Archive for the 'Film technique' Category
The spectacle of skill: BUSTER SCRUGGS as master class
The Ballad of Buster Scruggs (2018).
DB here:
Craft isn’t everything in art, but it counts for a lot. Even when you’re going against tradition, you can’t just willy-nilly do whatever. You need to create a counter-craft (as Bresson, Brakhage, Ozu, and others showed us). Reviewers, in their urge to thump out quick judgments, often don’t address craft practice directly. So if we simply talk of the Coens’ Ballad of Buster Scruggs as a grim, occasionally grotesque and zany take on Western conventions, we’re apt to take for granted just what a trim, absorbing piece of sheer filmmaking it is.
It’s worth attuning ourselves to what Adam Gopnik called his collection of Robert Hughes’ writings: The Spectacle of Skill. Paying attention to that enhances our appreciation for what filmmakers accomplish, and maybe it can nudge aspiring filmmakers to consider things to try.
So, herewith a quick analysis of the very beginning of the film’s second episode. The whole piece is not as audacious as the title episode, and not as poignant as “Meal Ticket” or “The Gal Who Got Rattled.” It’s more of a light interlude. But we shouldn’t let its shaggy-dog payoff (“Your first time?”) make us think there’s anything slapdash about it.
There follow spoilers.
All the meanness in the Used-To-Be
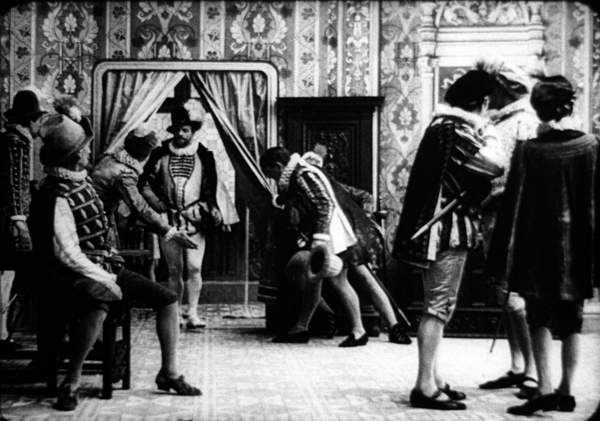
In the book that frames each tale, this one is called “Near Algodones.” As in the other episodes, an illustration prepares us for something we’ll see in the scene. The caption reads: “Pan-shot!” cried the old man.
Lesson 1: Make everything clear and simple, except what you want to suppress.
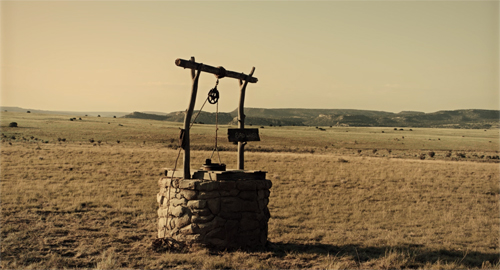
A master shot gives us the elemental situation: A bank, a well, and a lone rider with his horse.
These are the central components of the sequence. The isolation of the bank makes it a plausible target for a holdup. The geography will become important in the second stretch of the scene, while the well will provide cover to the Cowboy. His horse will prove notably reluctant to move.
Lesson 2: Attach the narration to a single character.
Throughout this episode, we’re “with” the Cowboy, not always through exact optical POV but more generally: our range of knowledge of the unfolding situation approximates his. This sort of restriction arouses curiosity (what’s going on in the bank?), as well as suspense and surprise (as we’ll see).
Lesson 3: Motivate new shots by offscreen sound.
Attachment to the Cowboy is reinforced by the play of his attention. Over the Leone-esque close-up we hear a creak. This motivates a cut to the bank’s hanging sign. As we hear a thump, he shifts his eyes; we see it’s caused by the bucket bumping against the well.
Lesson 4: Delay when you can.
Attachment doesn’t mean immersion. Instead of a shot from the Cowboy’s POV as he’s entering the bank, we get him pausing to size up the scene.
Only then do we get a shot of the bare bank and the teller’s windows, which (thanks to a wide-angle lens) seem impossibly far away.
Lesson 5: Let expectations go to work.
The holdup scenario, a convention of Westerns, is surely hovering in many viewer’s minds. When the Cowboy advances, we wait to see if our expectations pay off. You get suspense simply by having your actor move forward; what could be more economical?
Lesson 6: Prepare for later shots.
