“Up ahead was Pandora. You grew up hearing about it, but I never figured I’d be going there.”
DB here:
Actually it wasn’t originally a box but a jug. And it might not have been filled with all the world’s misfortunes; it might have housed all the virtues. In Greek mythology, the gods create her as the first woman, sort of the ancient Eve. We get our standard idea of her story not from the ancient world, however, but from Erasmus. In 1508 he wrote of her as the most favored maiden, granted beauty, intelligence, and eloquence. Hence one interpretation of her name: “all-gifted.” But to Prometheus she brought a box carrying, Erasmus said, “every kind of calamity.” Prometheus’ brother Epimetheus accepted the box, and either he or Pandora opened it, “so that all the evils flew out.” All that remained inside was Hope. (Don’t think there isn’t a lot of dispute about why hope was cooped up with all those evils.)
The idea of Pandora’s box spread throughout Western culture to denote any imprudent unleashing of a multitude of unhappy consequences. It’s long been associated with an image of an attractive but destructive woman, and we don’t lack examples in films from Pabst to Lewin. But there’s another interpretation of the maiden’s name: not “all-gifted” but “all-giver.” According to this line, Pandora is a kind of earth goddess. In one Greek text she is called “the earth, because she bestows all things necessary for life.”
The less-known interpretation seems to dominate in Avatar. Pandora, a moon of the huge planet Polyphemus, is a lush ecosystem in which the humanoid Na’vi live in harmony with the vegetation and the lower animals they tame or hunt. Nourished by a massive tree (they are the ultimate tree-huggers), they have a balanced tribal-clan economy. Their spiritual harmony is encapsulated in the beautiful huntress Neytiri. As the mate for the first Sky-Person-turned-Na’vi, Avatar Jake, she’s also an interplanetary Eve. And by joining the Na’vi on Pandora, Jake does find hope.
The irony of a super-sophisticated technology carrying a modern man to a primal state goes back at least as far as Wells’ Time Machine. But the motif has a special punch in the context of the Great Digital Changeover. Digital projection promises to carry the essence of cinema to us: the movie freed from its material confines. Dirty, scratched, and faded film coiled onto warped reels, varying unpredictably from show to show (new dust, new splices) is now shucked off like a husk. Now images and sounds supposedly bloom in all their purity. The movie emerges butterfly-like, leaving the marks of dirty machines and human toil behind. As Jake returns to Eden, so does cinema.
Avatar or atavism?
Kristin suggested the title for this series of blog entries, and I liked its punning side. For one thing, Avatar was a turning point in digital projection. 3D, as we now know, was the Trojan Horse that gave exhibitors a rationale to convert to digital. Avatar, an overwhelming merger of digital filmmaking (halfway between cartoon and live-action) and 3D digital projection, fulfilled the promise of the mid-2000s hits that had hinted at the rewards of this format.
With its record $2.7 billion worldwide box office, Avatar convinced exhibitors that digital and 3D could be huge moneymakers. In 2009, about 16,000 theatres worldwide were digital; in 2010, after Avatar, the number jumped to 36,000. True, theatre chains also benefited from JP Morgan’s timely infusion of about half a billion dollars in financing in November 2009, a month before the film’s release. Still, this movie that criticized technology’s war on nature accelerated the appearance of a new technology.
Throughout this series, I’ve tried to bring historical analysis to bear on the nature of the change. I’ve also tried not to prejudge what I found, and I’ve presented things as neutrally as I could. But I find it hard to deny that the digital changeover has hurt many things I care about.
The more obvious side of my title’s pun was to suggest that digital projection released a lot of problems, which I’ve traced in earlier entries. From multiplexes [3] to art houses [4], from festivals [5] to archives [6], the new technical standards and business policies threaten film culture as we’ve known it. Hollywood distribution companies have gained more power, local exhibitors have lost some control [7], and the range of films that find theatrical screening is likely to shrink. Movies, whether made on film or digital platforms, have fewer chances of surviving for future viewers. In our transition from packaged-media technology to pay-for-service technology, parts of our film heritage that are already peripheral—current foreign-language films, experimental cinema, topical and personal documentaries, classic cinema that can’t be packaged as an Event—may move even further to the margins.
