Archive for the 'Film theory' Category
Her design for living
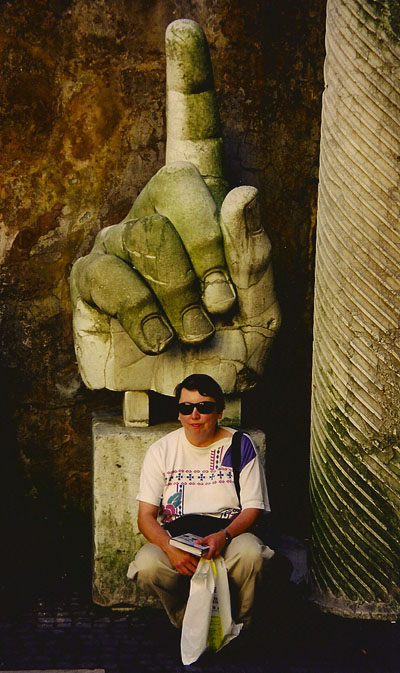
Kristin in Rome, 1997, in front of a “recent” hand from a colossal statue of Constantine. The Amarna statuary fragments she studies are twice as old.
DB here:
Kristin is in the spotlight today, and why not? She’s too modest to boast about all the good things coming her way, but I have no shame.
First, our web tsarina Meg Hamel recently installed, in the column on the left, Kristin’s 1985 book Exporting Entertainment: America in the World Film Market 1907-1934. It was never really available in the US and went out of print fairly quickly. Vito Adriaensens of Antwerp kindly scanned it to pdf and made it available for us. So we make it available to you. More about Exporting Entertainment later.
Second, Kristin is not only a film historian but a scholar of ancient Egyptian art, specifically of the Amarna period. (These are the years of Akhenaten and Nefertiti and their highly unsuccessful experiment in monotheism.) Every year she goes to Egypt to participate in an expedition that maps and excavates the city of Amarna. In recent years she’s focused on statuary, about which she’s given papers and published articles. Now we’ve learned that she has won a Sylvan C. Coleman and Pamela Coleman Memorial Fellowship to work in the Metropolitan Museum of Art’s collection for a month during the next academic year. So at some point then we’ll both be blogging from NYC. Think of the RKO Radio tower sending our signals to a tiny world below.
Third, she is about to turn 60, and in her honor the Communication Arts Department is sponsoring a day-long symposium. On 1 May we’ll be hosting Henry Jenkins, Charlie Keil, Janet Staiger, and Yuri Tsivian to give talks on topics related to her career interests. Kristin’s talk will survey her Egyptological work, with observations on how she has applied analytical methods she developed in her film research. You can get all the information about the event, as well as find places to stay in Madison, here.
Kristin came to Madison in 1973, a very good moment. Whatever you were interested in, from radical politics to chess to necromancy (there was a witchcraft paraphernalia shop off State Street), you could find plenty of people to obsess with you. Film was one such obsession.
The campus boasted about twenty registered film societies, some screening several shows a week. Fertile Valley, the Green Lantern, Wisconsin Film Society, Hal 2000, and many others came and went, showing 16mm films in big classrooms in those days before home video. Without the internet, publicity was executed through posters stapled to kiosks, and the fight for space could get rough. Posters were torn down or set on fire; a charred kiosk was a common sight. Another trick was to call up distributors and cancel your rivals’ bookings. One film-club macher reported that a competitor had cut his brake-lines.
What could you see? A sample is above. What it doesn’t show is that in an earlier weekend of February of 1975, your menu included Take the Money and Run, The Lovers, Ray’s The Adversary, Page of Madness, Fritz the Cat, The Ruling Class, Dovzhenko’s Shors, Chaney’s Hunchback of Notre Dame, American Graffiti, Wedding in Blood, Pat and Mike, Camille, Yojimbo, Faces, Days and Nights in the Forest, King of Hearts (a perennial), Sahara, The Fox, Day of the Jackal, Dumbo, Investigation of a Citizen above Suspicion, Slaughterhouse-Five, Mean Streets, A Fistful of Dollars, Triumph of the Will, and The Cow. Not counting the films we were showing in our courses.
In addition, there was the Wisconsin Center for Film and Theater Research, recently endowed with thousands of prints of classic Warners, RKO, and Monogram titles. (There were also TV shows, thousands of document files, and nearly two million still photos.) When Kristin got here she immediately signed up to watch all those items she had been dying to see. She suggested that the Center needed flatbed viewers to do justice to the collection, and director Tino Balio promptly bought some. Those Steenbecks are still in use.
 Out of the film societies and the WCFTR collection came The Velvet Light Trap, probably the most famous student film magazine in America. Today it’s an academic journal, though still edited by grad students. Back then it was more off-road, steered by cinephiles only loosely registered at the university. Using the documents and films in the WCFTR collection, they plunged into in-depth research into American studio cinema, and the result was a pioneering string of special-topics issues. When I go into a Parisian bookstore and say I’m from Madison, the owner’s eyes light up: Ah, oui, le Velvet Light Trap.
Out of the film societies and the WCFTR collection came The Velvet Light Trap, probably the most famous student film magazine in America. Today it’s an academic journal, though still edited by grad students. Back then it was more off-road, steered by cinephiles only loosely registered at the university. Using the documents and films in the WCFTR collection, they plunged into in-depth research into American studio cinema, and the result was a pioneering string of special-topics issues. When I go into a Parisian bookstore and say I’m from Madison, the owner’s eyes light up: Ah, oui, le Velvet Light Trap.
