Archive for the 'Film comments' Category
Manual labors
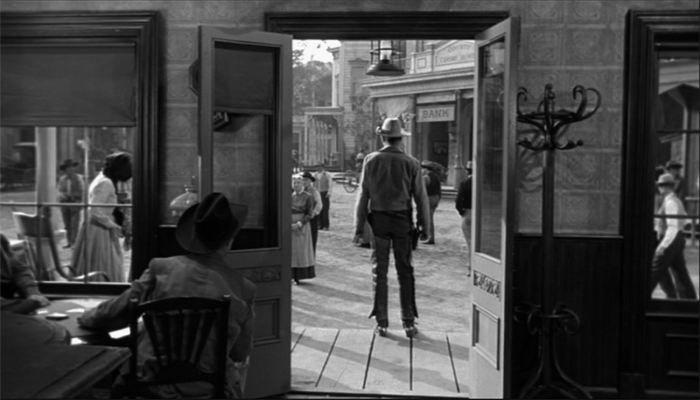
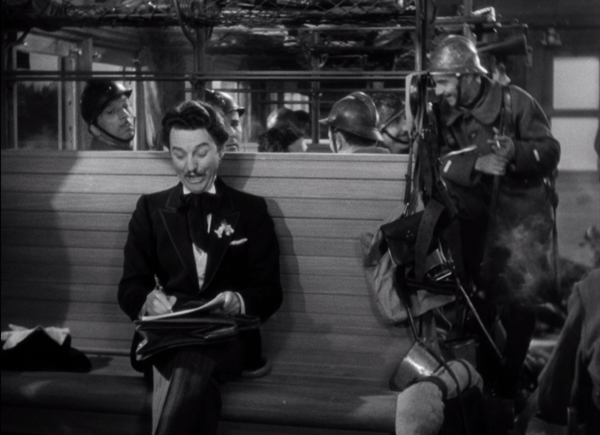
The Tin Star (1957).
DB here:
Type “screenplay writing” into Amazon and you’ll get over 6000 hits. Some of those books will be biographies of writers or screenplays of released films. But there’s still a huge number of DIY books with titles like How to Write a Movie in 21 Days and Writing Screenplays That Sell. A lot of people are apparently only one manual away from a finished script.
Screenplay manuals trigger suspicion. Can it really be that easy? Wouldn’t this be a paradise for grifters? A successful writer would hardly share trade secrets, so most of these books would be written by losers and wannabes. And if you read enough of the manuals, you’ll see the inevitable repetition of banalities. Make your protagonist “relatable.” Keep the conflicts going. Try for a twist.
Reading through them can be mind-numbing, but if you’re interested in how filmmakers tell stories, sometimes they can open up your thinking. Or so I’ll argue.
DIY scripting
The tide of manuals rose during the 1910s, when the emerging American studio system was seeking talent. The tide subsided between the 1930s and the 1960s, when screenwriting was contract labor in that system. But as filmmaking turned “independent,” ambitious people outside the industry could break in with an original script. Manuals, most famously Syd Field’s Screenplay (1979), began to pop up, and the market for how-to books expanded. Field’s book remains in vigorous circulation today, among many competitors.
 What should film researchers do with the manuals? Skepticism is warranted. Literary scholars don’t typically consider advice books and columns in The Writer to be significant bodies of evidence. But in other fields, manuals are valuable documents. Art historians study manuals devoted to composition, color preparation, and other techniques. Musicologists find evidence in primers on sonatas and fugues. At bottom, when we want to study craft practices, we look for any evidence we can find about the range of choices available within a tradition.
What should film researchers do with the manuals? Skepticism is warranted. Literary scholars don’t typically consider advice books and columns in The Writer to be significant bodies of evidence. But in other fields, manuals are valuable documents. Art historians study manuals devoted to composition, color preparation, and other techniques. Musicologists find evidence in primers on sonatas and fugues. At bottom, when we want to study craft practices, we look for any evidence we can find about the range of choices available within a tradition.
If your research touches on matters of style, you may find it illuminating to study the way practitioners pick solutions to practical problems. Which is to say that the manuals can point us toward norms. Norms are, I’ve argued, like a menu of more and less preferred options for treating the material. We developed this angle of inquiry in our Classical Hollywood Cinema, and now it seems well-established that the manuals can sometimes point us toward tacit norms of construction or visual style. For examples of how this can work, see Kristin’s Storytelling in the New Hollywood, my The Way Hollywood Tells It, and Patrick Keating’s Hollywood Lighting from the Silent Era to Film Noir. Many of our blog entries have also explored these paths. With screenplay manuals, we just have to be particularly careful to distinguish valuable data from bilge–which means checking the manual’s precept against many films.