Moreover, as many as eight thousand of America’s forty thousand screens may close. Their owners will not be able to afford the conversion to digital. Creative destruction, some will call it, playing down the intangible assets that community cinemas offer. But there’s also the obsolescence issue. Equipment installed today and paid for tomorrow may well turn moribund the day after tomorrow. Only the permanently well-funded can keep up with the digital churn. Perhaps unit prices will fall, or satellite and internet transmission will streamline things, but those too will cost money. In any event, there’s no reason to think that the major distributors and the internet service providers will be feeling generous to small venues.
Did this Pandora’s box leave any reason to be optimistic? I haven’t any tidy conclusions to offer. Some criticisms of digital projection seem to me mistaken, just as some praise of it seems to me hype or wishful thinking. In surrendering argument to scattered observations, this final entry in our series is just a series of notes on my thinking right now.
What you mean, celluloid?
First, let’s go fussbudget. It’s not digital projection vs. celluloid projection. 35mm motion picture release prints haven’t had a celluloid base for about fifteen years. Release prints are on mylar, a polyester-based medium.
Mylar was originally used for audio tape and other plastic products. For release prints of movies, it’s thinner than acetate but it’s a lot tougher. If it gets jammed up in a projector, it’s more likely to break the equipment than be torn up. It’s also more heat-resistant, and so able to take the intensity of the Xenon lamps that became common in multiplexes. (Many changes in projection technology were driven by the rise of multiplexes, which demanded that one operator, or even unskilled staff, could handle several screens.)
Projectionists sometimes complain that mylar images aren’t as good as acetate ones. In the 1940s and 1950s, they complained about acetate too, saying that nitrate was sharper and easier to focus. In the 2000s they complained about digital intermediates too. Mostly, I tend to trust projectionists’ complaints.
But acetate-based film stock is still used in shooting films, so I suppose digital vs. celluloid captures the difference if you’re talking about production. Even then, though, there’s a more radical difference. A strip of film stock creates a tangible thing, which exists like other objects in our world. “Digital,” at first referring to another sort of thing (images and sounds on tape or disk), now refers to a non-thing, an abstract configuration of ones and zeroes existing in that intangible entity we call, for simple analogy, a file.
George Dyson [8]: “A Pixar movie is just a very large number, sitting idle on a disc.”
Big and gregarious
Sometimes discussion of the digital revolution gets entangled in irrelevant worries.
First pseudo-worry: “Movies should be seen BIG.” True, scale matters a lot. But (a) many people sit too far back to enjoy the big picture; and (b) in many theatres, 35mm film is projected on a very small screen. Conversely, nothing prevents digital projection from being big, especially once 4K becomes common. Indeed, one thing that delayed the finalizing of a standard was the insistence that so-called 1.3K wasn’t good enough for big-screen theatrical presentation. (At least in Europe and North America: 1.3K took hold in China, India, and elsewhere, as well as on smaller or more specialized screens here.)
Second pseudo-worry: “Movies are a social experience.” For some (not me), the communal experience is valuable. But nothing prevents digital screenings from being rapturous spiritual transfigurations or frenzied bacchanals. More likely, they will be just the sort of communal experiences they are now, with the usual chatting, texting, horseplay, etc.
Of course, image quality and the historical sources and consequences of digital projection are something else again.
Irresolution
It’s a good thing the pros kept pushing. Had filmmakers and cinephiles welcomed the earliest digital systems, we might have something worse. Here’s George Lucas in 2005, talking less about photographic quality than the idea of the sanitary image.
The quality [of digital projection] is so much better. . . . You don’t get weave, you don’t get scratchy prints, you don’t get faded prints, you don’t get tears. . . The technology is definitely there and we projected it. I think it is very hard to tell a film that is projected digitally from a film that is projected on film.
And he’s referring to the 1280-line format in which Star Wars Episode I was projected in 1999.
Probably the widespread skepticism from directors and cinematographers helped push the standard to 2K. (So did the adoption of the Digital Intermediate.) Optimistic observers in the mid-2000s expected the major studios to make 4K the standard right away. Given the constraints of storage at that time, the 2K decision might be justified. But like the 24 frames-per-second frame rate of sound cinema, it was a concession to the just-good-enough camp.
At the same time, George seems to grant that progress will be needed in the area of resolution.