Above all there were the people. The department had only three film studies profs–Tino, Russell Merritt, and me–though eventually Jeanne Allen and Joe Anderson joined us. Posses of other experts were roaming the streets, running film societies, writing for The Daily Cardinal, authoring books, and editing the Light Trap. Who? Russell Campbell, John Davis, Susan Dalton, Tom Flinn, Tim Onosko, Gerry Perry, Danny Peary, Pat McGilligan, Mark Bergman, Sid Chatterjee, Richard Lippe, Harry Reed, Michael Wilmington, Joe McBride, Karyn Kay, Reid Rosefelt, Dean Kuehn, Samantha Coughlin, and Bill Banning. Most of these were undergraduates, but Maureen Turim and Diane Waldman and Douglas Gomery and Frank Scheide and Peter Lehman and Marilyn Campbell and Roxanne Glasberg and other grad students could be found hanging out with them. A great many of this crew went on to careers as writers, teachers, scholars, programmers, filmmakers, and film entrepreneurs.
Into the mix went film artists like Jim Benning, Bette Gordon, and Michelle Citron. There were film collectors too; one owned a 70mm print of 2001 and didn’t care that he could never screen it. ZAZ, aka the Zucker brothers and Jim Abrahams, were concocting Kentucky Fried Theater. Andrew Bergman had recently published We’re in the Money, and soon Werner Herzog would be in Plainfield waiting for Errol Morris to help him dig up Ed Gein’s grave. Set it all to the musical stylings of R. Cameron Monschein, who once led an orchestra the whole frenzied way through Intolerance. The 70s in Madison were more than disco and the oil embargo. (To catch up on some Mad City movie folk, go here.)
These young bravos worked with the same manic passion as today’s bloggers. The purpose wasn’t profit, but living in sin with the movies. Film society mavens drove to Chicago for 48-hour marathons mounted by distributors. Traditions and cults sprang up: Sam Fuller double features, noir weekends, hours of debates in programming committees. Why couldn’t Curtiz be seen as the equal of Hawks? Why weren’t more Siodmak Universals available for rental? Was Johnny Guitar the best movie ever made, or just one of the three best?
There was local pride as well. Nick Ray had come from Wisconsin, and so had Joseph Losey, not to mention Orson Welles (who claimed, however, that he was conceived in Buenos Aires and thus Latin American). During my job interview, Ray came to visit wearing an eye patch. It shifted from eye to eye as lighting conditions changed. When he showed a student how to set up a shot, he bent over the viewfinder and lifted the patch to peer in. Was he saving one eye just for shooting?
In the big world outside, modern film studies was emerging and incorporating theories coming from Paris and London. Partly in order to teach myself what was going on, I mounted courses centering on semiotics, structuralism, Russian Formalism, and Marxist/ feminist ideological critique.
Back in placid Iowa City, where Kristin got her MA in film studies and I my Ph.D., we grad students had seen our mission clearly. Steeped in theory, we pledged to make film studies something intellectually serious: a genuine research enterprise, not mere cinephilia. Madison was the perfect challenge. Here cinephilia was raised to the level of thermonuclear negotiation, backed with batteries of memos, scripts, and scenes from obscure B-pictures. Confronted with a maniacal film culture and a vast archive, Kristin and I realized that there was so much to know–so many films, so much historical context–that any theory might be killed by the right fact.
Watch a broad range of movies; look as closely as you can at the films and their proximate and pertinent contexts; build your generalizations with an eye on the details. Our aim became a mixture of analysis, historical research, and theories sensitively contoured to both. The noisy irreverence of Mad City, where a former SDS leader had just been elected mayor and city alders could be arrested for setting bonfires on Halloween, wouldn’t let you stay stuffy long.
Kristin’s work in film studies would be instantly recognizable to humanists studying the arts. Essentially, she tries to get to know a film as intimately as possible, in its formal dimensions–its use of plot and story, its manipulations of film technique. I suppose she’s best known for developing a perspective she called Neoformalism, an extension of ideas from the Russian Formalists. Armed with these theories, she has studied principles of narrative in Storytelling in the New Hollywood and Storytelling in Film and Television. She has probed film style in Herr Lubitsch Goes to Hollywood and her sections of The Classical Hollywood Cinema. And she has examined narrative and style together in her book on Eisenstein’s Ivan the Terrible and the essays in Breaking the Glass Armor.
Contrary to what commonsense understanding of “formalism” implies, she has always framed her questions about form and style in a historical context. She situates classic and contemporary Hollywood within changes in the film industry–the development of early storytelling out of theatre and literature, or current trends responding to franchises and tentpole films. For her, Lubitsch’s silent work links the older-style postwar German cinema and the more innovative techniques of Hollywood. She situates Tati, Ozu, Eisenstein, and other directors in the broad context of international developments, while keeping a focus on their unique uses of the film medium.
Perhaps her most ambitious accomplishment in this vein is her contribution to Film History: An Introduction. She wrote most of the book’s first half, and though I’m aware of the faults of my sections, I find hers splendid. After twenty years of research, she produced the most nuanced account we have yet seen of the international development of artistic trends in American and European silent film.
Kristin has also illuminated the history of the international film industry. Everybody knows that Hollywood dominates world film markets. The interesting question is: How did this happen? Exporting Entertainment provides some surprising answers by situating film traffic in the context of international trade and changing business strategies. One twist: the importance of the Latin American market. The book also opened up inquiry into “Film Europe,” a 1920s international trend that tried to block Hollywood’s power. In all, Exporting Entertainment led other researchers to pursue the question of film trade, and I was gratified to see that Sir David Puttnam’s diagnosis of the European film industry, Undeclared War, made use of Kristin’s research.