The tracking shot of the Cowboy’s boots and spurs might seem mere decoration, but it further delays his arrival at the window and sets up an important shot to come.
Lesson 7: Scale your shots according to the information they present.
Reverse shots are the workhorses of mainstream storytelling cinema. They are vehicles for character interaction, either based in dialogue or just the exchange of glances. The over-the-shoulder (OTS) version specifies the spaces the characters occupy, typically in a conversation. OTS framings also serve as a transition to closer views. Here the Cowboy’s goal in the scene is to learn how fortified the bank is against robbery.
After the opening stretch of purely visual storytelling, dialogue takes over. For us to grasp it better, the OTS framings give way to singles, which enlarge the teller’s performance and the Cowboy’s reactions.
The geezer’s chatter joins the motif of flowery monologues and eloquent bafflegab we’ll encounter throughout the film. The framing also lets us enjoy the performance, which suggests that this scatterbrain might be an easy mark. He does, however, mention that he has put down one attempted robber and “shredded the legs” of another.
The climax of the exchange is the Cowboy’s drawing his pistol and the teller’s explanation that he has to stoop to get “the large denominations.” The result is more shot-scale calibration: We need a single to see the gun looming (an OTS wouldn’t be as punchy), but the reverse shot can be OTS because we need to see how the teller’s stooping maneuver is concealed from the Cowboy. We are still attached to him and what he knows–or doesn’t know.
Another benefit: as variants of framings we’ve seen before, these let us quickly grasp what’s new in them (brandishing the pistol, ducking down).
Lesson 8: Use a cut, a crisp gesture, or a discrete sound to arrest attention.
Actually, the next shot does all three. The Cowboy tries to peer over the till, and a shot shows him taking a step forward as we hear a click. This framing pays off the shot of striding boots we saw in Lesson 6.
Within the same shot, the front of the teller’s window is blasted open. The Cowboy jumps sideways as another hole explodes, then another.
We’re back to visual storytelling. Now we understand why the teller has “shredded the legs” of another would-be robber. When the debris clears, a camera tilt shows that the Cowboy has sprung to the counter.
A mini-spectacle of skill: Handling the three blasts and the Cowboy’s evasion in a single percussive shot.
Lesson 9: Stagger the reveals.
Alexander Payne once remarked: “Whenever you can do a reveal, do it.” Here we have a suite of reveals, but they’re handled in a simple, cogent way.
When the Cowboy crouches on the counter, we have several questions. Is the teller going to fight? What created the blasts? And will the Cowboy get to the money?
These questions are answered, purely pictorially, in the shots to come. First, from his perch the Cowboy sees the partly open door. The teller has escaped, but because we’re restricted to the Cowboy’s perspective, we don’t know where he’s gone.
Just as one concise shot showed us the gunblasts and the Cowboy’s leap to the counter, now his descent and landing, followed in a single tilt, reveals the teller’s infernal machine: a row of shotguns poised to fire.
Another director would have devoted a POV shot to this revelation, but here it’s provided without fuss or forcing, as we follow the Cowboy’s crouch. He barely reacts and smoothly sets about finding the money. He grabs it in a single crisp close-up. And another cut takes us to the doorway, as the Cowboy hopes a view outside will reveal where the teller has gone.
Once more a POV is recruited, but it shows how much our protagonist doesn’t know.
The elements we were given at the start–bank, well, horse–are laid out again, from the opposite angle. Thanks to the clarity of presentation, we fully understand that the old teller is hiding somewhere (probably with his lauded scattergun) and the Cowboy has to make a run for it. But to where?
There are other things to talk about here, such as the homages to Leone (the mention of Tucumcari from For a Few Dollars More, the creaking of the sign recalling Once Upon a Time in the West‘s operatic opening). Perhaps the device of the book owes something to William S. and Mary Hart’s Pinto Ben (1919).
But we’re so used to considering the Coens pasticheurs that these allusions don’t interest me as much as the compact finesse of their style.
The rest of this scene will depend on reworking the narrative, auditory, and pictorial elements we’ve already encountered. You could go through that, and indeed the rest of the film, and trace the artisanal precision on display. (Let alone the sheer boldness of certain depth shots.) And the Coens are expert at using visual ideas for humor, as in the later scene when the Cowboy’s horse, browsing for more grass to nibble, stretches his noose-rope to the limit (see top image).
But I think I’ve said enough to indicate how rich an apparently straightforward handling can be. When we speak of careful pacing; when we think of building a scene; when we think of a movie that’s easy and graceful to follow, what Otis Ferguson called “a smooth clear line”–this is what we’re talking about.
