991 The Prince of Tides. Barbra Streisand and Andrew S. Karsch.
1994 Forrest Gump. (WINNER) Wendy Finerman, Steve Tisch, and Steve Starkey.
The Shawshank Redemption. Niki Marvin.
Wendy Finerman (right) becomes the third woman producer to win a Best Picture Oscar.
This is the first year when two women are nominated. From this point to the present, there has been no year without at least one female producer nominated.
1995 Sense and Sensibility. Lindsay Doran.
1996 Shine. Jane Scott.
1997 As Good as It Gets. James L. Brooks, Bridget Johnson, and Kristi Zea.
The first year when four women are nominated.
The first time two women are nominated for the same film.
1998 Shakespeare in Love. (WINNER) David Parfitt, Donna Gigliotti, Harvey Weinstein, Edward Swick, and Marc Norman.
Elizabeth. Alison Owen, Eric Fellner, and Tim Bevan.
Life Is Beautiful. Elda Ferri and Gianluigi Brasch.
Gigliotti is the fourth woman to win a producing Oscar.
1999 The Sixth Sense. Frank Marshall, Kathleen Kennedy, and Barry Mendel.
First year when a woman producer, Kennedy, is nominated for a second time.
2000 Chocolat. David Brown, Kit Golden, and Leslie Holleran.
Erin Brockovich. Danny DeVito, Michael Shamberg, and Stacey Sher.
For the second time, two women are nominated for the same film.
2001 The Lord of the Rings: The Fellowship of the Ring. Peter Jackson, Fran Walsh, and Barrie O. Osborne.
2002 The Lord of the Rings: The Two Towers. Peter Jackson, Fran Walsh, and Barrie O. Osborne.
2003 The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King. (WINNER) Peter Jackson, Fran Walsh, and Barrie O. Osborne.
Lost in Translation. Ross Katz and Sofia Coppola.
Mystic River. Robert Lorenz, Judie G. Hoyt, and Clint Eastwood.
Seabiscuit. Kathleen Kennedy, Frank Marshall, and Gary Ross.
Walsh is the fifth woman to win in this category.
Walsh and Kennedy tie for the first woman nominated three times.
The second year when four women are nominated.
2004 Finding Neverland. Richard N. Gladstein and Nellie Bellflower.
2005 Crash. (WINNER) Paul Haggis and Cathy Schulman.
Brokeback Mountain. Diana Ossance and James Schamus.
Capote. Caroline Baron, William Vince, and Michael Ohoven.
Munich. Steven Spielberg, Kathleen Kennedy, and Michael Mendel.
Cathy Schulman is the sixth woman to win.
The third time four women are nominated.
Kennedy becomes the first woman nominated four times.
2006 The Queen. Andy Harris, Christine Langan, and Tracey Seaward.
2007 Michael Clayton. Jennifer Fox and Sydney Pollack.
Juno. Lianne Halfon, Mason Novack, and Russell Smith.
There Will Be Blood. Paul Thomas Anderson, Daniel Lopi, and JoAnne Sellar.
The first year in which five women are nominated in this category.
2008 The Curious Case of Benjamin Button. Kathleen Kennedy, Frank Marshall, and Céan Chaffin.
 The Reader. Anthony Minghella, Sydney Pollack, Donna Gigliotti, and Redmond Morris.
The Reader. Anthony Minghella, Sydney Pollack, Donna Gigliotti, and Redmond Morris.
First time a woman, Kennedy, reaches a fifth nomination.
The third time two women are nominated for the same film.
2009 The first year of up to ten nominations. Ten films nominated.
The Hurt Locker. (WINNER) Kathryn Bigelow, Mark Boal, Nicholas Chartier, and Greg Shapiro.
District 9. Peter Jackson and Carolynne Cunningham.
An Education. Finola Dwyer and Amanda Posey.
Precious. Lee Daniels, Sarah Siegel-Magness, and Gary Magness.
Kathryn Bigelow becomes the seventh woman to win in this category. (Right, with her producing and directing Oscars.)
The fourth time two women are nominated for the same film.
2010 Ten films nominated.
Inception. Christopher Noland and Emma Thomas.
The Kids Are All Right. Gary Gilbert, Jeffrey Levy-Hinte, and Celine Rattray.
The Social Network. Pana Brunetti, Céan Chaffin, Michael De Luca, and Scott Rudin.
Toy Story 3. Darla K. Anderson.
Winter’s Bone. Alex Madigan and Ann Rossellini.
The second year five women are nominated in this category.
2011 Nine films nominated.
Midnight in Paris. Letty Aronson and Stephen Tenebaum.
Moneyball. Michael De Luca, Rachael Horovitz, and Brad Pitt.
The Tree of Life. Sarah Green, Bill Pohlad, Dede Gardner, and Grant Hill.
War Horse. Steven Spielberg and Kathleen Kennedy.
Kennedy receives her sixth nomination.
The third year in which five women are nominated in this category.
The fifth time two women are nominated for the same film.
2012 Nine films nominated.
Amour. Margaret Mengoz, Stefan Arndt, Veit Heiduschka, and Michael Katz.
Django Unchained. Stacey Sher, Reginald Hudlin, and Pilar Savone.
Les Misérables. Tim Bevan, Eric Fellner, Debra Hayward, and Cameron Mackintosh.
Lincoln. Steven Spielberg and Kathleen Kennedy.
Silver Linings Playbook. Donna Gigliotti, Bruce Cohen, and Jonathan Gordon.
Zero Dark Thirty. Mark Boal, Kathryn Bigelow, and Megan Ellison.
Eight female producers nominated, besting the previous record by three.
The first year in which each of two nominated films has two female producers.
Kennedy receives her seventh nomination.
2013 Nine films nominated.
12 Years a Slave. (WINNER) Brad Pitt, Dede Gardner, Jeremy Klein, Steve McQueen, and Anthony Katugas.
American Hustle. Charles Roven, Richard Suckle, Megan Ellison, and Jonathan Gordan.
Dallas Buyers Club. Robbie Brennert and Rachel Winter.
Her. Megan Ellison, Spike Jonze, and Vincent Landay.
Philomena. Gabrielle Tana, Steve Coogan, and Tracey Seaward.
The Wolf of Wall Street. Martin Scorsese, Leonardo DiCaprio, Joey McFarland, and Emma Tillinger Koskoff.
Dede Gardner becomes the eighth woman to win an Oscar in this category.
Megan Ellison becomes the first woman nominated for two films in the same year.
2014 Eight films nominated.
Boyhood. Richard Linklater and Cathleen Sutherland.
The Imitation Game. Nora Grossman, Ido Wostrowskya, and Teddy Scharzman.
Selma. Christian Colson, Oprah Winfrey, Dede Gardner, and Jeremy Kleiner.
The Theory of Everything. Tim Bevan, Eric Fellner, Lisa Bruce, and Anthony McCarten.
Whiplash. Jason Blum, Helen Estabrook, and David Lancaster.
2015 Eight films nominated.
Spotlight. (WINNER) Blye Pagon Faust, Steve Golin, Nicole Roaklin, and Michael Sugar.
The Big Short. Dede Gardner, Jeremy Kleiner, and Brad Pitt.
Bridge of Spies. Steven Spielberg, Marc Platt, and Kristie Macosko Krieger.
Brooklyn. Finola Dwyer and Amanda Posey.
The Revenant. Arnon Milchan, Steve Golin, Alejandro G. Iñárittu, Mary Parent, and Keith Redmon.
Blye Pagon Faust and Nicole Roaklin become the ninth and tenth winners.
For the first time two women win for the same film.
For the second time, two nominated films have two female producers.
2016 Eight films nominated.
Moonlight. (WINNER) Adela Romanski, Dede Gardner, and Jeremy Kleiner.
Hell or High Water. Carla Haaken and Julie Yorn.