More recently, Kristin has turned her attention to the contemporary industry, the main result of which has been The Frodo Franchise, a study of how a tentpole trilogy and its ancillaries were made, marketed, and consumed. Her love of Tolkien and her respect for Peter Jackson’s desire to do LotR justice led her to study this massive enterprise as an example of moviemaking in the age of winning the weekend and satisfying fans on the internet. She maintains her Frodo Franchise blog on a wing of this site.
Most readers of this blog know Kristin as a film scholar. They may be surprised to learn that she also wrote a book on P. G. Wodehouse’s Bertie Wooster books. Wooster Proposes, Jeeves Disposes; or, Le Mot Juste is a remarkable piece of literary criticism. Here she shows how Wodehouse developed his own templates for plot structure and style. Again, the analysis is grounded in research–in this case, among Wodehouse’s papers. So assiduously did she plumb Plum that she became the official archivist of the Wodehouse estate. This is also, page for page, the funniest book she has yet written.
Her Egyptological work is no joke, though, and she has become one of the world’s experts on Amarna statues. She has published articles and given talks at the British Museum and other venues. Soon she’ll trek off for her ninth season at Amarna. There, joined by her collaborator, a curator at the Metropolitan, she’ll study the thousands of fragments that she’s registered in the workroom seen above. It’s preparation for a hefty tome on the statuary in the ancient city.
You can learn more about Kristin’s career here, in her own words. These are mine, and extravagant as they are, they don’t do justice to her searching intelligence, her persistent effort to answer hard questions, and her patience in putting up with my follies and delusions. You’d be welcome to visit her symposium and see her, and people who admire her, in action. While you’re here, you can watch a restored print of Design for Living, by one of her favorite directors, screening at our Cinematheque. In 35mm, of course. We can’t shame our heritage.
Poster design by Heather Heckman. Check out our Facebook page too.
Motion-capturing an Oscar
Kristin here:
Six years ago, when The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King was nominated for eleven Oscars, there was considerable grumbling over the fact that Andy Serkis was absent from the acting categories. Many argued that his pivotal role in creating Gollum, the first convincing human-like computer-generated character, should have qualified him for a nomination.
Now we’re seeing a similar debate over the lack of actor nominations for Avatar, with Zoe Saldana’s performance as Neytiri especially mentioned as unfairly overlooked. An intriguing article on the subject appeared in the Los Angeles Times a few days ago. In it, James Cameron expresses annoyance with both the Screen Actors Guild and the Academy for the lack of nominations for his actors:
I’m not interested in being an animator. . . . That’s what Pixar does. What I do is talk to actors. ‘Here’s a scene. Let’s see what you can come up with,’ and when I walk away at the end of the day, it’s done in my mind. In the actor’s mind, it’s done. There may be a whole team of animators to make sure what we’ve done is preserved, but that’s their problem. Their job is to use the actor’s performance as an absolute template without variance for what comes out the other end.
Because of innovations in the motion-capture process, including a tiny camera hung in front of an actor’s face to capture its every nuance, Cameron insists on calling the new technology “performance capture.” In some sense it may be true that the performance is preserved, but once the film runs through the theater projector, can the audience really tell what that “template” was like? I think not, and that’s why there is a reluctance to nominate these actors.
Where is the elusive boundary?
Don’t get me wrong. I’m not saying that Zoe Saldana and Andy Serkis aren’t fine performers or that their acting did not contribute enormously to the characters they played. Indeed, Serkis’ mo-cap contribution to the creation of Gollum was originally intended to be far more limited than it turned out to be. His facial expressions and gestures were so useful to the special-effects people that he was involved for a much longer period, and techniques to allow him to perform onset with the other actors were developed.
But however fine the original acting and however great the aid it provides to the special-effects team are, the process doesn’t stop there. To a notable degree other factors intervene between the actors’ original performances and the characters’ final appearance on the screen. Let’s do some comparisons, using the publicity images that the studios themselves considered good indications of how close the expressions of original actors were to those of their characters.
Take the widely circulated image of Saldana juxtaposed with Neytiri shown above. There are numerous differences. For a start, the filmmakers obviously needed to make the Na’vi look like an alien species. They didn’t just give them tails and make them blue and really tall. Human as the creatures seem in many ways, their faces have a subtle suggestion of large felines.
The effectiveness of Neytiri’s snarl has a lot to do with the fact that she has been given exaggeratedly long canine teeth. Moreover, given the changes in the shape of the face, the mouth is not as large proportionately to the entire head as Saldana’s is; the tongue is not nearly as prominent or noticeable. Both tongue and lips are blue as well. All of these features allow the teeth stand out more by contrast.
Na’vi ears are pointed, and some of the lobes are apparently pierced with a small dark disk in the hole. Saldana’s ears played no role in her performance, but the laid-back ears in the Neytiri image, mimicking those of an enraged animal, contribute considerably to the shot’s impact. I remember noticing them while watching the film.
The nose and the wrinkles on and above it have been considerably changed. Unlike human noses, those of the Na’vi are smaller at the bottom than at the top, somewhat resembling lions’ noses. The wrinkles seem to be derived from canine or feline faces as well, extending from the inner end of the eye and arcing down toward the tip of the nose. The human frown lines at the lower center of Saldana’s forehead are transformed into larger, longer, curved wrinkles at either side; these start between the eyebrows and move up and to the sides. There they get extended by the curved areas of darker blue that radiate across the upper forehead, so that the lines of anger seem to cover more of the face. I suspect that relatively little of what the actors did with their noses has survived the special-effects processing. (In the image below, even the shape of Saldana’s naso-labial folds has been slightly altered.)