There’s plenty of spectacle here, what with landscapes and gun blasts, but there’s another sort of spectacle as well: the quiet virtuosity of craft. You don’t see it that often these days, so when we encounter it, we should acknowledge it.
For another study of the Coens’ technique, see Jim Emerson on No Country for Old Men.
Other blog entries celebrate this sort of precision. See, for example, this analysis of Panic in the Streets, or the mind-boggling visual engineering of Fritz Lang (here and here). Otis Ferguson’s ideas about smooth cinematic storytelling are discussed in The Rhapsodes: How 1940s Critics Changed American Film Culture.
My first impressions of Scruggs, after seeing a magnificent big-screen presentation in Venice, are here. Netflix and Annapurna are to be congratulated for backing this movie, but it really deserves a wider theatrical release than it got. At least, please give us a Blu-Ray!
The Ballad of Buster Scruggs (2018).
ON THE HISTORY OF FILM STYLE goes digital
Dust in the Wind (1986).
DB here:
I was born to write this book.
 So I rashly claim in the Preface to the new edition of On the History of Film Style. That’s not to say somebody else couldn’t have done it better. It’s just that the book’s central questions tallied so neatly with my enthusiasms and personal history that I felt an exceptional intimacy with the project.
So I rashly claim in the Preface to the new edition of On the History of Film Style. That’s not to say somebody else couldn’t have done it better. It’s just that the book’s central questions tallied so neatly with my enthusiasms and personal history that I felt an exceptional intimacy with the project.
Baby-boomer narcissism aside, there are more objective reasons for me to tell you about the book’s revival. It came out in late 1997 from Harvard University Press, and it went out of print last fall. Thanks to our web tsarina Meg Hamel, it has become an e-book, like Planet Hong Kong, Pandora’s Digital Box, and Christopher Nolan: A Labyrinth of Linkages.
The new edition is substantially the original book; the pdf format we used didn’t permit a top-to-bottom rewrite. Errors and some diction are corrected, though, and the color films I discuss are illustrated with pretty color frames, not the black-and-white ones in the first edition. The new Preface and a more expansive Afterword explain the origins of the book and develop ideas that I pursued in later research.
The book analyzes three perspectives on film style as they emerged historically. One, what I call the Basic Version, was developed in the silent era and saw the discovery of editing as the natural development of film technique.
The second version, associated with critic André Bazin, modified that conception by stressing the importance of other stylistic choices, notably long takes and staging in depth. I call this the Dialectical Version because Bazin claimed that these techniques were in “dialectical” tension with the pressures toward editing.
A third research program, spearheaded by filmmaker and theorist Noël Burch, argued that the development of film style was best understood as the ongoing interplay between two tendencies. There’s a dominant style Burch called the Institutional Mode. Responses to that mode are crystallized in alternative practices–the cinema of Japan, for instance, or the “crest-line” of major works associated with modernist trends.
The book goes on to show how a revisionist research program launched in the 1970s built upon these earlier perspectives. Younger scholars sought to answer more precise questions about certain periods and trends. The revisionist impulse is best seen in debates on early cinema, which I survey.
The book so far is historiographic, tracing out other writers’ arguments about continuity and change in film style. In my last chapter I try to do some stylistic history myself. I analyze particular patterns of continuity and change in one technique, depth staging. Certain conceptual tools, like the problem/solution couplet and the idea of stylistic schemas, can shed light on how certain staging options became normalized in various times and places. In turn, directors like Marguerite Duras, in India Song (1975), can revise those norms for specific purposes.
On the History of Film Style was generally well-received. John Belton, while voicing reservations, called it “a very good book. Anyone seriously interested in Film Studies should read it.” Michael Wood wrote in a review that “Bordwell is always sharp and often funny” (I try, anyhow) and called the last section “a brilliant account of the history of staging in depth.” The book has been used in some courses, and I’m happy to learn that there are filmmakers who find it useful. It’s been translated into Korean, Croation, and Japanese.
The book is available for purchase on this page. It’s priced at $7.99, a middling point between our other e-pubs. It’s a bigger book than Pandora ($3.99) and the Nolan one ($1.99), but it’s not an elaborate overhaul like Planet Hong Kong 2.0 ($15). Selling the book helps me defray the costs of paying Meg and digging up color frames. In any event, the new version is much cheaper than the old copies available at Amazon. It’s almost exactly the price of two Starbucks Caffe Lattes (one Grande, one Venti).
