Archive for February 2009
Acting up
Germinal (1913).
DB here:
Film performance is notoriously difficult to analyze. We don’t lack zesty celebrations of actors; I think especially of Richard Schickel on Doug Fairbanks and Gary Giddins on Jack Benny and Bob Hope (praised in an earlier entry). But we have long found it difficult to penetrate actors’ secrets with the same precision that we bring to editing or framing or a film’s musical score.
Actors’ performances don’t offer themselves in neat slices, the way that shots come to us. There isn’t a firm notational system that lets us capture performances the way that scores can pick out important patterns in music.
Moreover, it’s hard to dissect something that seems so evanescent, so direct, and so natural. When we see someone smile on the bus or at a party, we react immediately and without any apparent thought. When someone smiles in a movie, we’re tempted to say that we respond just as directly. But then, what is acting? Just doing what comes naturally?
Acting is clearly an art and a craft. Not everyone can do it, and comparatively few do it well. So if there is a skill or a technique involved, surely acting goes beyond ordinary behavior. And if as in other arts there are creative choices involved, there is likely to be a menu of options to be chosen from. Some of those options are likely to be conventions sanctioned by tradition. How strongly, then, is acting conventionalized? If it’s conventionalized to some degree, we should be able to analyze it.
A small-scale debate has gone on for some years in film studies about whether film acting is heavily conventionalized, even coded. Advocates of the coding view point to the fact that acting styles vary in different places and change across time. What does Kabuki performance have in common with Method acting? It’s hard to claim that there is a universally realistic acting style that naturally represents human behavior. Against this, others have argued that even if there is no absolute and unchanging standard of realism, we can speak of more or less realistic aspects of performance. Some styles, like Method are just less artificial than others, like Kabuki—even if both are somewhat stylized with respect to realistic behavior.
My own view, explored in Poetics of Cinema, is that performance traditions streamline or stylize a common core of widely shared human behaviors. In everyday life, smiling expresses happiness and/or serves as a social signal of openness. We’re unlikely to find a distant culture in which smiling expresses rage. (Of course we can have an instance of smiling concealing rage, but that would acknowledge the difference between the two states.) Some acting traditions, like Kabuki, retain certain common behaviors like weeping or proud walking, but make them more dancelike. Other acting traditions stylize core behaviors in different ways–the mumble of the Method, or the comic double-take. The differences lie in what aspects of facial expressions, gestures, gait, and the like are on the tradition’s menu, and how they become “streamlined” for expressive purposes and spectatorial uptake.
In short, I’m a moderate constructivist about such matters. I agree that we have to learn to comprehend performances in different traditions. But our learning is fast and spontaneous, not at all like learning Morse code or English, because we already have strong hunches about what a frown or a wail might express. Frowning or wailing are likely to be contingent universals of human behavior. An intuition about the meaning of the performance guides us to recognize the more stylized aspects of the presentation. When Cesare coasts along walls in The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari, we take that to be a stylized representation of the act of stalking. That construal relies on the hunch that he’s doing something we already understand–stalking–in an unusual way. Although sometimes we might have to revise our intuitions about the meaning, those intuitions serve as a point of departure. (Where do our intuitions ultimately come from? Short answer: The evolution of humans as a social species.) E. H. Gombrich put it well: “It is the meaning which leads us to the convention and not the convention which leads us to the meaning.”
Assunta Spina (1915).
The faculty and alumni of the Film Studies program here at Wisconsin keep in touch through a (closed) listserv, and thanks to Jonathan Frome we also have a wiki, to be found here. It’s just starting to fill up, mostly with ideas for teaching and examples of sample sequences to illustrate film techniques. But now the wiki has gained striking essays on acting from two scholars of early cinema.
Ben Brewster and Lea Jacobs’ book, Theatre to Cinema, took on the problem of what early feature films owed to the stage, and they concluded: Quite a lot. But instead of condemning this tradition as “uncinematic,” as most historians have, they showed that a highly engaging form of cinema arose by reshaping theatrical traditions. Specifically, Ben and Lea examined how “situational” plotting principles were carried into film, and they discussed film’s debt to the “pictorialist” drama of the nineteenth century. Many scholars had argued that melodramatic theatre was replaced by the Naturalist theatre, derived from the literary movement associated with Émile Zola. But Lea and Ben argued that a pictorialist conception of theatre and its modified form in early feature films cut across this distinction. A film that was avowedly Naturalist in plot or theme could maintain conventions of earlier forms.