Hidden Figures. Donna Gigliotti, Peter Chernin, Jenro Topping, Pharrell Williams, and Theodore Melfi.
Lion. Emile Sherman, Iain Canning, and Angie Fielder.
Manchester by the Sea. Matt Damon, Kimberly Steward, Chris Moore, Lauren Beck, and Kevin J. Walsh.
Adela Romanski and Dede Gardner become the eleventh and twelfth winners.
For the second time, two women win for the same film.
For the second time, eight women are nominated, which so far remains the record.
Why should these names be hidden?
So we have overall 88 nominations for women, with twelve women winning Oscars for producing films. That compares with four nominations and one win for female directors. Women have not come all that close to parity with men in the producing category, but compared to the directors category, which people seem to take as a bellwether for the status of professional women in Hollywood, it’s spectacular. Moreover, we can see a fairly steady growth over the past twenty-three years, to the point where seven or eight producing nominations a year routinely go to women.
Of course, Oscars are not the only or the most objective way of measuring women’s power in Hollywood. One could try a similar examination of the number of women producing Hollywood’s top box-office films over the years. I assume there would be a similar growth in numbers, but the measurement would probably be a little more nuanced. That would be a much bigger project than would fit in a blog entry–even entries as long as the ones we occasionally favor our readers with. The San Diego State University study I mentioned earlier took an approach of this sort, and I’m sure there is deeper digging to be done among the statistics revealed by such research..
Given the way the Oscars have captured the public’s and the industry’s imaginations, however, the growing number of female producers being honored is a good way to point out that things may be better than they seem when one focuses narrowly on the directors category.
After all, the prescription for putting more women in the director’s chair and behind the camera and so forth is always that more female producers and writers are needed, making films for women and by women. This seems reasonable, and yet the question remains, if women are doing so well, relatively speaking, in rising to the top as producers, why, over the twenty-three years since 1994 haven’t they hired more women at every level for their film crews? (Of course, some of them have acted as producer-directors on their own projects.) Why hasn’t Kennedy, who has been firing and hiring male directors for Star Wars projects lately, ever given a female director a shot at it? Maybe she will at some point, as the evidence grows that women can create hits.
Perhaps most women producers are constrained by their fellow producers on projects, who are often men. They may feel pressured to reassure studio stockholders and financiers by sticking with the tried and true. And yet there do finally seem to be signs that studios are looking beyond the obvious pool of talent. Patty Jenkins, an indie filmmaker, directs Wonder Woman to unexpected success. Taika Waititi, a Maori-Jewish indie filmmaker from New Zealand, suddenly finds himself directing Thor: Ragnarok, which shows every sign of becoming a hit. With luck, the effect of the rise of female producers, as well as of more broadminded male ones, will finally have a significant impact on both gender and ethnic diversity in Hollywood filmmaking.
In closing, I would suggest to the press that it would be helpful for them in writing their endless awards coverage to list more than just the titles of the Best Picture nominees. Add the names of their producers, who are in effect nominated for Oscars. Treat them more like stars, the way you do with directors. I realize that there are often lingering disputes over which of the many producers attached to some films are actually the ones eligible to accept Oscars for them. But once such disputes are resolved, these “nominees” should be listed, and certainly after the awards are given out, they should be part of the historical record of Oscar nominees and winners. This would help both the public and the industry to get the big picture, not just the Best Picture.
[Oct. 24, 2017: My thanks to Peter Nellhaus for pointing out Julia Phillips’ win for The Sting in 1973. I have corrected the text accordingly.]
The Shawkshank Redemption (1994).
Oscar’s siren song: The revenge
King Richard
The Oscars are upon us again. The Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences may have decided that “Music (Original Score)” is one of the categories not important enough to show live along with the rest of the awarding of the golden statuettes. We, of course, think this is absurd. (Will the Oscar ceremony gain a single extra TV viewer through this tactic?)
We welcome back our friend and colleague Jeff Smith to continue his annual comments and predictions concerning the nominees in both musical categories: song and original score. This year he has, if anything, outdone himself in providing insights into the historical contexts and the formal qualities of the ten nominees.
‘Tis the season to pass out little gold men to people in gowns and tuxedos. This year’s Oscar ceremony is scheduled to take place on Sunday night, March 27th. And this is about the time when I offer my annual assessment of the nominees in the music categories.
The title I’ve given this blog post might appear to represent a failure of imagination. After posting the first of these surveys, I opted for a sequelitis motif by using Roman numerals and corny words like “Return.” Yet this year’s sequel title seems all too apt. The producers of the Academy Awards have been winnowing away the amount of airtime given to the music awards in the past two years. They no longer present all five of the Best Original Song nominees as part of the broadcast. This year the award for Original Score will be prerecorded before the broadcast and the winner announced in between other, presumably more important awards.
If the Academy Awards doesn’t seem to care about these categories, then why should I? Well, because as a scholar and educator, this is what I do. Consider this blog post the petty revenge of someone who believes these categories still matter, even if the organization sponsoring the awards doesn’t seem to think so.
In the case of the award for Best Original Score, there will be some bitter irony in the fact that we’ll never see the faces of the composers on the big five-way split screen used to show nominees. But we’ll hear their scores played as walk-up music if Penelope Cruz wins for Best Actress. Or if Greig Fraser wins for Best Cinematography. Or Encanto wins for Best Animated Film. Or Jane Campion wins for Best Director. Or Adam McKay wins for Best Original Screenplay.
At the end of each award preview, I’ll make an educated guess as to who the winner of the category will be. All the usual caveats apply. These predictions are not intended for wagering purposes, I offer the usual disclosure that my predictions over the years typically yield one right and one wrong. (It’s up to you to figure out which is which.)
Lastly, a warning of some spoilers. I do my best to try to avoid giving away too much information about a film. But sometimes it is unavoidable if you want to get into the nitty gritty of the choices composers make in how they score their films.
The Susan Lucci of songwriting
Last month, Diane Warren earned her 13th Oscar nomination for Best Original Song, the most by a woman in any category without a win. This isn’t the most, though, in the music categories as composers Thomas Newman and Alex North both earned 15 nominations for Best Score without ever taking home Oscar. Last April, Warren told Billboard that she the old saw about it being “nice to be nominated” was true, but that she really would like to finally win an Oscar. Said Warren, “I’m like a sports team that has lost the World Series for decades. This is 33 years since my first nomination.” Warren’s record begs comparison with soap opera star Susan Lucci, who earned 18 Daytime Emmy nominations for her role as Erica Kane on All My Children before finally winning the award in 1999.
Warren’s current nomination is for her song, “Somehow You Do,” which is featured in Rodrigo Garcia’s drama about opioid addiction, Four Good Days. Sung by Reba McEntire, Warren’s number is a countrified version of the sort of power ballad that the tunesmith has specialized in for decades. The first verse is modestly arranged for two guitars, one an acoustic and the other pedal steel. The song gradually adds more texture as it nears the chorus, with the bass adding some bottom end and a chorus punching up McEntire’s lead vocal.
The second verse continues to build with the addition of a drum kit that firmly establishes the song’s 6/8 meter and slow tempo. The song’s bridge introduces a contrasting melody and roughens up the sweetness of McEntire’s voice with some pulsating power chords played by an electric guitar. This prepares for the requisite key change as the song shifts to the final verse and chorus. The tune reaches its emotional peak here and then gradually tapers down. A brief coda returns us to the spare sound of McEntire’s voice accompanied by an acoustic guitar.
The song is very well-crafted if a bit by the numbers. It is a testament to Warren’s mastery of her craft that she finds new ways to enliven the venerable AABA structure of classic songs and fit them to the dramatic needs of the films she works on.
Yet Warren’s chances of winning seem to be hampered by a couple of factors. If you asked yourself, “What is Four Good Days?”, you are not alone. The film garnered little attention from critics and fans, earning less than $900,000 during its theatrical release. Moreover, although McEntire is a huge star in the world of country music, that probably won’t cut much ice for voters in the Academy music branch who represent a different industry demographic.