The archives and festivals that made the book possible are thanked inside, and they’ve continued to be hospitable and encouraging over the last two decades. Equally supportive are the students, colleagues, and cinephile friends with whom I’ve discussed these issues. So I reiterate my thanks to them all. And I hope this new edition, if nothing else, stimulates both viewers and researchers to explore the endlessly interesting pathways of visual style in cinema.
La Mort du Duc de Guise (1908).
THE LOST WORLD refound, piece by piece
Kristin here:
Like just about all kids, I was fascinated by dinosaurs for a while. That’s probably why my mother bought a copy of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s 1912 fantasy-adventure novel, The Lost World, at a yard sale and gave it to me to read while I was sick in bed. I must have been about nine. It was a battered photoplay edition, complete with photos of scenes from the 1925 movie. I read other Victorian-Edwardian fantasy-adventure books, mostly Verne and Haggard, at around the same time. I suppose they prepared me for reading The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings at age 15 and developing a life-long attachment to them. This doesn’t mean that I consider The Lost World a masterpiece, but having come to it so young, I retain a fondness for it. I was interested to find out what the new Flicker Alley release of a new restoration of the film is like.
Doyle’s novel deals with a scholar and explorer, Professor Challenger, who has recently visited a remote site in South America and is ridiculed by all for his claims that dinosaurs survive on an inaccessible plateau there. The hero, Edward Malone, a lovelorn reporter courting a woman who insists she wants a daring, heroic husband, enlists on an expedition to test Challenger’s stories. So does a skeptical rival of Challenger’s, Professor Summerlee, and a hunter-adventurer, Sir John Roxton, who wants to add a stuffed dinosaur to his other trophies. Many adventures follow, including vengeful Spanish guides marooning the expedition atop the plateau, where they encounter dinosaurs, ape-men, and Indians. The team escapes and manages to take a pterodactyl back to London. Challenger’s reputation is restored.
Following on the novel, I saw the 1960 Irwin Allen version of The Lost World. At the age of perhaps ten or eleven I enjoyed it, though I did recognize that Jill St. John’s character was a total and unnecessary fabrication and the “dinosaurs” were lizards with prostheses.
The 1925 version
Naturally when I was a grad student in film studies, I took my first opportunity to see the 1925 version. It was produced by the important studio and distributor First National Pictures three years before it was absorbed by the upstart Warner Bros. In those days the only version available was a 50-minute abridgement made by Kodascope, and it was not, to say the least, impressive.
I cannot say that I paid much attention to the subsequent restorations: the 1998 George Eastman House version, which, while still incomplete, was a distinct improvement, and the the 2000 David Shepard version, which was basically the same but with digital improvements to sound and image.
The 2016 restoration by Serge Bromberg’s Lobster Films as presented now on Blu-ray by Flicker Alley, has added considerable footage. This extends the film to 103 minutes, close to its original running time. The main thing missing is a scene of cannibals attacking the expedition members as they travel upriver to the controversial plateau, as well as a few other brief moments.
As an adaptation, it’s a distinct improvement on the 1960 version. After all, the novel was only 13 years old when it was made. Doyle was still alive; he would not publish his final Sherlock Holmes story until 1927 and his final works of fiction until 1929. Conventions and tastes in popular fiction, whether filmic or literary, had not changed nearly as much as they had by Irwin Allen’s day.
The main casting was impeccable, with Wallace Beery the perfect choice for the powerful, pugnacious Challenger (above) and Lewis Stone for the epitome of British stalwart rectitude. The film even managed to do a good job of concocting a love interest by introducing Paula White (Bessie Love), the daughter of the original discoverer of the lost-in-time plateau and eager to participate in an expedition to rescue her marooned father. Then it gave her little to do. Bessie Love just has to look terrified at intervals, in a series of close-ups surrounded by an iris and with a blank background–clearly shot later with someone telling Love just to glance in all directions and register fear. These moments add up to something a realization of a Kuleshov experiment.
Her presence does, however, allow Stone to give perhaps the most subtle and sympathetic performance in the film. He’s in love with White but nobly gives her up to Malone. As Malone, Lloyd Hughes manages to look suitably handsome and impetuous. Arthur Hoyt, older brother of director Harry O. Hoyt), plays Professor Summerlee. His many “little man” roles later included the hotel owner in It Happened One Night, and he was one of Preston Sturges’ regular actors. (“Looking perpetually befuddled was Hoyt’s stock-in-trade,” as I. S. Mowis puts it in his IMDb biography of Hoyt.) Unfortunately the film exaggerates Summerlee’s somewhat amusing traits, thereby making him a strictly comic character. (One wonders how Claude Rains, so very dissimilar from Beery, could be chosen for the same role in the 1960 version. Casting against type, presumably.)