Consequently, they argued that film acting of the period, even when it seemed to be moving toward greater realism, was still building on the stereotyped expressions, gestures, and attitudes of pictorialist theatre. Actors were called upon to execute vivid stage tableaus. Standard gestures had to be imbued with fresh emotional intensity, and actors were expected to move gracefully from one expressive picture to another.
Now Ben and Lea have extended their book’s argument in two in-depth studies posted on the UW wiki. Ben’s essay examines that great Capellani film Germinal (1913) and shows that it often perpetuates the poses and expressions of pictorialism, while also scaling them down. Lea tackles the work of the diva Francesca Bertini, including an analysis of the wonderful Assunta Spina (1915). Her piece is a companion to Ben’s. She writes:
While I do not doubt that the plot of Assunta Spina fits under the rubric of naturalism, and that the acting and staging of some scenes in the film also show the influence of naturalism in the theatre, it seems to me that Bertini’s technique (and incidentally that of [Asta] Nielsen as well) is more reminiscent of Bernhardt than it is of the Duse, and that the blocking and use of gesture in the film is largely governed by what Brewster and I have discussed in terms of “pictorialism” in acting.
By considering 1910s performance as a modification of theatrical poses, attitudes, and staging conventions, Jacobs and Brewster are led to remarkably detailed analyses. They have studied the conventions of acting at that period, and because they are alert to standard bits of business, so they are able to show fine points of performance that we would ordinarily miss.
They’re also able to hold the realism/ artifice dispute in suspension by concentrating on particular historical traditions. They shrewdly note that as acting styles change, the newer one is likely to be praised as more realistic than the styles it supplants. In turn, that style will be considered artificial when a still newer one comes along. For this reason, Method acting may seem less realistic and more artfully contrived today than it did in the 1950s.
Apart from the subtle discussion of acting styles, one merit of these essays is that they recognize how films can take bits and pieces of different traditions and modify them for particular ends. I’m sympathetic to this perspective. For instance, I still think that many of today’s Hollywood films, despite their contemporary look and feel, draw on principles of narration and plot structure that we can find in classic American studio cinema.
In addition, you ought to visit the site to see how detailed their analyses are and how extensively they draw on frame stills. Indeed, one reason they published these pieces online was that no academic film journal could have accommodated so many illustrations. So much the better for us. The frames, taken from 35mm prints with a Nikon lens and negative film, are among the most beautiful you’ll find on the Internets. I swiped some here.
Sangue bleu (1914).
The quotation from E. H. Gombrich comes from his essay “Image and Code: Scope and Limits of Conventionalism in Pictorial Representation,” in The Image and the Eye: Further Studies in the Psychology of Pictorial Representation (Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 1982), 289.
Kristin has written a couple of blog entries concentrating on performance, here and here.
Coraline, cornered
DB here:
It’s common for academics in one field to borrow ideas from other domains of research. But people outside academe sometimes object when a film scholar talks about movies using a term or idea originating elsewhere. These people usually think of themselves as hard-headed pros. Everything we need to understand film, they think, can be derived from the concepts already used by practitioners.
No doubt, we should be attentive to the ways in which filmmakers think and talk about their work. There’s a lot to be learned from shop talk and insider information–hence the enduring value of interviews, DVD commentaries, and the like. Yet no activity explains itself. Often practitioners do things intuitively, without making their background ideas explicit. We can often illuminate a filmmaker’s creative choices by spelling out the unspoken premises behind the work.
Further, filmmakers themselves have traditionally drawn ideas from other arts and sciences. For example, storytelling techniques referred to as exposition, point of view, or motivation have their origin in theories of literature and drama. Filmmakers have been quite pluralistic in their creative practices; why can’t critics and historians be open to outside influences?
Back in the 1980s I began speculating on how the film image represented space, and I adopted the then-current terminology of perceptual psychology. Researchers spoke of depth cues, those features of the real world that prompt our visual system to make fast inferences about a three-dimensional layout. Classic depth cues are the Gestalters’ figure/ ground relation, da Vinci’s “atmospheric perspective” (the haze that envelops more distant planes), and Helmholtz’s “kinetic depth effect,” the way that when you’re moving, closer objects change at a different rate than more distant ones.
These features can also be invoked in two-dimensional images, as I tried to show in Narration in the Fiction Film. Nowadays, deeper explanations of these effects are available using geometrical or computational approaches to perception. But depth cues remain a useful informal way of studying how artists manipulate images. For this reason, in Film Art: An Introduction, we’ve continued to itemize some depth cues that are important in cinema. These concepts furnish analytical tools for understanding things that filmmakers do spontaneously when they compose or light a shot.
So imagine my happiness when I hear filmmakers talk directly about depth cues.