There seems little doubt that Warren has a dedicated following within the music branch. However, although it is big enough to consistently yield nominations, it isn’t large enough to deliver the big prize. Warren likely will have to content herself with “It’s nice to be nominated.” If she starts to feel too downhearted, Warren can console herself by looking at her royalty statements for “Rhythm of the Night.” Or “I Don’t Want to Miss a Thing.” Or “How Do I Live.” (You get the idea…)
The Legends (and I don’t mean John, Chrissy, Luna, and Miles)
The next two nominees are among pop music’s biggest icons, representing more than ninety years of combined experience in the biz. A bit surprisingly, though, both artists also are first-time Oscar nominees.
First up is the man who epitomizes Northern Soul: Irish singer and songwriter Van Morrison. Morrison is nominated for “Down to Joy” from Kenneth Branagh’s Belfast. Like Branagh, Morrison was born and raised in Belfast. He also has been closely associated with the city throughout his career, receiving the monikers of “the Belfast Cowboy” and “the Belfast Lion.” The early peak of Morrison’s career also coincides with the onset in 1969 of “the Troubles” depicted in Belfast. Besides “Down to Joy,” Branagh selected eight other Morrison tracks for the film’s soundtrack, many of them lesser-known tracks like “Caledonia Swing” and “Carrickfergus.” By digging deep into Morrison’s catalog, Branagh is not only able to provide a musical biography of his childhood, but also indicates how deeply Van the Man’s music was woven into the fabric of everyday life in Belfast.
Morrison’s “Down to Joy” also shows the durability of AABA form, albeit in this case channeling the sound of his early mid-tempo rockers like “Caravan” and “Domino.” The latter recordings are among the songs that would cement Morrison’s status as a Celtic interpreter of the revue style of sixties soul music, especially the Stax sound epitomized by singers such as Solomon Burke, Wilson Pickett, Sam and Dave, and Otis Redding. Morrison based his entire career on melding those influences with more native elements of Irish folk music. For nearly sixty years, Morrison has demonstrated that the idiom of sixties soul seems almost timeless, an impression confirmed by even more modern practitioners, like Sharon Jones & the Dap Kings or Nathaniel Rateliff & the Night Sweats.
Appearing over the end credits, “Down to Joy” neatly encapsulates the overall tone of Belfast and its mix of nostalgia, melancholy, and hope. At the end of Belfast, young Buddy and his family have been displaced by “the Troubles,” forced to relocate by threats of IRA retaliation. Their journey to England is colored by the pain of family separation. Yet it also represents a horizon of new possibilities. “Down to Joy” reflects that latter sentiment with lyrics describing a new morning after a dark night, and the glory and gratitude expressed through Buddy’s child-like naivete.
So, what are the chances that Van the Man wraps his hands around a small golden dude? Not very good, if you ask me.
Don’t get me wrong! Morrison albums of the late sixties and seventies – Astral Weeks, Moondance, Tupelo Honey, Saint Dominic’s Preview – are stone cold classics. It’s Too Late to Stop Now is among the finest live albums ever recorded. Morrison’s “Brown Eyed Girl” is my wife’s very favorite song ever!
I’m a Van fan, but his public statements about the United Kingdom’s Coronavirus restrictions have probably killed his chances of winning an Oscar. If younger members of the Academy know Morrison at all, it is likely as a conspiracy crank who is now recording with equally obnoxious anti-vaxxer Eric Clapton. I just can’t see Academy voters giving Morrison a platform to air his views on social distancing and lockdowns. If they did, it would produce the kinds of news clips and headlines that the Academy would like to avoid. Just imagine the public response to an acceptance speech in which the boos from the crowd rain down on the winner. I imagine that a lot of folks in the music branch just can’t bring themselves to vote for Morrison in the current political landscape. And, even as a lifelong fan, I can’t really blame them.
The third nominee for Best Original Song is “Be Alive” by DIXSON and Beyoncé Knowles Carter. The song appears in the end credits of King Richard, the biopic about Richard Williams, the father of tennis phenoms Serena and Venus. The tone of the music and lyrics succeed in doing something the film itself struggles to do, namely give voice to the two women who end up rewriting the record books of professional tennis.
In contrast, King Richard casts Williams the elder as a Svengali figure shepherding his young prodigies into the world of big-time sports. He acts as the girls’ agent, manager, coach, and protector, shielding Serena and Venus from the sorts of predations that characterize an industry with a bad reputation for chewing up and spitting out young talent. The lyrics of “Be Alive” speak to the family’s sense of fierce independence and Williams’ own “bootstrap” mentality. This is evident in couplets like:
Couldn’t wipe this black off if I tried
That’s why I lift my head with pride
Later, Beyoncé sings the praises of sisterhood, a theme that can be heard in some of her biggest hits, such as “Single Ladies (Put a Ring on It)” or “Independent Women Part I,” the latter recorded as a member of Destiny’s Child.
With its steady marching tempo borrowed from the Doors’ “Five to One” and Beyoncé’s soaring vocals, “Be Alive” bespeaks a mood of strength and defiance. Yet, it isn’t as well placed as some of the other songs in the category and, unlike many of Beyoncé’s popular records, it also isn’t the kind of earworm that lights up record charts. “Be Alive” peaked at #40 in Billboard’s Hot 100, likely a disappointment considering how well King Richard has performed in other audience metrics.
Come Sunday, I suspect that Beyoncé will likely go home empty handed. Like Diane Warren, she’ll need to console herself with the mantra “It’s nice to be nominated” and the many other Grammys, ASCAP, Billboard, BET, MTV, and American Music Awards that line her trophy case.
The Young Bloods
The final two nominees had big years in the world of entertainment in 2021. An Oscar would put a capper on a period of creative ferment that’s the envy of most singers and songwriters. Yet, for these two performers, it just seems like another day at the office.
Lin-Manuel Miranda received his second Oscar nomination for “Dos Oruguitas,” one of several songs he wrote for the Disney animated musical Encanto. The song is performed by Columbian singer Sebastián Yatra and appears in a flashback that dramatizes Abuela Alma’s tragic backstory. As a young woman, Alma, her husband Pedro, and their triplets attempt to escape their village after war breaks out. During their journey, they are beset by armed horsemen. The refugees scatter, but Pedro is killed when he halts the charging caballeros, presumably to ask for mercy for himself and his family. A candle Alma is holding protects the rest of the group, and its magical properties transform their future home into the “Casita,” a fantastic space where its denizens are revealed to have supernatural abilities and the house has a mind of its own.
The sequence itself is reminiscent of similar moments from films made by Disney’s friendly rival, Pixar. The montage that encapsulates an entire life in a couple of minutes of screen time recalls the opening of Up (2008) which depicts the long, happy marriage of Carl and Ellie until her illness and untimely death. The song that accompanies a flashback explaining the source of a character’s trauma and grief is also seen in Toy Story 2. Cowgirl Jessie relates how she once was her owner Emily’s favorite doll, but ends up forgotten and left behind when Emily grows up. This is all set to the strains of Sarah McLachlan’s “When She Loved Me.” The montage from Encanto nicely fuses together both these narrative devices but gives them a Latin pop spin.
Like “Somehow You Do,” “Dos Oruguitas” begins quietly with a brief introduction played on an acoustic guitar. The slight syncopation of the guitar figure, though, gives it a bit of Hispanic flair. As Yatra’s voice enters, the song’s chord structure follows a chromatically descending bass line, a device that heightens the harmonic tension until it circles back to the tonic. The tune pauses briefly as Abuela confesses her guilt for forgetting what the purpose of the magic was for. Mirabel reassures her that the Madrigal family’s entire livelihood is due to the earlier sacrifices the Abuela made and the suffering she endured. When they embrace, “Dos Oruguitas” kicks back in with a slightly faster tempo and with fuller orchestration that includes strings, percussion, a chorus, and a harp. With the rift between Alma and Mirabel healed, the Madrigals band together to rebuild the “Casita.” The harmony created by the restored family bonds allows it to regain its sentient properties.