The change in the eyes is particularly important. Saldana’s eyes have dark irises within which the pupil is barely, if at all, visible. Na’vi eyes are much larger, to begin with, and the irises are light in color, a sort of yellowish tan. The irises fill more of the visible part of the eye, so that the whites of Na’vi eyes are minimized. As a result, the black pupil stands out dramatically. In terms of color, the model seems to be cats’ eyes, though the pupils remain round rather than slits, to avoid making the Na’vi too alien looking. Since the nose has been widened at the top, the eyes are also further apart than on human faces. (The norm with humans is for the eyes to be separated by a distance roughly equal to the width of one eye.)
Even in a less dramatic scene, when Neytiri is relaxed and smiling, some of these differences remain. The pointed ear is not laid back, but it sticks out from the side of the head at an angle that draws the spectator’s attention and makes the human-shaped face seem exotic–especially given that the Na’vis’ ears are placed higher on the skull than human ears are: while the human ear canal is about even with the cheekbone, in the Na’vi it opens at mid-temple level. Although the points of the canine teeth are not visible in this image, the teeth remain prominent because of their bright whiteness against the blue skin. Though partially masked by the headgear, the vaguely feline nose still differs considerably from Saldana’s. In keeping with the extraordinary height of these beings, Saldana’s neck has also been lengthened.
Again, I’m not saying that Saldana and the other actors in Avatar did not contribute enormously to the believability of their characters or that they did not aid us to empathize with them. On the contrary, although the big blue creatures did seem very odd in the trailers and posters, I have to admit that they quickly came to seem like real characters. Their design’s balance of human and alien is remarkable. I did not continually think of them as walking combinations of numerous elaborate special effects. The new facial-capture system renders expressions very well, as the frame at the bottom shows.
What I’ve pointed out here with relation to Saldana’s contributions to the creation of Neytiri applies as well to Serkis’ earlier contributions to Gollum. In the comparison images below, similar changes were made.
While Serkis’ ears were covered, Gollum’s are pointed and prominent. Here, too, the eyes have been enlarged and made a light blue so that the pupils stand out. Where the actor’s teeth are straight and even, Gollum’s are pointed, crooked, and separated by gaps. The cheeks have been hollowed and the eyebrows arched nearly to a point near their outer ends. Crucially, the body has been made inhumanly skinny, with long bony legs and arms that are not apparent in this image. I suspect that some naive audience members believed that a real actor had played Gollum, but to most the scrawny figure was a guarantee that no human could have performed the role. (The very thin waists of the extraterrestrials in District 9 served as a similar guarantee that these were not just guys in monster suits à la Invaders from Mars.)
With all the kinds of changes that I’ve pointed out, how would Academy members be supposed to judge these performances were they to be nominated in the traditional acting categories? Where is the boundary between acting and special effects? Despite actors’ and directors’ claims to the contrary, the movements and expressions caught by performance capture are changed in many obvious and not so obvious ways. A close inspection of the comparison photos reveals the details of the transformation, but in watching the film, the viewer cannot necessarily gauge what sorts of changes were made. I can well imagine that actors like Meryl Streep or Jeff Bridges would be justified if they objected to competing in the same Oscar category as what are essentially hybrid performances seamlessly combining the original acting and the digital transformation.
Possible new categories
One way I can imagine actors competing for awards would be for the Academy to create a separate category for motion-capture performances. To judge such performances fairly, the members would have to see videos running the original performance side-by-side with the finished film. This method might allow them to make a reasonable assessment of what the actor truly contributed.
At this stage in the history of film technology, such a category seems unlikely. So far, not that many people have been spoken of as deserving an Oscar nomination for a mo-cap performance. Even Bill Nighy, who was widely praised for his turn as Davy Jones in the second Pirates of the Caribbean film, was not touted as a possible nominee—probably because his face was so thickly covered with tentacles and partly because comic fantasy films tend not to be Oscar bait. So far the argument has primarily been made for Serkis and Saldana. Plus if the Academy did take the approach of requiring the sort of comparison film I’ve suggested, it would be a difficult and expensive thing to produce. Who knows whether Academy voters would watch five such films?
Maybe, though, as performance capture becomes less expensive and more widely used, there will be enough actors to make up a separate category. We’ve seen the animated-feature category grow from three to five nominees this year, and the number of such films being made suggests that five will become the norm. Animated films and live-action ones heavily dependent on motion-capture are somewhat similar technically, so a new category makes some sense.
A simpler and more logical alternative might be to create a category specifically for vocal performances. As has been pointed out in relation to animated films, an actor who is heard but never seen onscreen could in principle be nominated. Such a thing has never happened, but it’s not against the rules. (It’s easy to imagine that it could have happened for a performance like Celeste Holm’s unseen narrating character in Letter to Three Wives.) But with animated-feature and motion-captured performances becoming more common, a best-vocals category seems to make sense. After all, Serkis and Saldana and others like them do speak their characters’ lines, and their voices are typically not altered or enhanced very much. The digital manipulation of sound still lags considerably behind that of images.
The idea is not exactly a new one. The Annies, the awards given out each year by the International Animated Film Society, has two “Vocal Acting” categories, one each for film and television.
Very similar motion-capture technology can be used to create films that most people would agree are animated (The Polar Express, A Christmas Carol) and others that embed animated characters in a live-action setting (The Lord of the Rings, Avatar). Creating an Oscar category for vocal acting in animation or motion-captured, effects-based performances would make sense.