And we shouldn’t expect the manuals or professional journals to identify every normalized device. For example, screenwriters now love to start scenes with friends greeting one another with “Hey” and “Hey,” but I doubt that there’s an explicit decision to avoid “Hi.” Similarly, I’ve never found anyone writing in the classic era who mentions the common Hollywood device of the double plot, with one line of action devoted to a goal-oriented activity and another, interdependent one devoted to heterosexual romance. Even the rather elaborate 180-degree classical editing system wasn’t apparently spelled out anywhere; it was learned by imitation and reinforced because it was economical and efficient. People can learn and follow rules that are simply taken for granted as “the way we do things.”
I think my soft spot for the manuals owes a good deal to my long-term affection for one item I saw in a 1913 guide. J. Berg Esinwein and Arthur Leeds’ Writing the Photoplay contains a lot of hints about standard practices of the period, but one of their diagrams changed my basic attitude about silent film technique.
The cinematic stage
In the late 1990s I became interested in the norms of scene staging in early film. I assumed that filmmakers had to call attention to story action without benefit of cutting to closer views, so I tried itemizing in a straightforward way the staging choices that could guide the viewer’s eye.
Many of the choices could be called “theatrical.” Lighting and setting could emphasize an actor’s gesture or facial expression. Performance factors operated as well, especially since actors were typically facing the viewer. Filmmakers’ reliance on these cues seemed to confirm the standard impression that early film was less “cinematic” than what came later.
Yet there were purely pictorial factors in play as well–notably, the placement of figures in the overall image. Composition of the frame, as in painting (and theatre) played a crucial role in guiding our attention.
There was something else. I was fascinated, for reasons sketched here, with the depth that many scenes in “tableau cinema” displayed. Here’s a quick example from Alfred Machin’s Le Diamant noir (1913). The entire film is available from the Belgian Cinematek.
The young secretary Luc is accused of stealing the missing diamond. He protests his innocence, but the accusation will force him to leave the country.
All the cues I’ve mentioned are at work here: centered figure placement, frontally facing characters, attention-grabbing gesture, favorable setting (the rear doorway and curtains highlight Luc’s arrival), and so on. In addition, a tunnel of information bores through the frame, leading from the distance and culminating in action in the foreground.
But this tunnel couldn’t fairly be considered “theatrical,” since if the action were played on a stage, not all viewers would have the optimal view presented in the shot. Most of the audience simply couldn’t see this alignment of players. Theatrical staging tends to be lateral and fairly shallow, so that people sitting in different seats can all see the scene. A good part of planning a stage production is calculating sightlines. But in film, there’s only one sightline, that of the camera lens.
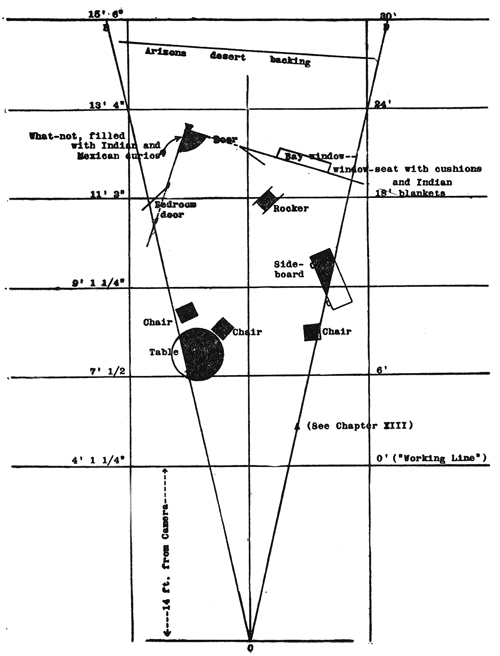
We tend to see film space as cubical, a room with a missing fourth wall. Actually, the playing space–what Esenwein and Leeds call “the photoplay stage”–is a tapering pyramid whose point touches the lens. Because the film image captures an optical projection, the space is narrow but deep. The authors provide a diagram of a scene to explain. (For the sake of clarity, I’ve removed some of their annotations; the full version is on p. 160 of their book.) The effect is of wedge shape that carves into what would be the wide space of a theatre scene.
In 1910s cinema, the camera lens (at point 0) is assumed to be some distance from the “working line,” the layer of maximal attention. For some filmmakers this line was nine or eleven feet from the camera, rather than the 14 feet assumed here. The rest of the space falls away in the distance, and depending on the lens and lighting used, these areas can be in more or less sharp focus. Filmmakers of the period often marked out the pyramid on the studio floor so that actors would know when they were out of shot.