In a fascinating article in American Cinematographer, Pete Kozachik, Director of Photography on Coraline, explains that the filmmakers were very conscious of perceptual factors throughout, and not just in creating the stereoscopic effect. For example, they designed and filmed our heroine’s alternative world in normal perspective, but her boring normal world was designed to seem off-kilter and flat by means of inconsistent depth cues within the shots. “The compositions match in 2-D, but the 3-D depth cues evoke a different feel for each room.”
This is hard to illustrate in a two-dimensional medium, but the Coraline trailer offers some examples. Consider this image.
The tiles in the family shower don’t recede into the distance, either across or upward. They are more or less the same size, just arrayed along a diagonal. A degree of recession is supplied by tonality and lighting, but the corner of the shower stall remains somewhat ambiguous. If you try to do a Gestalt flip, you can see the corner as a chimney poking out at you rather than one receding inward. (To see this, try covering the rest of the shot with your hands.)
In the garden of the “Good Household,” however, the bricks recede naturalistically in shape and size. The lighting and tonal gradients create a strong sense of depth.
Here is the Good Family’s hallway.
It displays central perspective, with everything receding as it should (as if seen by a wide-angle lens).
By contrast, here is an oblique shot of Coraline’s real-world bedroom. The doorway’s edges recede pretty steeply, but the baseboard doesn’t taper as it moves toward and past the corner. Instead, it moves in parallel lines. The same thing is happening with the floor planks.
You can see the effect more clearly if we drain the color and lower the contrast. (Sorry, Messrs. Selick and Kozachik.)
Now you can also see the weird, almost cubistic edges of floorboards poking up just behind the carton. Again, lighting and tonality create a sense of depth that the geometry of the edges denies. The depth cues within Coraline’s normal life are inconsistent.
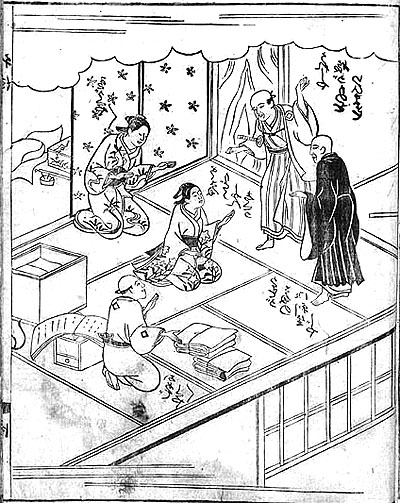
Stare at the rear stretch of the baseboard awhile, and you’ll find that its contours may look a bit wider than those in the foreground. This sort of “parallel perspective” can be found throughout Asian art. Here is a Japanese book illustration from 1713, in which many of the edges run in parallel perspective. Again, instead of meeting in the distance, diagonals seem to be converging out in front of the picture plane, making some areas appear wider in the rear than in the front.
If my invocation of other artistic traditions seems a highfalutin way of talking about an animated movie, check the Van Gogh joke in the Coraline frame at the bottom of this entry.
Kozachik also explains how he spent a lot of time trying to vary the two images’ interocular distance, the distance between our two eyes, in order to give a greater sense of volume. The care paid off, at least for me. Coraline is the best 3D film I’ve seen, as well as the scariest. (For our take on Beowulf see this entry.)
In addition, Coraline helps me push a general point: Cinema is at least partly an affair of perception. Filmmakers are practical psychologists, artists who have mastered the skill of playing with our senses. We can open up their secrets a little by using tools borrowed from the sciences of mind.
For more on Coraline, see Bill Desowitz’s Animation World interview with Tadahiro Uesugi and his interview with Henry Selick. Background on the production is supplied by Thomas J. McLean’s article from last year.
For an overview of spatial perception, see Maurice Hershenson, Visual Space Perception (MIT Press, 1999). A more detailed account is Stephen E. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology (MIT Press, 1999). A geometrical explanation of the kinetic depth effect is offered in James E. Cutting, Perception with an Eye for Motion (MIT Press, 1986).
An old-fashioned, sentimental avant-garde film
Kristin here–
A great many silent films that were almost impossible to see when David and I were in graduate school are now available on DVD. And it’s not just a matter of titles becoming available. In those days we might be able to see a classic film, but it was likely to be a shortened, fuzzy version made from a worn distribution print. Now government support for film archives and revenues from home video have promoted many more restorations. There are still companies releasing poor-quality DVDs of silent films, but beautiful prints, complete with tinting, toning, hand-coloring, and specially composed musical tracks, as well as supplementary material, are becoming more common.