If actors are not yet being recognized for motion-captured performances, the Academy has been quick to honor the top scientific and technological innovators of the area of motion capture. In 2004, when The Return of the King won its golden statuettes, the less celebrated Academy technical awards included one to the Weta Digital team for its new approach to the creation of Gollum. (The award was shared with ILM for its similar use of the technique in creating Jar Jar Binks.) This year, on February 20, the Academy honored a team that included one Weta Digital member for “the design and engineering of the Light Stage capture devices and the image-based facial rendering system developed for character relighting in motion pictures” which was used on Avatar and The Curious Case of Benjamin Button.
Despite fears that motion-capture may someday make directly photographed actors obsolete, there seems little chance of that happening. These techniques are fantastically expensive and are likely to remain that way for some time to come. There seems little point to using such elaborate technology to make an actor look like a real person when traditional cameras can do it so much more easily, so motion-capture performances seem suitable primarily for fantasy beings who cannot be as believably created in any other way.
Thanks to Cathy Root for calling my attention to the Los Angeles Times article.
February 25: See also Mark Harris’ essay in Entertainment Weekly. He argues that the ineffable qualities of an actor’s performance simply cannot be conveyed through motion-capture.
December 14, 2011: A member of the special-effects team at Weta Digital who worked on Avatar has sent me a comment on this entry: “Your Avatar article nails it–there were so many daily discussions about secondary ear and tail animation!”
May 18, 2014: Thanks to David Cairns for alerting me to two recent items on Cartoon Brew: Amid Amidi’s “Andy Serkis Does Everything, Animators Do Nothing, Says Andy Serkis,” which comments on an interview with Serkis on io9, and Amidi’s follow-up interview with Lord of the Rings animation supervisor Randall William Cook, which quite convincingly argues that the animators changed and extended Serkis’ performance.
Light is a law
DB here:
What do we see when we look around us? A world teeming with creatures and things. We tend to ignore what enables us to see all that: light. To a great extent, that bias is wired into our perceptual systems. An orange looks the same color to us in sunshine and in shade. But photograph it, and you’ll see that actually it throws off very different wavelengths in the two situations. We evolved, it seems, to mute all the variations in light we encounter. Psychologists call this “the primacy of object perception.”
It takes an artist to shift from the what to the how, to notice how different patterns of illumination can alter the shape and texture of an object. A painter, a photographer, and a cinematographer must learn to see light itself.
This was the core message of Steven Poster, an outstanding Director of Photography who came to visit Madison last weekend. Steven is probably most famous for working with Richard Kelly on Donnie Darko, Southland Tales, and The Box, but he has shot dozens of feature films, shorts, television movies, and pilots. He also has several Madison connections; he hung around the campus in his college years, saw Jules and Jim for the first time in the Memorial Union, and built a production house in Chicago with Mik Derks, who now works for Wisconsin Public Television.
Steven gave a workshop on cinematography that bristled with energy (five hours with only a brief break) and followed that with a screening of The Box, accompanied by a Q & A. Across a single packed Saturday, he took students and faculty on an adventure in seeing.
Seeing the light
Steven started as a still photographer at about age ten, and his ideas of visual design are very much allied with classic image-making. (He carried a Leica with him on his visit, and a display of his photos is currently mounted in a campus gallery.) He has a modernist bent too. He credits his years as a student at Southern Illinois University with introducing him to the ideas of the Bauhaus. He plunged more deeply into Bauhaus ideas at the Illinois Institute of Technology, where Mies van der Rohe and Moholy-Nagy taught.
Later in his career, he studied at the Los Angeles Art Center College of Design. A turning point in his understanding came in Charles Potts’ photography course, when Potts began the semester by announcing softly, “Light is a law.” Steven’s talk for us, he explained modestly, was a “profoundly simple subset” of Potts’ course. Put it another way: In the Bauhaus spirit, he showed how simple principles yield subtle results. Armed with only a white ball, a white cube, and a white cylinder, he gave us a tutorial in the delicate modulations of vision.
 There are, Steven suggested, basically only two kinds of light: direct and indirect (or diffuse). Sunshine yields direct light; a cloudy day yields diffuse light. And when light falls on an object, the encounter has five components. The object gains a highlight, the bright region that suggests the direction of the light source. The object also acquires a shadow area. Between the highlight and the shadow is the boundary, or core—an important hint about the quality of the source light. (If the core has a crisp edge, the light is hard; if the core is a mild transition, the light is softer.) The fourth component is the shadow that the object casts on another surface. Finally, there is the specular or incident highlight, a spot of reflected light within the lit region. A specular highlight is a cue for texture as well as shape and light source. As Steven spoke, I kept thinking about Hollis Frampton’s Lemon (1969), a masterfully simple demonstration of many of these principles: slightly changing light reveals a prototypical shape (what other things have the outline of a lemon?) and a surface that is both shiny and bumpy.
There are, Steven suggested, basically only two kinds of light: direct and indirect (or diffuse). Sunshine yields direct light; a cloudy day yields diffuse light. And when light falls on an object, the encounter has five components. The object gains a highlight, the bright region that suggests the direction of the light source. The object also acquires a shadow area. Between the highlight and the shadow is the boundary, or core—an important hint about the quality of the source light. (If the core has a crisp edge, the light is hard; if the core is a mild transition, the light is softer.) The fourth component is the shadow that the object casts on another surface. Finally, there is the specular or incident highlight, a spot of reflected light within the lit region. A specular highlight is a cue for texture as well as shape and light source. As Steven spoke, I kept thinking about Hollis Frampton’s Lemon (1969), a masterfully simple demonstration of many of these principles: slightly changing light reveals a prototypical shape (what other things have the outline of a lemon?) and a surface that is both shiny and bumpy.