As an Oscar nominee, “Dos Oruguitas” has a lot going for it. It accompanies a very emotional scene of intergenerational reconciliation. It is a featured track on the Encanto soundtrack, which has spent the past nine weeks atop Billboard’s Top 200 album chart. And Lin-Manuel Miranda is on a roll having served as the director of Tick, Tick…Boom!, the musical biopic of Rent composer Jonathan Larson, and as the producer of In the Heights, the screen adaptation of Miranda’s own hit Broadway play.
Perhaps the only thing working against it is the fact that it’s been overshadowed by another song from Encanto. “We Don’t Talk About Bruno” is a certified pop culture sensation, spending five weeks as the #1 song on Billboard’s Hot 100, accumulating more than 300 million views on Vevo, and featured in 21 different languages on Instagram. Did Disney submit the wrong song for nomination? Maybe, but “Dos Oruguitas” still might been benefit from the reflected glory of its more popular sibling. This and the fact that Encanto is up for some other major awards have kept Miranda among the frontrunners.
The last nominee is the title song from the most recent entry in the venerable James Bond series, No Time to Die. The tune is performed by Billie Eilish and written by Eilish and her frequent songwriting partner, brother Finneas. Like Miranda, 2021 has been a good year for Eilish. Her new album Happier Than Ever topped the charts in 26 countries across the globe, including the US. It also earned two Grammy awards and landed on several year-end “best of” lists. In addition to her music, Eilish also appeared in two films: a concert film featuring songs from Happier Than Ever and a “behind the scenes” documentary distributed by Neon and Apple TV+ called Billie Eilish: The World’s a Little Blurry.
In some respects, Eilish seems like an exemplary contributor to the amazing catalog of songs written for the Bond canon. She is an immensely popular artist. She is also someone who could update the template for the series by adding emo, dream-pop, and electro-pop touches to the usual Bond formula.
In other respects, though, Eilish represents something of a departure from previous Bond songstresses. When one thinks of iconic Bond songs, one thinks of tunes like “Goldfinger,” “Diamonds Are Forever,” “Licence to Kill,” “Goldeneye,” “The World is Not Enough,” “Skyfall,” and “Another Way to Die.” What do these songs all have in common? They are all sung by women with big voices, belters like Gladys Knight, Tina Turner, Adele, Alicia Keys, and the two Shirleys: Bassey and Manson. In contrast, Eilish is known for a much softer style of singing: hushed, sensitive, and intimate. That seems fitting for a performer whose best-known album was inspired by lucid dreaming and night terrors. Yet it seems less well-suited for an almost mythic film character defined by his swagger, toughness, and even a streak of cruelty.
Yet, if there was moment to rethink the traits of the typical Bond song, this was certainly it. In retrospect, the selection of Eilish was a masterstroke by the Bond brain trust led by Barbara Broccoli, the current head of Eon Productions. As the last film to feature Daniel Craig as James Bond, No Time to Die not only caps off his five-film arc, but also serves as a reflexive meditation on the series as a whole. At one level, the explicit meaning of No Time to Die is both simple and banal: everyone dies. Yet, by making references to several earlier films in the series, the accumulated weight of intertextual resonances invests the many deaths that occur in No Time to Die with an unusual sense of depth and gravity.
No Time to Die begins with a scene where Bond visits the tomb of Vesper Lynd, the fellow agent featured in Casino Royale who helps Bond defeat the evil Le Chiffre. Lynd and Bond fall in love, but she proves to be a double agent working for a rival operative. At film’s end, Lynd sacrifices herself when she drowns in a locked elevator car that has submerged.
M then reveals that she was an unwilling accomplice, a victim of blackmail after her previous boyfriend was abducted and threatened.
Bond’s pilgrimage to Lynd’s grave presages several additional deaths in the film. Bond’s best friend, CIA Agent Felix Leiter, and his mortal enemy, Ernst Stavro Blofeld, are killed in separate incidents. Even Bond himself perishes in the climax of No Time to Die. He sacrifices himself to foil a scheme by Lyutsifer Safin to unleash a bioweapon upon the world that is transmitted by touch and kills its victims based upon their DNA. After a missile strike is launched against Safin’s compound, Bond stays behind to assure that the silo’s blast-proof doors stay open. Bond’s gesture that not only saves the world but allows his current paramour, Madeleine Swann, and the young daughter he never knew he had, to safely escape the island.
Given how much of No Time to Die is pervaded by a sense of grief and sorrow, the decision to include a title song reflective of the film’s solemnity and melancholy makes perfect sense. Like some of the other nominees, Eilish’s tune begins slowly and quietly with a piano plunking out a repeated four note motif accompanied by strings and low brass. Eilish intones the first lyric, “I should have known” in a sung whisper. The serpentine melody unwinds through the verse and chorus, eventually taking Eilish into the upper range of her soprano on the lines:
Fool me once, fool me twice
Are you death or paradise?
You’ll never see me cry
There’s just no time to die
Just as the chorus ends, a thunderous bass chord enters, and the opening four note motif returns. The song continues to build, and more instruments are added as the song reaches its second chorus. Our four-note motif returns once more, but this time played in full orchestral splendor by the strings and the full brass section. The musical bombast ultimately fulfills the remit of other classic Bond songs. Eilish even follows suit by loudly belting out the chorus, revealing a power and huskiness to her voice that most of her fans probably hadn’t heard before.
“No Time to Die” finishes with a coda that returns to the sparse arrangement of the tune heard at the start. Eilish also goes back to the shivery murmur that is her stock in trade for one last iteration of the chorus’ last two lines.
No Time to Die larger themes of love, death, grief, and martyrdom presented a special challenge. Billie and Finneas rise to it beautifully. Moreover, the Eilishes also cleverly incorporate musical elements that evoke the harmonies and tonalities of John Barry’s best-known scores in the series. The four-note motif that serves as a spine for the song sounds like it could have easily been drawn from From Russia with Love, Goldfinger, or Thunderball. They also conclude the song with an electric guitar strumming an EmMaj9 chord, the so-called spy chord that Vic Flick plays at the end of the famous James Bond theme that started it all.
Does this mean that “No Time to Die” is the odds-on favorite to win? Perhaps, but it also seems to be overshadowed by another song, much as “Dos Oruguitas” was. In this case, the song was written for a completely different Bond film and mostly functions as an Easter Egg for die-hard fans of the series. It is “We Have All the Time in the World,” which was written by John Barry and Hal David and performed by Louis Armstrong over the end credits of On Her Majesty’s Secret Service (1968). Notably, the song appears just after Bond’s new bride, Tracy, has been killed in a drive-by shooting by Blofeld and his assistant, Irma Bunt. It is yet another evocation of death in No Time to Die with Tracy, like Vesper Lynd, implicitly included in the film’s mounting body count. Notably Hans Zimmer’s score for No Time to Die incorporates the melody to “We Have All the Time in the World” in three of the cues he wrote for the film. Indeed, long-time fans like me might well recognize the older Bond song in Zimmer’s score much more readily than the new one specifically written for it.
Prediction for Best Original Song
An Oscar would confer EGOT status on Lin-Manuel Miranda, a distinction held by just a handful of other entertainment luminaries. In fact, because Miranda also won a Pulitzer Prize for Hamilton and a MacArthur Genius Award, an Oscar would place him in entirely unique category. Say hello to the MacPEGOT.
Yet, although an award for “Dos Oruguitas” would make history, recent Oscar ceremonies have favored Bond songs. Adele won for “Skyfall” in 2013. Sam Smith repeated the feat with “Writing’s on the Wall” in 2016. “No Time to Die” also has already won a Grammy, a Golden Globe, and more than a dozen awards from prominent critics’ societies. Eilish is also a newly minted pop star, whose personal story is the kind of underdog narrative that Oscar voters seem to like.