A case in point is the new DVD version of Abel Gance’s 1922 epic, La roue (“The Wheel”), which the enterprising company Flicker Alley released last year. In its short existence since 2002, Flicker Alley has done exciting work. Its recent “A Modern Musketeer” collection finally makes a selection of Douglas Fairbanks’ pre-swashbuckler comedies and dramas available. I personally prefer these lively, witty, imaginative films to Fairbanks’ 1920s costume pictures. Flicker Alley’s George Méliès set is one of the great achievements of DVD production and deservedly won last year’s prize for the best silent DVD set at Il Cinema Ritrovato. Other highlights include F. W. Murnau’s rare psychological drama Phantom (1922) and Louis Feuillade’s serial, Judex (1917). I wrote about Flicker Alley’s release of Discovering Cinema, on early sound and color.
David and I first saw La roue in 1973, in a 16mm print at George Eastman House. It lasted around two hours projected at sound speed. We had another chance to see it at a 1979 screening of a 35mm nitrate print at the Museum of Modern Art. Again, it was a truncated version. In short, you had to see La roue at an archive.
The restoration
The original 32-reel version would have run between seven and eight hours. That doesn’t survive, but versions longer than the ones we had seen survived in various collections. A more common release version made in the 1920s reduced the film to 12 reels, or about three hours. Other still shorter versions also circulated.
Flicker Alley’s version is none of these. The liner notes say that it’s 20 reels, and it runs about 260 minutes. (The total time given on the box is 270 minutes, which I assume includes an eight-minute making-of supplement.) So what we have here is not an approximation of one of the release prints, but an attempt to reassemble as much footage as possible.
Here’s what Flicker Alley’s press release said about the restoration:
La Roue was originally shown in France over three days, in 32 reels, with a running time of almost eight hours, but was soon shortened to 12 reels, the maximum length for a typical feature film at the time. This new restoration, produced by Eric Lange, David Shepard and Jeff Masino with invaluable support from Turner Classic Movies, began with a 35mm master positive of this 12-reel version, a Russian print of an 8-reel version, two incomplete tinted nitrate prints of a longer French version, and finally, for two short but critical scenes, a 4-reel abridged version released by Pathe on 9.5mm for home movie screening. Conflating all of this material, the Lobster Film Studios restoration team headed by Eric Lange was able to prepare and digitally restore a 20-reel version, by far the most complete edition of La Roue seen anywhere since 1923. This release possesses exceptional pictorial quality and English titles that use the type font and moving photographic backgrounds of the original film.
The notes call this restoration “the fullest presentation of La Roue to reach the public since 1923,” which may or may not be true. I have seen a print of La roue of roughly the same length which has a significant number of scenes that aren’t present in the Flicker Alley release-and lacks several of the scenes included here. That was at the Royal Film Archive of Belgium, though they don’t hold the original material on it; that’s in a French archive. That version runs 287 minutes at 18 frames per second; I can’t find an indication of projection speed on the DVD, though I would guess that it’s comparable.
I definitely don’t want to suggest that the Flicker Alley DVD is not worth buying or viewing. Quite the contrary, it’s a valuable release of an extremely influential and important film. Perhaps a longer version will eventually be assembled, but I doubt that will happen any time soon. Those who have been waiting for years to see La roue should pounce on this, and it’s ideal for instructors who want to show clips of highly influential sequences in classes.
The visual quality of the print is mostly excellent, apart from a few passages where the restorers had to use a 9.5 mm print to fill in a few scenes–and even those look pretty good. Blue tinting is used in the night scenes, and the film is accompanied by Robert Israel’s effective score.
Gance’s innovations
[SPOILER ALERT]
Gance has many ardent admirers, to judge by the effusive reviews of the DVD on Amazon. But I find his major silent features a maddening blend of exciting stylistic innovation and old-fashioned, maudlin storytelling. La roue was, as far as we know, the first film to use rapid, rhythmic editing, at times going down to single-frame images. It’s also full of the subjective camera techniques typical of French Impressionist filmmaking: out-of-focus shots, white masks, superimpositions, and so on.
The plot, however, is simple and melodramatic; it centers on Sisif, a train engineer, and his secret adopting of a little girl who survives a train wreck in the opening scene. Norma grows up assuming herself to be his daughter, and Sisif’s son Elie, a sensitive violin-maker, believes her to be his sister. Sisif falls in love with her but stifles his feelings, giving her in marriage to a rich man whom she doesn’t love. When Elie learns the truth, he comes to love her as well but also hides his secret. A great deal of suffering ensues, over which Gance lingers lovingly with many shots of agonized faces.