You’ve got to think of this [our current situation] as the movie business in 1901. Go back and look at the films made in 1901, and say, “Gee, they had a long way to go in terms of resolution. . . .”
Actually, in films preserved in good state from 1901, the resolution looks just fine—better than most of what we see at the multiplex today, on film or on digital.
The invisible revolution
Speaking of sound cinema: Is the changeover to talkies the best analogy for what we’re seeing now? Mostly yes, because of the sweeping nature of the transformation. No technological development since 1930 has demanded such a top-to-bottom overhaul of theatres. Assuming a modest $75,000 cost for upgrading a single auditorium, the digital conversion of US screens has cost $1.5 billion.
In an important respect, though, the analogy to sound doesn’t hold good. When people went to talkies, they knew that something new had been added. The same thing happened with color and widescreen. And surely many customers noticed multi-track sound systems. But what moviegoers notice that a theatre is digital rather than analog? Many probably assume that movies come on DVDs or, as one ordinary viewer put it to me, “film tapes.” Anyhow, why should they care?
There was a debate during the 2000s that audiences would pay more for a ticket to a digital screen. But that notion was abandoned. People aren’t that easy to sucker. So we’re back with 3D as the killer app, the justification for an upcharge. Whether 3D survives, dominates, or vanishes isn’t really the point. It’s served its purpose as the wedge into digital installation.
By the way, according to one industry leader [11], 2D ticket prices are likely to go up this year while 3D prices drop. Is this flattening of the price differential a strategy to get more people to support a fading format?
Mommy, when a pixel dies, does it go to heaven?
Digital was sold to the creative community in part by claiming that at last the filmmaker’s vision would be respected. Every screening would present the film in all its purity, just as the director, cinematographer et al. wanted it to be seen.
Last week I went to see Chronicle with my pal Jim Healy. The projector wasn’t perpendicular to the screen, so there was noticeable keystoning. The masking was set wrong, blocking off about a seventh of the picture area. And two little pink pixels were glowing in the middle of the northwest quadrant throughout the movie. I’m assuming that Chronicle’s director didn’t mandate these variants on his “vision.”
Jim went out to notify the staff, and two cadets came down to fiddle with the masking. The movie had already been playing in that house for several days. Maybe the masking hadn’t been changed for months? And of course the projector couldn’t be realigned on the fly. As for those pixels: There’s nothing to be done except buy a new piece of gear. Chapin Cutler of Boston Light & Sound [13] tells me that replacing the projector’s light engine runs around $12,000. At that price, there may be a lot of dead pixels hanging around a theatre near you.
Video to the max
Not so long ago, the difference was pitched as film versus video. That was the era of movies like The Celebration and Chuck and Buck. Then came high-definition video, which was still video but looking somewhat better (though not like film). But somehow, as if by magic, very-high-definition video, with some ability to mimic photochemical imagery, became digital cinema, or simply digital.
We have to follow that usage if we want to pinpoint what we’re talking about at this point in history. But damn it, let’s remember: We are still talking about video.
The Film Look
Ever since the days of “film vs. video,” we’ve been talking about the “film look.” What is it?
I’m far from offering a good definition. There are many film looks. You have orthochromatic and panchromatic black-and-white, nitrate vs. acetate vs. mylar, two-color and three-color Technicolor, Eastman vs. Fuji, and so on. But let’s stick just with projection. Is there a general quality of film projection that differentiates it from digital displays?
Some argue that flicker and the slight weaving of film in the projector are characteristic of the medium. Others point to qualities specific to photochemistry. Film has a greater color range than digital: billions of color shades rather than millions. Resolution is also different, although there’s a lot of disagreement about how different. A 35mm color negative film is said to approximate about 7000 lines of resolution, but by the time a color print is made, the display yields about 5000 lines—still a bit ahead of 4K digital. But each format has some blind spots. There’s a story [15] that the 70mm camera negative of The Sound of Music recorded a wayward hair sticking straight out on the top of Julie Andrew’s head. It wasn’t visible in release prints of the day, but a 4K scan of the negative revealed it.