If you are looking for a dark horse in the field, you might consider “Be Alive.” (Although when would you ever consider Beyoncé a dark horse for anything?) But I am sticking with the favorite. On Sunday, I expect Eilish to win. It is the clubhouse leader in terms of the betting markets and also my personal favorite among the field.
An ode to the new cleffer
One of the first things you might notice about this year’s slate of nominees for Best Original Score is the relative absence of the “usual suspects” in the music branch, such as Thomas Newman, Alexandre Desplat, or John Williams. Between them, these three composers have received a total of 78 nominations. Admittedly, only one of the five nominees this year – Germaine Franco – is a first timer. However, aside from Hans Zimmer’s twelve previous nominations, none of the other composers has received more than four.
Franco’s nomination is significant for other reasons. In February, she became the sixth woman nominated for Best Original Score and the first Latina. The field has a decided international flair with nominees from Britain, Germany, and Spain joining two Americans.
Of the five nominees, Alberto Iglesias’ music for Parallel Mothers (above and at bottom) comes closest to the style of a classical score. Yet it also presents a slight departure from those norms in its use of a chamber orchestra with most cues arranged for strings, piano, and the occasional wind instrument. Some feature the strident bowing style associated with Bernard Herrmann’s famous score for Psycho (1960). Others create lush combinations of strings and solo piano, an approach reminiscent of Frank Skinner’s music for older Universal melodramas like All That Heaven Allows (1956).
If that sounds a bit odd, it shouldn’t. Alfred Hitchcock and Douglas Sirk have been prominent influences on Pedro Almodovar’s cinema over the years. Parallel Mothers is the thirteenth film that Iglesias has scored for the great Spanish auteur. The composer admits that Almodovar’s films are always rooted in melodrama. But Parallel Mothers also had the generic trappings of a thriller, and his music strived to infuse scenes of psychological intimacy such that they crackled “with energy and light.” Iglesias also sought to accentuate the protagonists’ intertwined lives at a macro-level, using parallel musical structures to underscore how Ana enters and exits Janis’ life at several points in the film.
Iglesias is a four-time nominee and his score for Parallel Mothers is among his best. But I fear this is not his year. Parallel Mothers is among the biggest longshots in the Oscar betting markets not only for Iglesias in the Best Score category but also for Penelope Cruz as Best Actress. Moreover, the fact that Spain snubbed Parallel Mothers when submitting its nominee for Best International Feature Film also doesn’t bode well. Iglesias is once again a very deserving nominee whose work is likely to be overlooked in a highly competitive field.
Stretching the classical style: Incorporating novel idioms
Nicholas Britell earned his third Oscar nomination for Don’t Look Up, Adam McKay’s acrid satire of contemporary politics and media. The film’s dark humor and its apocalyptic conclusion undoubtedly posed a conceptual challenge for Britell. How do you preserve the comedic qualities of the story while still respecting the existential crisis that hints at larger issues around climate change, COVID, and the increasing distrust of science and medicine? As Britell acknowledges, he was “unprepared for the wild ride” that viewers experience over the course of the film. Britell’s solution? A hyperbolic paean to science, a smattering of wacky electronic sounds, some rollicking big band jazz, and garage-band style Farfisa organ.
In an interview with The Hollywood Reporter, Britell notes that two cues were especially important in articulating the overall concept for the score. Even before production had wrapped, Britell created a demo cue entitled “Overture to Logic and Knowledge” that McKay played on set to enable the cast to get in the right frame of mind.
The piece unfolds as a canon performed on a piano that’s been recorded with heavy reverb. After the statement of the initial theme, Britell interweaves additional voices in contrapuntal harmony, approximating the sort of mathematical precision one associates with Bach fugues. Afterward, Britell then tried to suss out what the opposite of that compositional style might be, eventually landing on big band jazz. The idiom is evident in the film’s main title, which features walking bass, a simple brass and bass saxophone riff, and a soaring trumpet obligato. Another cue – “It’s a Strange Glorious World” – reprises that big band style, yet further estranges the viewer from the serious global crisis dramatized in Don’t Look Up with the use of banjo and toy piano for instrumental color.
Britell saves his most savage musical satire for a theme written for Peter Isherwell, the billionaire tech genius played by Mark Rylance.
The composer arranges the theme for celestas, toy pianos, Farfisa organ, and bass synthesizers. These instrumental colors suggest Isherwell’s childlike faith that new technology can solve all of humankind’s biggest problems. Of course, Isherwell exudes this relentless optimism to mask his real intentions. Isherwell proposes a foolhardy mission to try and capture the streaking comet rather than deflecting or destroying it. He does so to feed his corporate greed as the comet possesses rare minerals that Isherwell hopes to harvest for use in his production of microchips.
Britell’s score displays incredible musical sophistication even as it is asked to underscore scenes that occasionally seem silly or in which the satire seems all too crude. That being said, I have some doubts that it will win for Best Original Score. This is not to gainsay Britell’s extraordinary ingenuity in devising his music. Rather, it is just the brute reality that other films have better odds in what seems to be a close race.
Germaine Franco’s music for Encanto also pushes the bounds of the classical score. In this case, though, it does so by incorporating various styles of Latin pop music rather than using big band jazz. To be sure, there was a strain of this type of composition in earlier eras, Think, for example, of the music written by Henry Mancini, Nelson Riddle, and Quincy Jones for films of the 1960s. That music, though, reflected the predominant Latin pop styles of the period, which included congas, rhumbas, cha-chas, sambas, and bossa novas.
In contrast, Franco drew upon a different repertoire of Latin rhythms to fashion her score for Encanto, including some folk music styles specific to the film’s Colombian setting. These not only include more familiar idioms like salsa, but also more modern developments like reggaeton. The latter is a style that originated in Panama in the 1990s and mixes hip-hop beats with Jamaican riddims. It rapidly spread through Spanish-speaking countries in the Caribbean.
In Encanto, reggaeton can be heard in Luisa Madrigal’s big number, “Surface Pressure.” The song, of course, was written by Lin-Manuel Miranda. Franco then incorporated the style into certain cues to ensure a strong sense of unity between the mood and vibe of the songs and those of the score.
Other cues, however, are written in folk styles native to Colombia with Franco once again taking her cues from the rhythms of Miranda’s songs. Encanto’s opener, “The Family Madrigal,” is an up-tempo vallenato song played in standard 2/4 meter. It features marimba, three-button accordion, and guachara, a Colombian percussion instrument played by rubbing a fork over a wooden, ribbed stick. Mirabel’s “I want” song, “Waiting on a Miracle,” uses bambuco rhythms. It unfolds in a fast triple meter characteristic of the idiom. As the only song featuring this rhythm, Miranda used it to further underline how Mirabel feels separated from her family due to her lack of a special gift for magic.
Perhaps Franco’s most important gesture, though, was using cumbia rhythms to underscore Mirabel’s movement. Cumbia is popular style throughout South America but has its origins among enslaved African populations on the coasts of Colombia and different Caribbean nations. It uses a clave rhythm common in Afro-Cuban music. As the style spread throughout Colombia in the early 1900s, musicians incorporated indigenous drums and wind instruments, including tambora, llamador, and gaitas. As Franco has noted in interviews, she uses the cumbia to accompany Mirabel’s first entrance into the “Casita.” From that point on, according to Franco, “The rhythm of the cumbia becomes the forward motion of her trying to find a solution to the problem.”
I suspect Franco’s fellow composers in the music branch are as impressed as I am by her attention to details of rhythm and orchestration. To get the precise tone color needed for some of these Latin pop and folk styles, Franco had a special marimba native to the Choco rainforest region of Colombia disassembled and shipped to her in parts. After it was put back together, Franco played the marimba herself, two mallets in each hand.