By varying the type of light (direct or indirect) and the angle and distance of the source, Steven showed how these five components can be manipulated to bring out expressive qualities of the object. The cube, for example, can gain sharper contours through sidelong lighting, and illuminating the background can bring out its volume. Likewise, an object’s shadow area can be controlled through fill light—though Steven warned about over-filling, which can work against the precision provided by the key light. Another example is the way in which shooting glass or metal with pinpoint sources yields a scatter of specular reflections. If those aren’t wanted, as in some car commercials, the DP can use broad, diffuse illumination. This “liquid light” brings out contours through a softer gleam.
Of course a shot typically combines many objects, so the task of controlling how light hits them, and how they are arranged in relation to each other, becomes much more complicated. The shapes, textures, and emotional qualities of the elements have to be harmonized. “Elegant” was a word Steven used frequently: the composition, like the light, should be clear and well-defined. Needless to say, the result on screen can be grasped at a glance, but achieving such clarity needs painstaking control.
So seeing the light involves grasping everything around you, from landscapes and furniture to people’s faces and clothing, within the framework of highlights, shadow, core, and the like. This alone is enough to change your visual habits. But there’s more. By and large Steven made his adjustments without checking the monitor displaying what the camera was taking in. Standing almost anywhere, he could shift the light, tune the fill, and “wrap” the object, and on the monitor we could see the effect click into place. That skill demands more than a change in how to look at things. It’s an eye-body coordination that takes years of expert practice, an acquiescence to the law of light.
Behind the scenes
The discussion following this demo ranged across many aspects of cinematography, and Steven filled in abstract points with examples from his experience. My notes run to eleven pages, but this sampling should give you an idea of his stimulating presence.
*A problem-solution dynamic emerged in one shot in Donnie Darko, above. We need to see Donnie’s face when he catches up with Gretchen, but the day was sunny and at first the faces display somewhat harsh shadows. But when the couple move toward a kiss, the solution came from their clothes: Donnie’s shirt and Gretchen’s blouse provide softer bounce light on his face.
*Steven stressed the need for complete trust and frankness between director and DP. “I won’t take a job if the director won’t look me in the eye.” Once that bond is established, the DP’s job is to protect the director and work to fulfill his or her vision. “My job is to protect the director.”
*Filmmaking is an intensely physical job, and so two concerns have to be paramount: safety and health. “No film is worth getting somebody hurt,” Steven remarked, so he insists that every crew member is a safety officer, looking out for everyone’s well-being. At the same time, filmmaking demands stamina, discipline, and a clear head, so everyone needs to have a healthy regimen and cultivate a certain “inner life” that keeps job pressures in perspective.
*Steven had much to say about the video assist. He suggested that it has led to directors using more close views, because such shots read better on small monitors. (I made a similar suggestion in The Way Hollywood Tells It.) Steven fights what he calls the “loss of scope” on video displays by presenting the digital dailies in full-size projection, as in the film-based days. “It reminds everybody that we’re making a big movie,” and it encourages directors not to overuse close-ups.
*Steven is happy with the digital intermediate process. As a cinematographer who wants to control all aspects of the image, he welcomes all the adjustments he can make in postproduction, especially thanks to the Lustre grading program. “It’s like being back in the darkroom again.”
*On Donnie, a low-budget film, Kelly and Steven were forced to shoot the family dinner scenes in a single night. To save time, they used “block shooting.” For each actor, a basic setup was established and all the actor’s lines from both scenes were taken at one time. It was faster to have the actor change clothes for the later scene than to shift the camera position and relight the setups.
*Speaking of table scenes, they pose a lot of problems. Even Steven finds such scenes “the hardest.” “Where’s the [180-degree] line in this situation? I’ve seen fights break out on sets about it.”
*At one point Steven talked about prominent objects in a scene, such as candelabra and ketchup bottles. If you use symmetrical reverse shots, those objects can jump distractingly from one side of the screen to the other. Steven tries to make sure that such eye-catchers appear in only one of the setups, not both. The coffee cup in this scene of Southland Tales is hidden in the reverse angles.
Steven’s point reminded me that Ozu breaks this rule of thumb and playfully lets his objects jump around the frame from cut to cut. Indeed, he often rearranged the props to heighten this peripheral dance. In one scene of Late Autumn, the tabasco sauce bottle pivots consistently, but the French’s mustard jar changes position.
*Steven thinks that 3-D will succeed this time, chiefly because of the push for 3-D television. The technique probably won’t work for all stories, and the format poses some technical problems. But the software is getting better, and filmmakers, such as Cameron in Avatar, are starting to avoid the gimmick of obects thrusting out of the screen. It’s better, Steven thinks, to let the depth recede into the movie’s world, making the screen a window. I recalled that this was the strategy used in Coraline, Up, and other films of last year, so perhaps this will become the dominant way that 3-D will be used.
*Steven urged students to get broad general educations and not become movie nerds. They should study history, political science, art, and literature. He pointed out that Werner Herzog, his friend and neighbor, insists in his Rogue Film School that literary classics are the basis of a film education.
*Steven has long been an advocate of unionization. As President of Local 600 of the International Cinematographers Guild, he explained how the Guild now welcomes members, especially women and people of color. I thought it was salutary to give students a taste of the practicalities of professional life by explaining what the Guild had accomplished.
*Steven did additional photography on Blade Runner, and he learned a great deal while gaining deep respect for Jordan Cronenweth, DP on the movie. Steven rewatches the film often, and each time he finds something new. On the last pass, he saw that in the search of Kowalski’s apartment, flickering streaks of light coming from inside the desk drawer call attention to the newspaper that Deckard finds there.