Most famous are three scenes. The film’s action begins dramatically with the train crash, vividly rendered in many fairly quick shots. In the second, Sisif decides to crash the train in which Norma is traveling to her marriage. Even faster, accelerating editing conveys both Sisif’s anguish and Norma’s growing alarm. It’s a bold and suspenseful scene, and required viewing for anyone interested in silent cinema and the history of film style. The second passage comes after a fight between Elie and Norma’s husband that ends with Elie dangling from a tree root over a cliff. As he hears Norma approaching in an attempt to save him, their life  together literally flashes before his eyes in a series of shorter and shorter shots that end with a flurry of single-frame images that end with his fall.
together literally flashes before his eyes in a series of shorter and shorter shots that end with a flurry of single-frame images that end with his fall.
Much of the imagery is also beautiful, in particular the shots of trains passing sinuously along rails, a motif that punctuates the film.
These innovative scenes and other flashy techniques tended to be retained as distributors cut out more and more footage. What got trimmed seems to have been details of the quadruple romance plot. Scenes in the Belgian print that aren’t on the DVD include two brief ones indicating that the husband’s fortunes are declining. This sets up for the moment when Norma is revealed to have been left destitute after his death, a development that comes abruptly in the DVD version. The Belgian print also contains a rather silly scene in which Sisif talks to his train engine and imagines it replying to him.
Modern viewers may find it a bit disconcerting that the interior scenes of Sisif’s small house, built between the rails in a real train-yard, are lit with bright sunlight. Immediately after World War I the French film industry was short on studios and lighting equipment. Using open-air sets and full sunlight was not uncommon there or in countries with small film industries.
A brief but valuable bonus
Most films of this era did not have making-of documentaries. In this case, though, poet Blaise Cendrars, a great cinema enthusiast, filmed some scenes of Gance and his team at work and put together a fascinating short. A couple of shots show the camera used to film the tavern scene mounted on a dolly.
One view reveals just how close to the rails the sets for Sisif’s house were built. Trains passed so close to them that someone had to be stationed nearby to warn the crew of oncoming trains. Cendrars also recorded a visit Charles Pathé paid to the location, and there’s a heroic view of the director in the cab of a moving locomotive. This film has hitherto been très rare, so we are lucky to have it now.
The booklet accompanying the discs has an excellent essay on the history of the production by William M. Drew and notes by Israel on his score.
David insisted on having the photo at the bottom included among the illustrations. Gance appeared at the Walker Art Center in Minneapolis when he was 91 years old, which means that must have been in 1980. He had come to introduce a screening of Bonaparte and the Revolution, an early attempt to restore Napoléon vu par Abel Gance. At a reception afterwards, M. Gance was gracious enough to inscribe a photo and our copy of a book he had published in the 1920s, purchased back in the days when one could still find such things fairly readily in Parisian used bookshops. He also let David take a picture of him and me. He died the following year.
Note: Filmmaker and blogger Kevin Lee has created two more of his “Shooting Down Pictures” video analyses, with me speaking about La roue (five minutes) and Variety (six minutes) to clips Kevin has edited.
Around the world in 750 pages
The Double Life of Véronique (1992).
DB here:
Just over twenty years ago Kristin and I embarked on a perilous task. We decided to write a synoptic history of world cinema.
The task wasn’t perilous because it was innovative. Since the 1930s, there has been no shortage of historical surveys of international filmmaking, and such items continue to be published. But when we decided on this project in 1987, we wanted something different.
Soon that book will appear in a third edition. We take this occasion to explain the whys and wherefores.
Just start over
Daisies (1966).
For a very long time, and sometimes still, film histories written by Americans took a very partial look at the phenomenon of cinema. For one thing, they tended to focus on a series of masterpieces, films that had been deemed important within a narrow canon. The earliest lineup went pretty much this way: Lumière films, Méliès’ Trip to the Moon, Porter’s Great Train Robbery, Griffith’s Birth of a Nation and/ or Intolerance. Then came national schools, such as German Expressionism (The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari), Soviet Montage (Battleship Potemkin), and Continental Dada and Surrealism (Entr’acte, The Andalusian Dog). Early sound was M and Sous les toits de Paris and maybe Love Me Tonight. The 1940s was Grapes of Wrath and Citizen Kane and Enfants du Paradis and Italian Neorealism. And so on.