Encanto isn’t the favorite to take home the prize for Original Score. But if you’re looking for a potential surprise on Sunday night, Franco seems to be in the best position to pull an upset.
Rock of the Westies
Many pop music fans know Jonny Greenwood from his work as a songwriter and lead guitarist in the British rock band, Radiohead. Greenwood, though, has also established a considerable reputation as a film composer. He is perhaps best known for his work with director Paul Thomas Anderson, who has collaborated with Greenwood on his past five projects. Beginning with There Will Be Blood (2007), Greenwood went on to score The Master (2012), Inherent Vice (2014), Phantom Thread (2018), and Licorice Pizza (2021).
In February, Greenwood earned his second Oscar nomination for Jane Campion’s The Power of the Dog. Much like the rest of the film, Greenwood’s score works against many of the conventions of the classic Hollywood Western. Many studio-era oaters developed their scores around orchestrated versions of tunes in the cowboy songbook or around Coplandesque rhythms and harmonies. Both these approaches strived to evoke the majesty of the films’ visuals, which often featured mountain vistas, endless prairies, and sunlit horizons.
Instead of looking to the “sweeping strings” style used in older Westerns, Greenwood was inspired by the atonal brass music that was used in old Star Trek episodes to underscore the exploration of unknown planets. When Peter ventures into the mountains and discovers a dead cow, Greenwood accompanies these scenes with a dissonant French horn duet to highlight the strange and forbidding quality this has on the impressionable teenager.
Similarly, instead of a big string sound, Greenwood opted for smaller ensembles, occasionally writing things for six cellos or four violas. Greenwood also plucked strings of a cello as a correlate for Phil’s onscreen banjo playing. Here again, the goal was to create a tone color that seemed just slightly off, emphasizing microtonal inflections to create a sound that was somber yet sinister.
Phil’s banjo playing also furnishes one of the most memorable scenes in The Power of the Dog. Peter’s mother, Rose, initially seems ill at ease after coming to live with George and Phil on the brothers’ ranch. At one point, she seats herself at the piano and proceeds to struggle through a piano reduction of Johann Strauss Sr.’s “Radetzky March.” Campion then cuts to Phil sitting in his bedroom offscreen. Phil then picks up the melody of the Strauss piece on his banjo, playing it almost effortlessly and improvising his own coda. In a test of wills, Phil’s virtuosity humiliates Rose, who increasingly turns to alcohol to soothe her emotional wounds.
Because of this scene, Greenwood used a detuned mechanical piano as a musical timbre associated with Rose.
To produce this effect, Greenwood used computer software to create the sound of a piano roll for his pianola. Then, as the music was played back, Greenwood used a tuning wrench to slightly alter the pitches to create a sound akin to the honkytonk pianos scene in the saloons of older Westerns. For Greenwood, the sound proved perfect for Rose’s character arc. As he states in an interview for Variety, “Not only is her story wrapped up in the instrument, but it was also a good texture for her gradual mental unraveling. I recorded hours of this stuff – poor Jane (Campion) had to hear quite a lot of it.”
Greenwood’s modernist take on the typical Western score makes him one of the top contenders in this year’s Oscars. Of course, it doesn’t hurt that Greenwood wrote music for two other nominated films: Licorice Pizza and Pablo Larraín’s Princess Diana biopic, Spencer. The betting markets have Greenwood as a longshot. However, since The Power of the Dog leads the field with a dozen nominations in all, Greenwood could prevail in the event of a Dog sweep.
Today’s sounds for tomorrow’s people
The last nominee for Original Score is the current favorite. Hans Zimmer earned his thirteenth Oscar nomination for Dune, Denis Villeneuve’s big budget adaptation of Frank Herbert’s classic science-fiction novel. As Zimmer notes in a New York Times profile, he self-consciously rejected the musical style associated with the Star Wars series and its many imitators. Those scores looked to the past for inspiration, finding it in Gustav Holst, Igor Stravinsky, Erich Wolfgang Korngold, and even Benny Goodman. Instead, Zimmer set himself an almost impossible task, trying to create sounds that no one had ever heard before.
The result is a score that Darryn King calls “one of Zimmer’s most unorthodox and most provocative.” The composer reports that he spent days contriving new sounds, sometimes commissioning the construction of new instruments or using conventional instruments in extremely unusual ways to get the effect he desired. Although synthesizers keep the score rooted in Zimmer’s pop music past, he combines these with several unusual sonorities that include Irish whistles, Indian bamboo flutes, and metallic scraping noises.
Many of these instrumental choices are keyed to aspects of Dune’s intergalactic setting. The rumble of distorted electric guitars evokes the seismic shifts occurring beneath the desert sands on the planet’s surface. Zimmer even used some of the environmental details to communicate what he wanted from the musicians performing on the soundtrack. Slide guitarist David Fleming reports that Zimmer told him for one cue, “This needs to sound like sand.”
Zimmer performed similar wonders in his use of other instruments. For the scene where the House of Atreides arrives on Arrakis, Zimmer recorded thirty bagpipes playing in a Scottish church. The added reverberance raised the volume of the ensemble to ear-splitting levels of 130 decibels. The highland players needed to wear earplugs to avoiding damaging their hearing. But Zimmer got the sound he wanted, the musical equivalent of a blaring air raid siren.
Zimmer’s desire to find new sounds not only altered the usual timbres of instruments but also of the voice as well. For Dune, Zimmer engaged the services of music therapist and singer Loire Cotler. To create the qualities Zimmer was seeking, Cotler drew on several non-Western singing styles. Her syncretic method combined Jewish niggun, South Indian vocal percussion, Celtic lamentation, and Tuvan throat-singing. The end result was a hybridized style that sounded wholly unique: a war cry expressed as though it were an ancient antecedent of Esperanto. Cotler tried to find a name for the new vocal technique, ultimately settling for the person responsible; she called it the “Hans Zimmer.”
Perhaps Zimmer’s most audacious gesture involved hiring winds player Pedro Eustache to build new instruments from scratch. Eustache created a 21-foot horn, a sort of modern version of the old animal horns fashioned into shofars and zinks during the Middle Ages. He also produced a contrabass version of the duduk, which King described as a “supersize version of the ancient Armenian woodwind instrument.”
What does it all add up to? A score that hits all the right notes in transposing Herbert’s imposing epic to the big screen. Zimmer’s music is at times quietly menacing, somber and pensive at other moments, and brooding but anthemic for Dune’s big action scenes. Zimmer’s score for Dune does not depict the kind of triumphalism found in Star Wars or other space operas. Rather, it opts to capture the elements of dark mysticism and doleful psychedelia that made Herbert’s novel a literary head trip in the 1960s. To be sure, Zimmer’s music doesn’t concoct earworms to evoke the sandworms. Yet it succeeds admirably where others have failed nobly. (If you think this is easy, just watch and listen to David Lynch’s misbegotten adaptation from 1984.)
Prediction
One could easily make the case for Germaine Franco to win for Encanto. The score and the album have dominated the popular music scene ever since the film was released in late November. Yet Dune stands a good chance at claiming several other craft awards, such as those for Sound and Production Design, which bodes well for Zimmer’s chances on Sunday.
In the world of film music today, the Burgomeister of Bleeding Fingers Music casts a shadow over the field as large as any of the luminaries who preceded him like Ennio Morricone, Jerry Goldsmith, or Dimitri Tiomkin. When I contemplate the sheer number of innovations Zimmer made in the music he composed for Dune, I can’t bring myself to bet against him. I think Hans takes home the Oscar on Sunday. He’ll walk away with another hunk of metal to scrape for the Dune sequel.
Once again, I want to give a shout-out to Jon Burlingame for his excellent coverage of Hollywood and international film music for Variety. As a subscriber, I always enjoy reading his work for the venerable trade journal, not just during awards season but year-round.