Back in 1980-1982, when Kristin and I were doing research on The Classical Hollywood Cinema, we found that Charles G. Clarke, Linwood Dunn, William Hornbeck, Stanley Cortez, and other professionals whom we interviewed were intellectuals, eager to explain the ideas informing their creative decisions. Steven Poster’s career is another outstanding example of how theory and practice work together, often unobtrusively, to conjure up the enthralling world on screen. I can’t imagine a film researcher, or just a movie lover, not wanting to know filmmakers’ craft and the principles informing it. Once you’ve visit the kitchen, movies gain a whole new flavor.
This blog has intersected with primary Bauhaus shapes before. I discuss “the dinner-table conundrum” in the first few pages of Figures Traced in Light. One of the best analyses I’ve read on illumination in the visual arts is E. H. Gombrich’s “Light, Form and Texture in Fifteenth-Century Painting North and South of the Alps,” in The Heritage of Apelles: Studies in the Art of the Renaissance (Ithaca: Cornell University Pres, 1976), 19-35. For more on Ozu’s penchant for letting brightly lit objects jump around the composition, see this chapter of my Ozu and the Poetics of Cinema. The Lustre program was devised for The Lord of the Rings, and Kristin discusses its origins and influence in The Frodo Franchise, pp. 280-281.
Special thanks to Steven for his visit, the Wisconsin Union Directorate for arranging it, and Erik Gunneson, Joel Ninmann, Justin Daering, and J. J. Murphy for setting up the workshop.
Blade Runner.
2-4-6-8, whose lipdub do we appreciate?
DB here:
“There is really no such thing as Art. There are only artists.” I tend to interpret the disarming opening of Ernst Gombrich’s Story of Art as a protest against the idea that art has an essence that unfolds through history. Those of us in film studies can spot the heritage of this Hegelian idea in one standard story that is told about how editing came to be a dominant technique. According to the formula, editing is “essentially cinematic,” but this essence didn’t reveal itself immediately. It emerged in phases, thanks to the insights of brilliant creators (Méliès, Porter, Griffith, the Russians). Understanding cinema’s history, according to this view, means tracking how film revealed its inherent nature.
In saying that Art doesn’t exist, Gombrich isn’t trying for an elaborate philosophical argument. He’s suggesting a way of understanding art history. His abrupt two sentences suggest that the historian shouldn’t presume that any art has an essence, a secret core that dictates how its history unfolds. He proposes seeing continuity and change in what we call the arts as springing from concrete activities of individuals and groups. Cinema’s history then becomes an account of the creative decisions of filmmakers faced with particular demands and problems. Some of those decisions can converge across the community. The results are trends, such as the increased use of editing, which have real consequences but which are aren’t the result of some secret, essential process.
Once we try to analyze art in terms of what creative communities have sought and achieved, we can ask how artists tend to behave. Across his career, Gombrich stressed that artists are sensitive to their circumstances. What tasks are assigned to the artists? What are the traditions and current fashions? What are the tastes of patrons? What constraints are put on the art-maker? How is art taught? How can the ambitious artist achieve distinction? (“What is there for me to do?”) What are the tricks of the trade at any moment? How do artists borrow from one another? And how might they compete with one another?
We often underrate competition as a stimulus to creativity. Gombrich notes that “the Dutch masters vied with each other, trying to outdo their rivals in certain accomplishments.”
Stressing the relevance of traditions not only implies an attention to the way art feeds on art; it should also make us aware of the cumulative nature of any such skill. What happens in such a hothouse atmosphere is that ambition leads to competition and frequently also to specialization, as it notoriously did in Holland.
In cinema, we might profitably consider competition as one source of the diversity within a tradition. I suspect that the great Soviet directors of the 1920s not only shared ideas but also competed by testing ever farther-out ideas about cutting. They also specialized in the manner Gombrich suggests by cultivating particular effects or genres: Pudovkin’s character-driven pathos, Eisenstein’s dynamic crowd effects, Kuleshov’s exploration of popular genres, Dovzhenko’s boldly elliptical storytelling. I’ve often thought that the Warner Bros. cartoonists probably walked out of the first screenings of Disney’s Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs (1937) with heavy hearts. How could they match that? They didn’t try. Instead, they cultivated something quite different: raucous, cynical, high-speed farce. And today, doesn’t it seem likely that Avatar took its final form as an effort to go beyond the CGI efforts of earlier directors—to prove that the director of Terminator II and The Abyss was still the King of the World of SPFX?
Boys and their long-take toys
One of the most visible arenas of cinematic competition is the sustained tracking shot following several characters. It requires a sort of virtuosity, or at least logistical skill, in coordinating everything—the speed and consistency of the movement, the passage of people in and out of the shot, the consistency of framing and focus, the timing of new information. Once somebody has executed such a shot, the challenge is thrown down to others. Can you make yours longer or fancier?
In The Way Hollywood Tells It, I noted that Brian De Palma saw just such a challenge in Raging Bull’s famous tracking shot from the dressing room to the prizefight ring. “I thought I was pretty good at doing those kind of shots, but when I saw that I said, ‘Whoa!’ And that’s when I started using those very complicated shots with the Steadicam.” This sort of schoolyard one-upsmanship is probably what Christine Vachon had in mind when she called the single-take scene a “macho” choice.
There are some longer-term trends as well. Elaborate takes used at the start of a film can be found in the 1930s and 1940s (e.g., Ride the Pink Horse, 1947), but Welles laid down a clear marker in the opening of Touch of Evil (1957). Thereafter, starting a movie with an intricate, sustained camera movement became something of an emblem of directorial ambition.