But in the 1970s archivists began opening their doors to researchers. Thanks to wider and deeper viewing, new film historians, young and old, were questioning the canon. André Gaudreault and Charles Musser showed that Porter’s Life of an American Fireman, which supposedly gave birth to crosscutting, did not do so; in fact the version people had used for years was a re-cut print! In Jay Leyda’s seminars at NYU, young scholars like Roberta Pearson were tracing what Griffith actually did and didn’t do, a task taken up by Joyce Jesionowski as well. At the same time, Eileen Bowser, Tom Gunning, Noël Burch, and others began questioning the idea that “our cinema” developed step by step from “primitive” beginnings. In England, Ben Brewster, Barry Salt, and others were minutely analyzing changes in film technique in the earliest years. Here at Madison, Tino Balio and Doug Gomery were revising the study of Hollywood as a business enterprise. Specialists working on national cinemas, from Russia, Italy, and the Nordic countries, were showing that there was far more diversity in world cinema than was dreamt of in orthodox histories.
 We were part of this generation of revisionists. In the 1970s and 1980s Kristin concentrated on European and American silent film, studying both stylistic movements and film distribution, as well as particular filmmakers like Eisenstein, Godard, and Tati. I did work on European and Japanese cinema. We spent years working on a reconsideration of the history of American studio film in collaboration with Janet Staiger. Writing The Classical Hollywood Cinema: Film Style and Mode of Production to 1960 we realized that asking fresh questions was both necessary and exciting.
We were part of this generation of revisionists. In the 1970s and 1980s Kristin concentrated on European and American silent film, studying both stylistic movements and film distribution, as well as particular filmmakers like Eisenstein, Godard, and Tati. I did work on European and Japanese cinema. We spent years working on a reconsideration of the history of American studio film in collaboration with Janet Staiger. Writing The Classical Hollywood Cinema: Film Style and Mode of Production to 1960 we realized that asking fresh questions was both necessary and exciting.
That’s what made our task perilous. Everything, it seemed, needed to be rethought.
Most obviously, countries outside Europe and North America had been neglected. One of my favorite film statistics is this, to quote from our book:
In the mid-1950s, the world was producing about 2800 feature films per year. About 35 percent of these came from the United States and western Europe. Another 5 percent were made in the USSR and the Eastern European countries under its control. . . . Sixty percent of feature films were made outside the western world and the Soviet bloc. Japan accounted for about 20 percent of the world total. The rest came from India, Hong Kong, Mexico, and other less industrialized nations. Such a stunning growth in film production in the developing countries is one of the major events in film history.
Traditional histories, and film history textbooks, had virtually ignored the bulk of film-producing nations. Only one or two major directors would step in from the shadows. Kurosawa summed up Japan, Satayajit Ray stood in for India. And the books’ layout of chapters indicated this second-class status. The history of film was Euro-American, with East Asia, Southeast Asia, South America, and Africa, appearing, if at all, in periods when westerners first got glimpses of their film culture. So Japan was typically first mentioned after World War II, when Rashomon won a prize at the Venice Film Festival. One would hardly know that there were many, and many great, Japanese filmmakers working in a long-standing tradition.
As if this weren’t enough, we were determined to include other varieties of artistic filmmaking. Documentary cinema, animation, and experimental film had attracted subtle historians like Bill Nichols, Mike Barrier, and P. Adams Sitney. We weren’t experts in these areas, but we were keenly interested in the debates in that domain, and so, guided by these and other scholars, we sought to integrate the histories of documentary, avant-garde, and animated cinema into our survey.
Kristin and David’s excellent adventure
Straight Shooting (1917).
In sum, we decided that we could write a plausible international history of cinema—not a be-all and end-all, but a new draft that reflected the rich variety of new findings and fresh perspectives. Like all historians, we had to be selective. We couldn’t, for instance, track every nuance of the “false starts and detours” in early film technique. More globally, we decided to concentrate on three lines of inquiry.
First, we studied changes in modes of film production and distribution. This inquiry committed us to a version of industrial history. How filmmaking was embedded in particular times and places, how it connected to local culture and national politics: these factors affected the ways films were made and circulated. For example, the early distribution of films followed the trade routes of late nineteenth-century imperialism. That global system started to crack with the start of World War I. A new world power, the United States, became the major film exporting country—a position it has enjoyed for most years since then.
Secondly, we studied changes in film form, style, and genre. We treated these artistic matters as not wholly the products of individual innovators but also as more widely-developed practices and norms. This emphasis on norms allowed us to link, in some degree, the development of technique to opportunities and constraints presented by film industries.