Film fans point to the characteristic film shimmer, the sense that even static objects have a little bit of life to them. Roger Ebert writes [16]:
Film carries more color and tone gradations than the eye can perceive. It has characteristics such as a nearly imperceptible jiggle that I suspect makes deep areas of my brain more active in interpreting it. Those characteristics somehow make the movie seem to be going on instead of simply existing.
Watch fluffy clouds or a distant forest in a digital display, and you’ll see them hang there, dead as a postcard vista. In a film, clouds and trees pulsate and shift a little. Partly the film is capturing very slight movements of them in air, or the movement of light and air around them. In addition, the film itself endows them with that “nearly imperceptible jiggle” that our visual system detects.
How? Brian McKernan points out that the fixed array of pixels in a digital camera or projector creates a stable grid of image sites. But the image sites on a film frame are the sub-microscopic crystals embedded in the emulsion and activated by exposure to light. Those crystals are scattered densely throughout the film strip at random, and their arrangement varies from frame to frame. So the finest patterns of light registration tremble ever so slightly in the course of time, creating a soft pictorial vibrato.
Another source of the film look was suggested to me by Jeff Roth, Senior Vice-President of Post-Production at Focus Features. Jeff notes that a video chip is a flat surface, with the pixels activated by light patterns across the grid. (We forget that in the earliest stages, “digital” image capture is “analog”—that is, photographic—before it gets quantized and then digitized.) But a film strip has volume. It seems very thin to us, but light waves find a lot to explore in there. Light penetrates different layers of the emulsion: blue on top, then a yellow filter, then green, then red. The light rays leave traces of their passage through the layers. Joao S. de Oliveira puts it more laconically:
There is a certain aura in film that cannot exist in a digital image. . . . From the capture of a latent image, the micro-imperfections created by light on a perfect crystalline structure—a very three-dimensional process—to its conversion into a visible and permanent artefact, the latitude and resolution of film are incomparable to any other process available today to register moving images.
For example, shadows and highlights are captured “deeply.” Bright areas move into shadow gracefully. Similarly, film is far more tolerant of overexposure than digital recording is; even blown-out areas of the negative can be recovered. (In still photography, darkroom technique allows you to “burn in” an overexposed area.) The blown-out elements are still there, but in digital they’re gone forever.
Film shown on a projector maintains the film look captured on the stock: You’re just shining a light through it. We’ve all heard stories, however, of those DVD transfers that buff the image to enamel brightness and then use a software program to add grain. One archivist tells me of an early digital transfer of Sunset Blvd. that looked like it had been shot for HDTV.
But today carefully done digital transfers can preserve some of the film look. When my local theatres were transitioning, I saw Tinker Tailor Soldier Spy first on film, then on digital, and then again on film. Although the digital looked a little harder, I was surprised how much graininess it preserved. So it seems to me that some qualities of the film look can be retained in digital transfers.
Marching orders
George Lucas, at the 2005 annual convention and trade show of the National Association of Theatre Owners: “I’m sort of the digital penny that shows up every year to say, ‘Why haven’t you got these digital theatres yet?'” (Variety 17 March 2005).
“His point to theater owners was that 3D, which can bring in new audiences and justify higher ticket prices, is only possible after they make the switch to digital projection” (Hollywood Reporter 10 February 2012).
Premonitions
In summer of 1999, Godfrey Cheshire published a two-part article, “The Death of Film/ The Decay of Cinema.” It’s proven remarkably far-sighted.
He predicted that within a decade your multiplex theatre would contain “a glorified version of a home video projection system.” He predicted that the rate of adoption would be held back by costs. He predicted that the changeover would mostly benefit the major distributors, and that exhibitors would have to raise ticket and concession prices to cover investments. He predicted what is now called “alternative content”—sports, concerts, highbrow drama, live events—and correctly identified it as television outside the home. He predicted the preshow attractions that advertise not only products but TV shows and pop music. He predicted what is being seriously discussed in industry circles now: letting viewers snap open their “second screen” and call, text, check email, and surf the net during the show. And he predicted that distractions and bad manners in movie theatres would drive away viewers who want to pay attention.
People who want to watch serious movies that require concentration will do so at home, or perhaps in small, specialty theatres. People who want to hoot, holler, flip the bird and otherwise have a fun communal experience . . . will head down to the local enormoplex.