Already, however, Dreyer, Ophuls, and Mizoguchi had used long takes, usually with camera movement, as building blocks of a film’s overall design. With Rope (1948) Hitchcock raised the possibility of making an entire film out of even fewer such shots, an initiative continued by the Hungarian Miklós Jancsó, who developed the choreography of such shots to a new level by incorporating crowds, zooms, and rack-focus passages. Béla Tarr and Gus van Sant have been modern exponents of the technique.
It was probably inevitable that somebody would try to make a feature-length film consisting of a single moving shot. Josh Becker’s Running Time (1997) renders a heist in what purports to be one take; there are cuts, but they’re pretty well disguised. Sokurov’s Russian Ark (2002; above) uses video technology to create a feature out of one genuine take, “a single breath” as he called it. At the same time, Sokurov added the condition that the shot would be an exploration of a labyrinthine space, in this case the Hermitage, and a trip through different eras of Russian history.
My lipdub can lick your lipdub
Perhaps it was Russian Ark, or maybe just TV walk-and-talks, that inspired the recent cycle of single-take video lipdubs. In these the camera moves through a locale and picks up one person after another, all lip-synching the soundtrack. September’s massively popular lipdub from l’Université de Quebec à Montréal may have furnished the prototype. In the US, a pair of current examples neatly illustrates how borrowing and competition among moviemakers can yield intriguing results.
As you probably know, Shorecrest High School in Shoreline, Washington, mounted a very complicated lipdub—one take coasting through the school, picking up dozens of teens lipsynching to Outkast’s “Hey Ya!” before they all assemble in a theatre for a final shout-out. There are some somersaults too, which make any movie better. It is here.
But high school rivalries resurfaced. Shorewood High School, traditionally at odds with Shorecrest in sports and band, struck back with a lipdub of Hall and Oates’ “You Make My Dreams Come True.” The new entry raised the stakes by shooting the action backward, somersaults included. Here it is.
There’s no shortage of backwards videos, but the Shorewood clip plays in clever ways with our biases in perceiving movement. Because we’re wired to grasp motion as advancing in time, we can’t easily reconstruct the actual movement that the figures executed. After seeing the film many times, I still found it hard to visualize the actual progression of the shoot, starting from the assembled crowd and ending on the young woman running backward to the vehicle that pulls away. (A forward version is here.) Moreover, both forward and backward motion have an uncanny symmetry, so that it’s hard to detect the latter except through subtle cues like the way garments fall or a gait with a special snap. Even the moments that flaunt the reverse-motion device, such as things originally tossed down into the frame, seem instead to fly up and into the hands of bystanders.
The stakes have been raised. What will Shorecrest come up with? A radical change of angle? (An entire lipdub done from a very high or low vantage point?) Or maybe a more demanding location? (With spring coming, I’d vote for a miniature-golf course.) Anyhow, my imagination is more limited than the filmmakers’. All that matters for my purposes is that the very fact of competition gave birth to a pair of ingenious and sprightly movies.
If you’re thinking that I wrote this simply to give everyone who Googles “Gombrich lipdup” at least one result, you miss my point. Just as Gombrich was never shy about using advertising imagery and children’s drawings to illustrate some basic principles of visual psychology, so we ought to notice any examples that vividly show how artists strategize in order to create something new within a tradition. Which is to say: Yes, I consider the young filmmakers of Shorecrest and Shorewood artists. Why not?
Gombrich’s essay on Dutch painting first appeared as “Mysteries of Dutch Painting,” New York Review of Books 30, 17 (10 November 1983), 13-17. It is reprinted in his Reflections on the History of Art (London: Phaidon, 1987). Shorewood has supplied a sort of making-of bonus here, with some more challenges to Shorecrest thrown in. To see the genre coopted by politicians (who apparently can’t get all their cohorts together in the same space), go here (thanks to Camilla Lugan). Maybe US politicos could get some more support if they tried bopping like this? They could hardly look sillier than they do already.
PS 31 January: Jason Mittell of Middlebury College has alerted me to his students’ lively long-take lipdub on the virtues of recycling.
PPS 1 February: Yogesh Raut writes that another historical precedent for the dueling lipdubs would be one older than the Quebec one I cited.
In your recent entry on lipdub videos you cite a video made in 2009 by students in Quebec as “the prototype.” I think a more likely candidate is this video made by a company called Connected Ventures and first uploaded in April 2007:
While there have obviously been a ton of similar videos made since then, I think the folks at CV (who I have no connection with) probably deserve a little hat tip as innovators. Of course, it’s possible that they were copying someone else, but in general they seem to be recognized as the starters of the craze (see here, for example).
It’s good to learn this. There are probably other precedents as well. I’d just say that a prototype need not be the first work in a genre tradition; rather, it’s a fully developed, typical instance. We take Little Caesar as a prototypical gangster film, but it’s not the first. The Connected Ventures project is indeed a single take, and it follows various people lip-synching. But it doesn’t explore a building in a targeted way, making the revelation of new space add visual variety, and the walking characters seldom pass us from group to group in tight choreography (it relies more on loose pans). Like other early efforts in a genre, it seems simpler and rougher than later entries. I suppose that supports my point that competition can spur filmmakers to surpass their peers; it seems that later lipdub adepts took up the challenge to make the single take more intricate. Still, I should probably have called the Canadian video “a prototype” rather than “the prototype.” Many thanks to Yogesh for calling my attention to a particularly early work in the genre.
2 May 2010: Tonight’s Simpsons episode, “To Surveille, with Love,” opens with a single-take lipdub pastiche/ parody showing Springfield’s citizens moving to Ke$ha’s Tik Tok video. Next morning: It’s here.