The Diane Warren interview with USA Today that I referenced can be found here. Additional interviews with Deadline and Gold Derby are found here and here.
Interviews with Lin-Manuel Miranda discussing the songs he wrote for Encanto can be found here , here, and here.
Vulture published a nice piece on the process of writing the title song for No Time to Die, which can be found here.
Alberto Iglesias discusses with work with director Pedro Almodovar here .
Nicholas Britell talks about his work Don’t Look Up with Indiewire and Variety here and here . One can find several interviews with Germaine Franco about her process on creating the score for Encanto. A sample can be found here, here, here, and here. A movie score suite featuring Franco’s themes for Encanto can be found here.
Jonny Greenwood talks with Variety about his collaboration with Jane Campion here and here.
The indie-music website provides an interesting review of Greenwood’s soundtrack for The Power of the Dog here.
Finally, Darryn King’s superb overview of Hans Zimmer’s score for Dune can be found here.
Parallel Mothers
PARASITE fever
Kristin here:
It seems like anyone writing for an online or print periodical, whether media-oriented or not, is searching for some sort of hook on which to hang an article about Parasite and Bong Joon Ho. Some of these are a bit of a stretch, others are a bit ephemeral but interesting. All testify to the surprisingly broad interest in a relatively little-known director of the first foreign-language film ever to win the Best Picture Oscar.
Some of this burst of coverage undoubtedly stems from the fact that relatively few people know anything about Bong. Predictably there are many quick overviews of his career to catch people up, as well as plenty of interviews and of where-you-can-stream-Bong’s-films guides.
Here I offer a some links to a fair sampling of some of the less predictable pieces that I have run across. Some are quite bemusing. A few were published before the February 9 Academy Awards ceremony, but the flood has, not surprisingly, come after it.
Such pieces tend to fall into categories.
Items of Mise-en-scene
People are fascinated by the Parks’ gorgeous (at least on the surface) house and yard. Back on October 31, 2019, Architectural Digest, of all places, published an interview with Bong about the set. This is surely one of the most prestigious of non-media outlets to publish on the film. After the Oscars, The Guardian, which has diligently published on various aspects of the film (see bottom), caught up and ran a piece about the set being the “real star” of the film and considering it from a genre point of view.
The mysterious “viewing stone” has been discussed. The Guardian again (see bottom line of bottom image), on February 17, ran a story entitled “Built on rock: the geology at the heart of Oscars sensation ‘Parasite.'”
The Translator
Everybody seems to be enchanted by Sharon Choi, who has accompanied Bong internationally during the long awards season from Cannes to the Oscars. On February 10, Buzzfeed reported, “There’s a Ton of Love and Memes for the interpreter of ‘Parasite’ director Bong Joon Ho.” Sure enough, all over social media there are people gushing about her (above, from the Buzzfeed story).
On February 18, a Variety headline trumpeted, “Bong Joon Ho Interpreter Sharon Choi Relives Historic ‘Parasite’ Awards Season in Her Own Words (EXCLUSIVE).” Choi had, the story reveals, turned down “hundreds of interview requests” before allowing Variety to print her story. In fact, there are interviews with Choi available on the internet, but the Variety story is not an interview. It’s a memoir by Choi in which she recalls the awards season.
Meta
There are articles about the popularity of Parasite and Bong.
On January 20, into awards season but before the Oscars, Morgan Sung posted a piece on Mashable: “Parasite director Bong Joon Ho became a proud dad meme.” On social media, people were posting photos of Bong taking “proud dad” photos of his cast and crew getting awards (above). Note the number of likes and people “talking about this,” plus the presence of Sharon Choi in the group. The Mashable piece presents several more such snips.
Two days after the Oscar nominations were announced, on January 15 Junkee’s Joseph Earp posted about “Bong Joon-Ho, Viral Superstar,” proposing that Bong has become one of those rare directors who becomes a brand in himself. He picks up on Quentin Tarantino’s remark that Bong could become the new Spielberg.
On February 19, the livemint site reported gleefully that the day after the Oscars saw a 857% surge in searches on “Parasite.” This as opposed to 117% for 1917 and 132% for Jojo Rabbit. As the author remarks, “Bong Joon-ho’s tragicomedy thriller has been sweeping all awards and cleaning up at the box office, and people have not been able to stop talking (or searching) on Google.”
And why? “Search for director Bong Joon-ho increased for not only being the mastermind behind the film but also for his quirky sense of humour.”
I suppose the blog entry that you are now reading falls into this category as well. (And then there are our earlier comments.)
Lessons to be learned
On February 10, one of the odder stories I’ve seen went up on CNBC’s “Make It” page entitled: “‘Parasite’ director says his success is due to ‘a very simple lifestyle,’ not meeting a lot of people.” Why a business-oriented website would consider a South Korean film director’s lifestyle relevant to people aspiring to make a lot of money is anyone’s guess. Clearly CNBC was not able to get an interview with Bong so soon after the awards ceremony. Instead, the insights are derived from an article in the British Telegraph (behind a paywall). That piece is also dated February 10, and since it’s a review (albeit a late one), one must presume that its author had interviewed Bong earlier or derived his information from yet another source.
The Guardian (yet again) ran a story on February 18 headlined “Trust your nose: what rich people can learn from Parasite.” This turns out to be a satirical piece, including such tips as not buying a huge coffee table that intruders can hide under without being noticed.
This ‘n’ that
Even a periodical devoted to cuisine found a way to work in a story. On February 10, the day after the awards, Eater Los Angeles ran a story, “Oscar-Winning ‘Parasite’ Cast Parties Until 5 in the Morning at LA Koreatown Restaurant.” We learn, among other things, that “Bong Joon-ho hadn’t eaten anything all day and was so famished that the restaurant cooked up galbi jjim (braised short ribs), eundaegu jorim (braised spicy black cod), galbi (grilled short ribs), bibimbap, and seafood tofu pancakes for him and the cast.”
On February 15, Indiewire‘s Anne Thompson took us “Behind the Scenes of Bong Joon Ho’s Oscar-Winning PR campaign.” Behind the scenes is publicist Mara Buxbaum, seen above with Bong. To Bong’s left is presumably Sharon Choi, who, Thompson tells us, is writing a book about her experiences as Bong’s interpreter.
I suppose the Parasite fever really does result in part from the fact that this is the first time that a foreign-language film has won a best picture Oscar. It’s probably also to a considerable extent the fact that Bong is a charming person, modest, humorous, straightforward, and very talented, and he comes across as such in his acceptance speeches and interviews. People want to know more about him, as is suggested by looper’s February 12 piece on unknown facts about Bong. If they want to know what his favorite films are and maybe watch them, they can read No Film School’s “25 Favorite Films of ‘Parasite’ director Bong Joon Ho” (February 7).
The only people who dislike Parasite and presumably its maker seem to be President T***p and his gormless fans. On February 20, he decried the awarding of the best-picture Oscar to a foreign film:
And the winner is… a movie from South Korea! What the hell was that all that about? We’ve got enough problems with South Korea, with trade. On top of that, they give them the best movie of the year. Was it good? I don’t know. Let’s get Gone With the Wind back, please? Sunset Boulevard. So many great movies.
I shan’t try to unpack the levels of ignorance and misunderstanding jammed into that passage, which was cheered by many who had never heard of Parasite and had no idea what he was going on about. It does make me pause at the notion of T***p watching Sunset Blvd., if indeed he has, and that he seems to think re-released films are eligible for Oscars decades after they were made. I’ve got to believe he at least knows that Gone with the Wind and Sunset Blvd. have already been “gotten back” and are easily available for viewing in numerous formats. The point though, is that even he has a vague notion that Parasite (or, since he doesn’t know the title, “a movie from South Korea”) is good copy.
Two Parasite items on The Guardian’s February 18 film alert.
Oscars by the numbers
Director Chris Butler: “Well, I’m flabbergasted!” with producer Arianne Sutner.