Godfrey goes on to make provocative points about the effects of digital technology on how movies are made as well. His essay should be prime reading for everyone involved in film culture—e.g., you.
WYSIWYG
I’ve mentioned the postcard effect that makes static objects just hang there. In less-than-2K digital displays, I see other artifacts, most of which I don’t know the terms for. Film has artifacts too, notably graininess, but I find the digital ones more off-putting. There’s a waterfall effect, when ripples rush down uniform surfaces. Sometimes I see diagonal striping from one corner to its opposite, an effect common on home and bar monitors. (I’m told it comes from interference from phones and the like.) On cheap DVDs, or commercial ones played on region-free machines, you can detect a weird pop-out effect, where the surfaces of different planes, usually marked by dark edge contours, detach themselves. The surfaces float up, wobbling out of alignment with their surroundings.
I am not hallucinating these things. When I point them out, others see them, and then, like me, they can’t ignore them. So I’ve stopped pointing them out, especially when a friend wants to show me his (always his) fancy home theatre. Why spoil their pleasure?
Same difference
Various positions on the split between film and digital (for want of a better term): I’ve held nearly all of them at various points, and sometimes simultaneously. I’ll confine myself, as usual, just to film-based projection and digital projection, and assuming minimal competence of staff in each domain. (Just because something’s shown in 35mm, that doesn’t mean it’s shown well.)
1. They’re not the same, just two different media. They’re like oil painting and etching. Both can coexist as vehicles for artists’ work.
2. They’re not the same, and digital is significantly worse than film. This was common in the pre-DCI era.
3. They’re not the same, and digital is significantly better than film. Expressed most vehemently by Robert Rodriguez and with some insistence by Michael Mann.
4. They’re not the same, and digital is mostly worse, but it’s good enough for certain purposes. Espoused by low-budget filmmakers the world over. Also embraced by exhibitors in developing countries, where even 1.3K is considered an improvement over what people have been getting.
5. They’re the same. This is the view held by most audiences. But just because viewers can’t detect differences doesn’t mean that the two platforms are equally good. Digital boosters maintain that we now have very savvy moviegoers who appreciate quality in image and sound. In my experience, people don’t notice when the picture is out of focus, when the lamp is too dim, when the surround channels aren’t turned on, when speakers are broken, and when spill light from EXIT signs washes out edges of the picture. (See Chronicle anecdote above.) As long as they can hear the dialogue and can make out the image, I believe, most viewers are happy.
‘Plex operators are notoriously indifferent to such niceties. In most houses, good enough is good enough. Teenage labor can maintain only so much.
Film/video
“The picture was nice and crisp.” “So much better than film.” “We showed a Blu-ray and it looked fine.”
I don’t trust people’s responses to such things unless the judgment is comparative. Show film and the digital program side by side and then judge. Or even show rival manufacturers’ DCI-compliant projectors side by side. I think you will see differences.
As they develop, new reproductive media improve in some dimensions but degrade on others. As the engineers tell us, there’s always a trade-off.
CD is more convenient than vinyl, but its clean, dry sound isn’t as “warm.” Mp3, even more convenient and portable, packs a sonic punch but is inferior in dynamics and detail [20] to CDs. Similarly, back in the 1990s, laserdiscs had to be handled more carefully than tape cassettes, and in playback they required interruptions as sides were flipped. But aficionados accepted these drawbacks because we believed that our optical discs looked and sounded much better than VHS. One well-known professor urged that classroom screenings could now dispense with film.
Now those laserdisc images would be laughed out of the room. Have a look at an image from the 1995 restoration of Disney’s Pinocchio. It’s taken from a transfer of the laserdisc to DVD-R. (You can’t grab a frame directly from a laserdisc.) In this and the others, I haven’t adjusted the raw image.
Actually, on a decent monitor, it looks better than this. Since you can’t grab a frame directly from a laserdisc, LD couldn’t stand up to home theatre projection today. The 2009 DVD and Blu-ray (below) are sharper.
Now compare the DVD with a dye-transfer Technicolor image from a 1950s 35mm print. There have been some gains and some losses in color range, shadow, and detail. For example, Stromboli’s trousers and the footlight area go very black, presumably because of the silver “key image” used for greater definition in the dye-transfer process. IB Tech restorations routinely bring out “hidden” color in such areas.