This angle of approach also meant looking at older works with a fresh eye, informed by others’ research but also by our own interests in film as an art. We were obliged to seek out films lying outside the orthodox story. Birth and Caligari and M feature in our account, but so do The Cheat and Assunta Spina and Liebelei. In those pre-DVD days, few of the titles we sought could be found on video, but we preferred to watch film on film anyway. So it was off to the archives. Fortunately, many collections were wide-ranging. We saw Egyptian and Swedish films in Rochester, French and Italian films in London, Indian and Japanese films in Washington, D. C., Polish and African films in Brussels. Committed to documenting our claims with frame enlargements, not production stills, we were lucky to be able to take photos from many of the movies we saw.
 In looking at national film industries and artistic change, we wanted to go beyond local observations. So a third question pressed upon us. What international trends emerged that knit together developments in different countries? We could not claim expertise in all the relevant national traditions, but we could, by drawing on films and other scholars’ writings, create a comparative study that gave a sense of the broad shape of film history.
In looking at national film industries and artistic change, we wanted to go beyond local observations. So a third question pressed upon us. What international trends emerged that knit together developments in different countries? We could not claim expertise in all the relevant national traditions, but we could, by drawing on films and other scholars’ writings, create a comparative study that gave a sense of the broad shape of film history.
For example, we could point to the emergence of tableau cinema in many countries in the 1910s. We could consider various models of state-controlled cinema in the 1930s and discover the “New Waves” that emerged not only in France but around the world in the late 1950s and early 1960s. Citizen Kane popularized a “deep-focus” look, but comparative study showed us that its principles were prefigured in Soviet cinema of the 1930s and spread to most major filmmaking nations in the 1940s. Not all trends march in lockstep, but there was enough synchronization to let us plot broad waves of change across the 100 years of film. Our aim was a truly comparative film history.
As a kind of overarching commitment, we wanted readers to think about what historical processes had shaped earlier historical frames of reference. How, for instance, did the “standard story” and the mainline canon get established in the first place? Part of the answer lies in the growth of film journalism and film archives. Why did Fellini, Bergman, Kurosawa, and other directors get so much fame in the 1950s and 1960s? True, they made exceptional films, but so did many other directors who remained unknown to a wider public. We suggested that the “golden age of auteurs” owed a good deal to developments in film criticism and to the postwar growth of film festivals. What led Japanese anime to a period of international popularity in the 1980s? Not only worldwide television distribution, but also devoted fans who spread their gospel through fanzines, videocassettes, and the youthful Internet. The “institutional turn” in film research of the 1970s and 1980s pushed us to consider how film industries and international film culture governed the way films were made and circulated.
The research programs that were launched in the 1970s were characterized by a greater self-consciousness than we had seen before. Historians questioned their assumptions and explanations. Why attribute originality only to “great men” without also examining their circumstances? Why presuppose that film technique grows and progresses in a linear way? To capture this new self-consciousness about purposes and methods, we incorporated something that had never been seen in a film history before: an introduction to historiography. In its latest incarnation it can be found elsewhere on this site. We also appended to each chapter short “Notes and Queries” discussing intriguing side issues, debates in the field, and topics for further research.
Up-to-date, and beyond
10 Canoes (2006).
The result of our efforts was first published by McGraw-Hill in 1994 as Film History: An Introduction. A second edition appeared in late 2002. More recently, we’ve spent about twenty months preparing a third edition, which will be published on 20 February this year.
We thought that writing the first edition was bloody hard, and it didn’t get any easier on the second or third pass. As usual, however, visiting new material broadens your compass. Writing my portions of the first edition had a profound impact on my research, but also on my personal tastes. The activity awakened my interest in Hindi cinema of the 1950s, Latin American cinema of the 1960s, experimental work of the 1980s, and African film of the 1990s. On this third round, I was caught up in the innovations of contemporary Korean film and of avant-gardists like Sharon Lockhart. Overall, our urge to trace cinematic creativity around the world led us to a greater appreciation of the wonders of film.
 Film History‘s third edition consists of six parts. The first looks at early cinema, from the 1880s to the end of the 1910s. The second considers the late silent era through the 1920s and slightly beyond. Part Three surveys the international development of sound film, up to 1945. The postwar era, from 1945 to the end of the 1960s, constitutes Part Four. We next consider the contemporary period, generously conceived as running from the 1970s to the present. The last section, Cinema in the Age of Electronic Media, makes up for the broad compass of Part Five by reconsidering trends that took shape during the 1980s.
Film History‘s third edition consists of six parts. The first looks at early cinema, from the 1880s to the end of the 1910s. The second considers the late silent era through the 1920s and slightly beyond. Part Three surveys the international development of sound film, up to 1945. The postwar era, from 1945 to the end of the 1960s, constitutes Part Four. We next consider the contemporary period, generously conceived as running from the 1970s to the present. The last section, Cinema in the Age of Electronic Media, makes up for the broad compass of Part Five by reconsidering trends that took shape during the 1980s.