By the way, although the film seems basically to be set in the Edwardian era of the novel’s original publication, the introduction to the final London portion of the story shows Piccadilly Circus at night, including a movie palace show The Sea Hawk (1924), another First National release that included Wallace Beery and Lloyd Hughes (Malone) its cast.
A little synergy that brings the story up to date.
Puppets and people
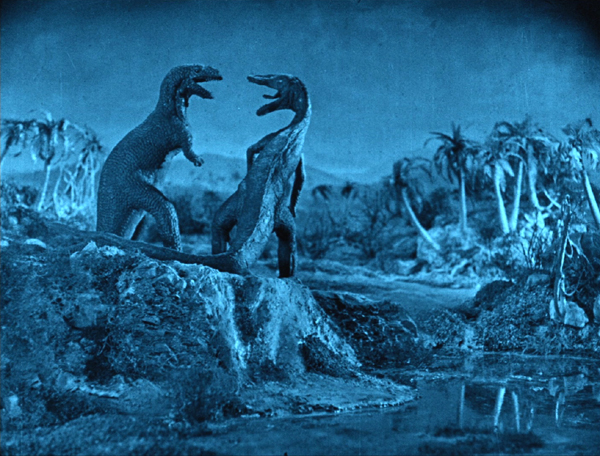
The main attraction of the film, of course, is its technology. Some of it was quite innovative. It is thought to be the first time when the special effects of a feature film were largely accomplished through puppet animation.
There had been earlier puppet films, including Ladislas Starevich‘s realistic creation of artificial insects apparently acting out conventional melodramas. Accomplished though they were, these did not mix live-action with real actors in the same shots, as do the miniature landscapes with the moving dinosaurs.
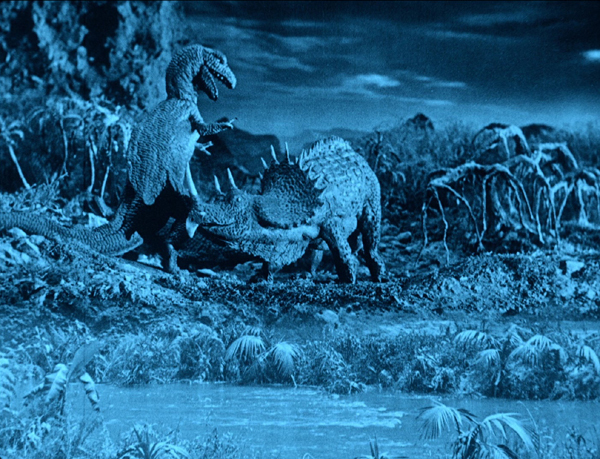
In The Lost World, combinations usually involve the actors placed in the lower foreground, observing the dinosaurs from varying distances. Atop this section, for example, in a very skillfully done shot, an allosaurus approaches the campsite of the expedition members. The place where the live-action at the lower right joins the miniature set at the upper left is difficult to discern, and the careful lighting of both areas aids in the illusion.
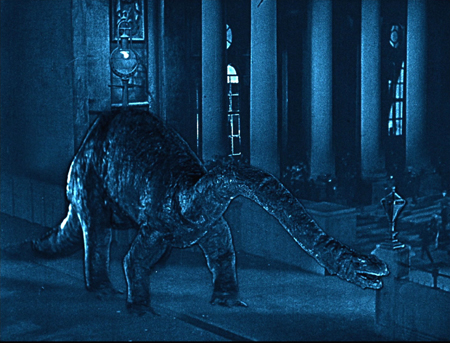
The late scenes of the film, where a brontosaurus escapes into London’s streets and causes panic resorted to a new and complex technology, moving mattes. This device involved using stencils cut for each frame and doubly exposing prints from two negatives. Moving mattes allowed figures filmed separately to be inserted into scenes without the use of superimpositions. The result usually was fairly obvious, betrayed by an evident join line around the added figure. Differences in texture and lighting also caused problems. Still, given the technical limitations of the day, the results are impressive. (The most famous use of moving mattes in this era was probably the reunited couple’s oblivious stroll through traffic in Sunrise.)