Kristin here:
The Oscars are looming large, with the presentation ceremony coming up February 9. But did they ever really go away? As I’ve pointed out before, Oscar prediction has become a year-round obsession for amateurs and profession for pundits. I expect on February 10 there will be journalists who start speculating about the 2020 Oscar-worthy films. The BAFTAs (to be given out a week before the Oscars, on February 7) and Golden Globes have also become more popular, though to some extent as bellwethers of possible Oscar winners. The PGA, DGA, SAG, and even obscure critics groups’ awards have come onto people’s radar as predictors.
How many people who follow the Oscar and other awards races do so because they expect the results to reveal to them what the truly best films of the year were? How many dutifully add the winners and nominees to their streaming lists if they haven’t already seen them? Probably quite a few, but there’s also a considerable amount of skepticism about the quality of the award-winners. In recent years there has arise the “will win/should win” genre of Oscar prediction columns in the entertainment press. It’s an acknowledgement that the truly best films, directors, performers, and so on don’t always win. In fact, sometimes it seems as if they seldom do, given the absurd win of Green Book over Roma and BlacKkKlansman. This year it looks as if we are facing another good-not-great film, 2017, winning over a strong lineup including Once upon a Time in … Hollywood, Parasite, and Little Women.
Still, even with a cynical view of the Oscars and other awards, it’s fun to follow the prognostications. It’s fun to have the chance to see or re-see the most-nominated films on the big screen when they’re brought back to theaters in the weeks before the Oscar ceremony. It’s fun to see excellence rewarded in the cases where the best film/person/team actually does win. It was great to witness Laika finally get rewarded (and flabbergasted, above) with a Golden Globe for Missing Link as best animated feature. True, Missing Link isn’t the best film Laika has made, but maybe this was a consolation prize for the studio having missed out on awards for the wonderful Kubo and the Two Strings and other earlier films.
It’s fun to attend Oscar parties and fill out one’s ballot in competition with one’s friends and colleagues. On one such occasion it was great to see Mark Rylance win best supporting actor for Bridge of Spies, partly because he deserved it and partly because I was the only one in our Oscar pool who voted for him. (After all, I knew that for years he had been winning Tonys and Oliviers right and left and is not a nominee you want to be up against.) Sylvester Stallone was the odds-on favorite to win, and I think everyone else in the room voted for him.
Oscarmetrics
 Pundits have all sorts of methods for coming up with predictions about the Oscars. There’s the “He is very popular in Hollywood” angle. There’s the “It’s her turn after all those nominations” claim. There are the tallies of other Oscar nominations a given title has and in which categories. And there is the perpetually optimistic “They deserve it” plea.
Pundits have all sorts of methods for coming up with predictions about the Oscars. There’s the “He is very popular in Hollywood” angle. There’s the “It’s her turn after all those nominations” claim. There are the tallies of other Oscar nominations a given title has and in which categories. And there is the perpetually optimistic “They deserve it” plea.
For those interested in seeing someone dive deep into the records and come up with solid mathematical ways of predicting winners in every category of Oscars, Ben Zauzmer has published Oscarmetrics. Having studied applied math at Harvard, he decided to combine that with one of his passions, movies. Building up a huge database of facts from the obvious online sources–Wikipedia, IMDb, Rotten Tomatoes, the Academy’s own website, and so on–he could then crunch numbers in all sorts of categories (e.g., for supporting actresses, he checks how far down their names were in the credits).
An early test of the viability of the method came in the 2011 Oscar race, while Zauzmer was still in school. That year Viola Davis (The Help) was up for best actress against Meryl Streep (The Iron Lady). Davis was taken to be the front-runner, but Zauzmer’s math gave Streep a slight edge. Her win reassured Zauzmer that there was something to his approach. His day job is currently doing sports analytics for the Los Angeles Dodgers.
Those like me who are rather intimidated by math need not fear that Oscarmetrics is a book of jargon-laden prose and incomprehensible charts. It’s aimed at a general public. There are numerous anecdotes of Oscar lore. Zauzmer starts with Juliet Binoche’s (The English Patient) 1996 surprise win over Lauren Bacall (The Mirror Has Two Faces) in the supporting actress category. Bacall was universally favored to win, but going back over the evidence using his method, Zauzmer discovered that even beforehand there were clear indications that Binoche might well win.
Zauzmer asks a different interesting question in each chapter and answers it with a variety of types of evidence. The questions are not all of the “why did this person unexpectedly win” variety. For the chapter on the best-animated-feature category, the question is “Do the Oscars have a Pixar bias?” It’s a logical thing to wonder, especially if we throw in the Pixar shorts that have won Oscars. Zauzmer’s method is not what one might predict. He posits that the combined critics’ and fans’ scores on Rotten Tomatoes genuinely tend to reflect the perceived quality of the films involved, and he charts the nominated animated features and winners in relation to their scores.
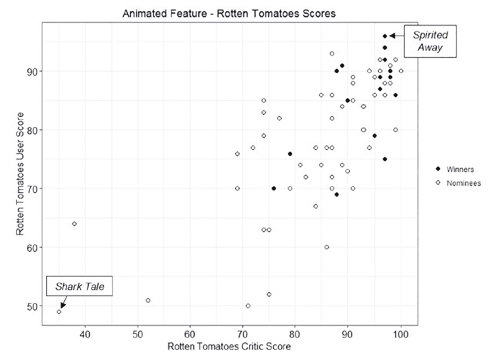 The results are pretty clear, in that Spirited Away is arguably the best animated feature made in the time since the Oscar category was instituted in 2001. In fact, I’ve seen it on some of the lists of the best films made since 2000, and it’s not an implausible choice either way. Shark Tale? I haven’t seen it, but I suspect it deserves its status as the least well-reviewed nominee in this category.
The results are pretty clear, in that Spirited Away is arguably the best animated feature made in the time since the Oscar category was instituted in 2001. In fact, I’ve seen it on some of the lists of the best films made since 2000, and it’s not an implausible choice either way. Shark Tale? I haven’t seen it, but I suspect it deserves its status as the least well-reviewed nominee in this category.
Using this evidence, Zauzmer zeroes in on Pixar, which has won the animated feature Oscar nine times out of its eleven nominations. In six cases, the Pixar film was the highest rated among that year’s nominees: Finding Nemo, The Incredibles, WALL-E, Up, Inside Out, and Coco.
In two cases, Pixar was rated highest but lost to a lower-rated film: Shrek over Monsters, Inc., and Happy Feet over Cars. I personally agree that neither Shrek nor Happy Feet should have won over Pixar. (Sorry, George Miller!)
Zauzmer finds three cases where Pixar did not have the highest rating but won over others that did: Ratatouille beat the slightly higher-rated Persepolis, Toy Story 3 should have lost to the similarly slightly higher-rated How to Train Your Dragon, and Wreck-It Ralph was way ahead on RT but lost to Brave. Wreck-It Ralph definitely should have won, and the sequel probably would have, had it not been unfortunate enough to be up against the highly original, widely adored Spider-Man: Into the Spiderverse.
The conclusion from this is that the Academy “wrongly” gave the Oscar to Pixar films three times and “wrongly” withheld it twice. As Zauzmer points out, this is “certainly not a large enough gap to suggest that the Academy has a bias towards Pixar.” This is pleasantly counterintuitive, given how often we’ve seen Oscars go to Pixar films.
Oscarmetrics offers interesting material presented in an engaging prose style, more journalistic than academic, but thoroughly researched nonetheless.
In his introduction, Zauzmer points out that the book only covers up to the March, 2018 ceremony. It obviously can’t make predictions about future Oscars, though it might suggest some tactics you could use for making your own if so inclined. Zauzmer has been successful enough in the film arena that he writes for The Hollywood Reporter and other more general outlets. You can track down his work, including pieces on this years Oscar nominees, here.