What’s new in this edition? Several small changes have been made in the early portions to reflect newly available films and filmmakers now recognized as important. We have updated coverage of documentary with discussions of the rise of the theatrical doc and its two most striking practitioners, Errol Morris and Michael Moore. We have likewise expanded our section on avant-garde filmmaking by considering “paracinema,” which should have been in earlier editions, and the increase in cinema presented as installations and gallery works.
As for national cinema developments, we have extended our survey of western Europe and the USSR (Chapter 25), continental and subcontinental cinemas such as Latin America, Africa, and India (Chapter 26), and East Asia and Oceania (Chapter 27). New coverage is given to the recovery of the Russian and Chinese industries, the increasing world presence of Bollywood, and fresh talent from the Middle East and South Korea.
The book’s last part continues to host a chapter (28) on American cinema’s development in the light of home video and the rise of independent filmmaking; the blockbuster and Mumblecore are among the subjects we tackle. As in the second edition, we devote a chapter to globalization, which lets us trace the struggle between Hollywood’s global blockbusters and countervailing trends in other regions. This chapter allows us to study other globalizing processes, such as multiplexing, the Internet, fan culture, piracy, and diasporic populations.
Chapter 30 is new to this edition. It examines the effects of the digital revolution on all aspects of film production, as well as on new means of distribution and exhibition. The subjects covered include 3-D animation, DIY independents, and online distribution. We end by recognizing film as no less international an art form than it was in the earliest decades, when silent films slipped freely across national borders.
As in the early editions, we’ve tried to synthesize contemporary contributions but also add our own research and our own interpretations. Here, for example, is our very cine-centric conclusion about “the death of film.”
Will this barrage of new media ultimately overwhelm the cinema? Will the Internet, video games, and personal music players take over as the preferred forms of entertainment? Possibly, but there is evidence against that notion.
Each time that a digital platform appeared, it initially lacked the capacity to show films. Yet each platform adapted itself in order to add that capacity. In the 1990s, computers acquired the power to display movies. The Internet originally did not show films, but now it has Quicktime and downloads. Cell phones started out as communication devices, but later models included a camera and screen so that users could shoot and view films. The first game consoles could not show movies, but after the advent of DVDs, the next generation of machines became combination players. The original iPod and other personal music devices were strictly for audio, but Apple added the capacity to download digital video from computers, DVDs, and the Internet. The iPod enlarged its screen to better display films, even though that meant abandoning the signature click-wheel in favor of touch-screen controls.
Far from killing movies, digital media have allowed them to leave the theater and our living rooms. Now they can travel with us almost anywhere. In effect, film has reshaped the new media to accommodate it. As new digital devices emerge, we suspect that they, too, will adjust themselves to the cinematic traditions that have developed over 110 years.
No book can be definitive, partly because things change astonishingly fast. When we wrote the revision, DreamWorks was firmly within the Paramount family, and our chart of media conglomerates on p. 683 left it there. In page proofs, we shifted it when it seemed all but certain to move to Universal. Now comes the news that DreamWorks has signed with Disney. Likewise, the flow of important research hasn’t abated, and valuable books, like Jay Beck and Tony Grajeda’s Lowering the Boom: Critical Studies in Film Sound, were published after we went to press. Another peril of writing contemporary history, then: Keeping up.
To squeeze in our new material, we’ve had to excise the historiography essay mentioned above, as well as our Notes and Queries and our plump bibliographies. Those, all updated, have appeared at the McGraw-Hill site. Even if you’re not reading the book, feel free to go to the Student Edition tab and browse through the Notes and Queries for each chapter. Some of these brief, bloggish items may pique your interest.
Without exactly planning to do it, we seem to have come up with the most wide-ranging, extensively illustrated survey of world cinema history available in English. The third edition of Film History: An Introduction runs to 750 large-format pages, not counting the index. It contains hundreds of black-and-white frame enlargements and thirty pages of color illustrations.
We hope that if you’re interested in film history you’ll take a look. Feel free to write to us with your thoughts, especially if you find misprints (we’ve been chasing them for months) and factual errors. We’d also appreciate comments about our larger arguments and interpretations. We improve only by constantly rechecking what we say and how we say it.
The quotation about 1950s world film output comes from Kristin Thompson and David Bordwell, Film History: An Introduction, third ed. (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2009), 373.
Tokyo Drifter (1966).