The Lost World drew more heavily on stationary mattes, and for the most part, the technology is pretty convincing. The scene of the allosaurus-triceratops-pterodactyl fight (at the top) contains a stationery matte. The lower part of the frame is a river with plants on the banks swaying in the breeze. About a third of the way up the composition, there is a join to the miniature set in which the action was animated. There the plants are completely stationery, but the movement of the real plants in the lower area gives a degree of verisimilitude to the whole scene. The shot of the team confronting the allosaurus at the top of this section also uses this technique.
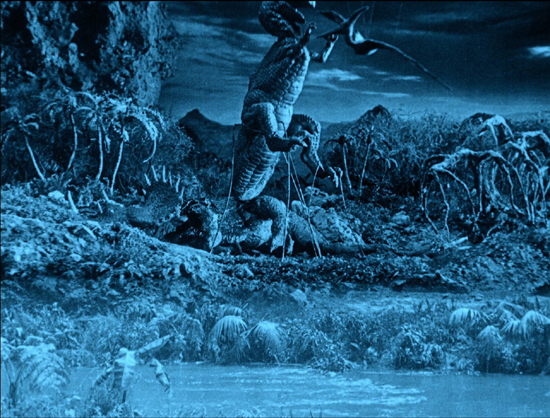
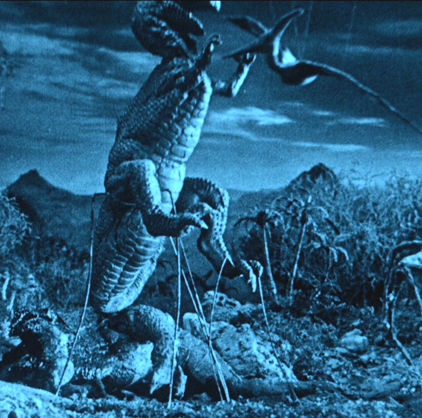
Digital copies let us pause and figure out some of O’Brien’s secrets. After the allosaurus has dispatched the unfortunate triceratops seen in the image at the top of this entry, a dramatic moment occurs in a blink-and-you’ll-miss-it flurry of motion as it suddenly snatches a pterodactyl in mid-flight and kills it. Pausing on the action, we can see that O’Brien used wires to support the allosaurus during its leap, as well as nearly invisible wires along which to slide the pterodactyl. I didn’t notice any other scenes in which O’Brien had to resort to visible props.
And at least the dinosaurs, unlike King Kong, didn’t have fur that ruffles almost continually, betraying the movements of the animators’ fingers in between exposures of the frames. As a result, the animation in The Lost World almost looks more sophisticated than that of Kong.
Moreover, O’Brien’s puppets, constructions of rubber and foam over metal skeletons, included balloons inside that could have air pumped in and out to simulate breathing. It’s a measure of the man’s inspiration that he realized how much this technique would contribute to the lifelike quality of the dinosaurs.
One of the supplements gives another insight. It is listed as “Deleted scenes,” or outtakes, but occasionally O’Brien or perhaps one of his assistants (the footage is too indistinct to tell which) pops into the image for a few frames, incongruously appearing submerged to his waist in a primordial landscape.
Such images give a sense of the considerable scale of the miniature landscapes and the puppets, as well as the labor involved in this novel endeavor.
The new print
This newest restoration, having been cobbled together from many disparate elements, inevitably is variable in its visual quality. Much of it is splendid, as indicated in most of the images reproduced in this entry, especially the one at the top. Others are clearly worn, with light lines, as in the shot above of Challenger and Summerlee watching a brontosaurus pass in the background. Again a matte shot has been used, its joint probably running along the top of the little sandy ridge behind which the men hide.
The rather poignant scene of the dinosaurs fleeing from a volcanic eruption is unfortunately worn as well. Such stretches, however, are in the minority.
The new version also includes tinting and toning based on recently discovered footage, as well as a brief scene combining red and blue colors when Malone throws a torch into the mouth of an allosaurus to drive it away.
The disc comes with a booklet by Bromberg outlining the extensive restoration work on the versions of The Lost World, as well as the disc’s two musical-track options, one by Robert Israel and one by the Alloy Orchestra. Supplements include a commentary track by Nicolas Ciccone and some short films and clips by O’Brien. The Silent Era website offers a detailed rundown on the many video releases of The Lost World. Once more Lobster Films and Flicker Alley are to be congratulated on another contribution to the retrieval of cinema’s history.