Which is best? You can take your pick, but you’re better able to choose when you’re not seeing one image in isolation.
Live/ Memorex
Of course side-by-side comparisons can fail when most viewers don’t notice even gross differences. In a course, I once showed a 16mm print of Night of the Living Dead, and a faculty friend came to the screening. (Yes, history profs can be horror fans.) In my followup lecture, I showed clips on VHS, dubbed from a VHS master. My friend came to the class for my talk. Afterward he swore that he couldn’t tell any difference between the film and the second-generation VHS tape.
This raises the fascinating question of changing perceptual frames of reference. My friend knew the film very well, and he’d watched it many times on VHS. Did he somehow see the 16 screening as just a bigger tape replay? Did none of its superiority register? Maybe not.
 [24]From 1915 to 1925, Thomas Edison demonstrated his Diamond Disc Phonograph by inviting audiences to compare live performances with recordings. His publicists came up with the celebrated Tone Tests. A singer on stage would stand by while the disc began to play. Abruptly the disc would be turned down and the singer would continue without missing a note. Then the singer would stop and the disc, now turned up, would pick up the thread of melody. Greg Milner writes of the first demonstration:
[24]From 1915 to 1925, Thomas Edison demonstrated his Diamond Disc Phonograph by inviting audiences to compare live performances with recordings. His publicists came up with the celebrated Tone Tests. A singer on stage would stand by while the disc began to play. Abruptly the disc would be turned down and the singer would continue without missing a note. Then the singer would stop and the disc, now turned up, would pick up the thread of melody. Greg Milner writes of the first demonstration:
The record continued playing, with [the contralto Christine] Miller onstage dipping in and out of it like a DJ. The audience cheered every time she stopped moving her lips and let the record sing for her.
At one point the lights went out, but the music continued. The audience could not tell when Miller stopped and the playback started.
The Tone Tests toured the world. According the publicity machine run by the Wizard of Menlo Park, millions of people witnessed them and no one could unerringly distinguish the performers from their recording.
Edison’s sound recording was acoustic, not electrical, and so it sounds hopelessly unrealistic to us today. (You can sample some tunes here [25].) And there’s some evidence, as Milner points out, that singers learned to imitate the squeezed quality of the recordings. But if the audiences were fairly regularly fooled, it suggests that our sense of what sounds, or looks, right, is both untrustworthy and changeable over history.
To some extent, what’s registered in such instances aren’t perceptions but preferences. Wholly inferior recording mechanisms can be favored because of taste. How else to explain the fact that young people prefer mp3 recordings to CDs, let alone vinyl records? It’s not just the convenience; the researcher, Jonathan Berger of Stanford University, hypothesizes that they like the “sizzle” of mp3 [26].
To some extent, we should expect that people who’ve watched DVDs from babyhood onward take the scrubbed, hard-edge imagery of video as the way that movies are supposed to look. Or perhaps still younger people prefer the rawer images they see on Web videos. Do they then see an Imax 70mm screening as just blown-up YouTube?
The epiphanic frame
Godard’s Éloge de l’amour: DVD framing vs. original 35mm framing.
Digital projection is already making distributors reluctant to rent films from their libraries, and film archives are likely to restrict circulation of their prints. When 35mm prints are unavailable, it will be difficult for us to perform certain kinds of film analysis. In order to discover things about staging, lighting, color, and cutting in films that originated on film, scholars have in the past worked directly with prints.
For example, I count frames to determine editing rhythms, and working from a digital copy isn’t reliable for such matters [29]. True, fewer than a dozen people in the world probably care about counting frames, so this seems like a trivial problem. But analysts also need to freeze a scene on an exact frame. For live-action film, that’s a record of an actual instant during shooting, a slice of time that really existed and serves to encapsulate something about a character, the situation, or the spatial dynamics of the scene. (Many examples here [30].) This is why my books, including the recent edition of Planet Hong Kong, rely almost entirely on frame grabs from 35mm prints.
Paolo Cherchi Usai suggests that for every shot there is an “epiphanic frame,” an instant that encapsulates the expressive force of that shot. Working with a film print, you can find it. On video, not necessarily.
Just as important, for films originating in 35mm, we can’t assume that a video copy will respect the color values or aspect ratio of the original. Often the only version available for study will be a DVD with adjusted color (see Pinocchio above) and in a different ratio. I’ve written enough about variations in aspect ratios in Godard [31] and Lang (here [32] and here [33]) to suggest that we need to be able to go back to 35mm for study purposes, at least for photographically-generated films. For digitally-originated films, researchers ought to be able to go back to the DCP as released, but that will be nearly impossible.
The analog cocoon
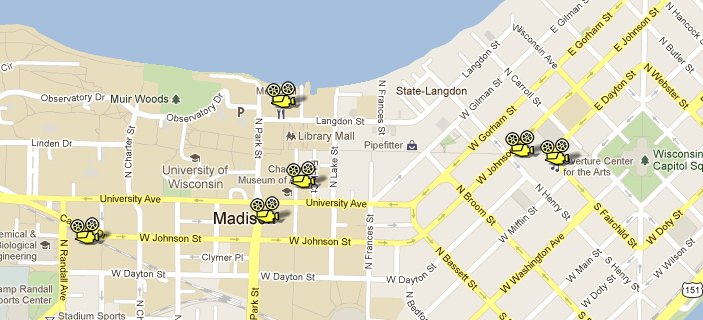
I began this series after realizing that in Madison I was living in a hothouse. As of this fall, apart from festival projections on DigiBeta or HDCam, I hadn’t seen more than a dozen digital commercial screenings in my life, and I think nearly all were 3D. Between film festivals, our Cinematheque, and screenings in our local movie houses, I was watching 35mm throughout 2011, the year of the big shift.
There are six noncommercial 35mm film venues within walking distance of my office at the corner of University Avenue and Park Street. And two of those venues still use carbon-arc lamps! Go here [35] for a fuller identification of these houses. Moreover, in my office sit two Steenbeck viewing machines, poised to be threaded up with 16mm or 35mm film. (“Ingestion” is not an option.)
But now I’ve woken up. We all conduct our educations in public, I suppose, but preparing this series has taught me a lot. I still don’t know as much as I’d like to, but at least, I now appreciate the riches around me.
I’m very lucky. It’s not over, either. The good news is that the future can’t really be predicted. Like everybody else, I need to adjust to what our digital Pandora has turned loose. But we can still hold on to hope.
This is the final entry in a series on digital film distribution and exhibition.
On the Pandora perplex, see Dora and Erwin Panofsky, Pandora’s Box: The Changing Aspects of a Mythical Symbol (Princeton University Press, 1956). The Wikipedia article on the lady [36] is also admirably detailed.
Godfrey Cheshire’s prophetic essay is apparently lost in the digital labyrinths of the New York Press. Godfrey tells me that he’s exploring ways to post it, so do continue to search for it. Another must-read assessment is on the TCM site. Pablo Kjolseth, Director of the International Film Series at the University of Colorado—Boulder, writes on “The End.” [37] See also Matt Zoller Seitz’s sensible take [38] on the announcement that Panavision has ceased manufacturing cameras. Some wide-ranging reflections are offered in Gerda Cammaer’s “Film: Another Death, Another Life.” [39]
Brian McKernan’s Digital Cinema: The Revolution in Cinematography, Postproduction, and Distribution [40] (MGraw-Hill, 2005) is the source of two of my quotations from George Lucas (pp. 31, 33) and some ideas about the film look (p. 67). My quotation from Greg Milner on the Tone Test comes from his Perfecting Sound Forever: An Aural History of Recorded Music [41] (Faber, 2009), 5.
NPR recently broadcast [20] a discussion of the differences, both acoustic and perceptual, among consumer audio formats. The show includes A/B comparisons. Thanks to Jeff Smith for the tip.
Thanks to Chapin Cutler, Jeff Roth, and Andrea Comiskey, who prepared the projector map of downtown Madison and the east end of the campus.
6 February 2012: This series has aroused some valuable commentary around the Net, just as more journalists are picking up on the broad story of how the conversion is working. Leah Churner has published a useful piece in the Village Voice [42] on digital projection, and Lincoln Spector has posted three essays at his blogsite, the last entry offering some suggestions [43] about how to preserve both film-based and digital-originated material.
“You get soft, Pandora will shit you out dead, with zero warning.”