This diagram makes explicit many of our taken-for-granted notions about film space. Someone moving closer to the camera gets larger, of course; but the figure also blocks out more and more of the background as the pyramid narrows. An actor’s forward movement on the stage inevitably takes up a small part of the overall area, but in cinema forward-thrusting action can dominate the frame.
Just as important, the fixity of the lens makes it possible to choreograph actors with a precision impossible in theatre. Luc’s confrontation with his employer in my second frame gives him pride of place, but once he’s slumped at the foreground desk, he can move his head and clear the central zone for us to see a servant waiting in the distance. In tableau cinema, staging isn’t just “blocking.” It’s blocking and revealing, a constant flow of information presented through shifting arrays of figures. I provide several examples in the lecture “How Motion Pictures Became the Movies.”
My heightened awareness of the visual pyramid made me more sensitive to staging in all periods of cinema. We might think that after the tableau cinema period, when filmmakers became more dependent on editing, their reliance on the “photoplay stage” vanished. But of course every shot, close or distant, presents us with the visual pyramid, and some filmmakers relied upon it to provide the graduated layers of space in an edited sequence. Specifically, the “deep focus” that became a favored technique of 1940s cinema around the world would seem a modernization of the principles of the 1910s recognition of wedge-shaped playing space. Here’s an outrageous example from Hawks’ Ball of Fire (1941), shot by Gregg Toland after Citizen Kane.
Less punchy imagery than this suggest that the skills of 1910s staging were never really lost. Another passage from Ball of Fire brings Professor Potts to the foreground in a way reminiscent of Machin’s film. Of course it helps when Gary Cooper is the tallest galoot in the scene.
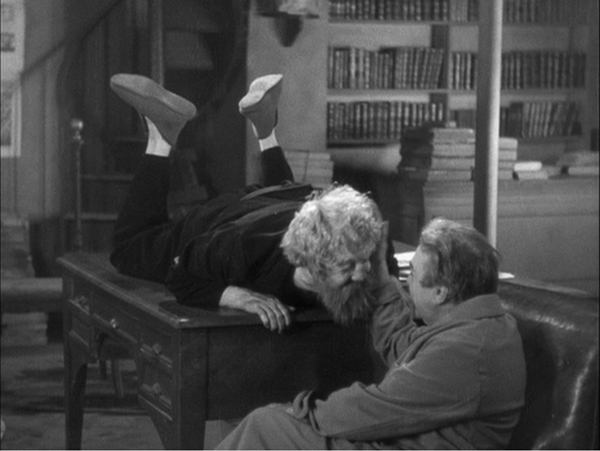
Cinema’s visual pyramid becomes almost sadistic at the climax of Anthony Mann’s Tin Star (1957). The young sheriff stops a lynching by shaming the town bully. The bully responds as you’d expect, but not in the sort of shot you’d expect.
Mann’s earlier films had experimented with foregrounds thrusting out at the viewer, but this sequence carries the idea to a limit. The actor collapses against the camera, inadvertently proving how lines of cinematic sight converge at the lens–that is, at our viewpoint. Try doing this on the stage!
This entry is more a piece of intellectual autobiography than anything else. I doubt many other people were opened up to the intricacies of staging thanks to a diagram in an old book. I mean it just as an example of how reading manuals can set you thinking about the expressive possibilities of film, and taking you in directions that you couldn’t predict.
More recently, in writing Perplexing Plots, I poked into manuals for would-be fiction writers, an area that literary historians seem to have neglected. These manuals yielded a lot of principles of what people thought went into good storytelling. In particular, I found that while Henry James and Joseph Conrad were making arguments about viewpoint and chronology, so too were people writing how-to manuals. The books indicated a new awareness of these techniques among writers aiming at mass audiences.
Terry Bailey surveys and analyzes early manuals in “Normatizing the silent drama: Photoplay manuals of the 1910s and early 1920s,” Journal of Screenwriting 5, 2 (Jun 2014), p. 209 – 224. For a comprehensive overview, see Steven Price, A History of the Screenplay.
The main argument here is developed in On the History of Film Style and Figures Traced in Light: On Cinematic Staging.
Ball of Fire (1941).
The reader is warned
Where the Crawdads Sing (2022; production still).
DB here:
When I wasn’t paying attention, along came Where the Crawdads Sing (2018 novel, 2022 film). The book was a huge bestseller, while the movie version was panned by critics but attracted a good-sized audience. It exemplifies how strategies of nonlinear storytelling have become deeply woven into mainstream entertainment.
It has an investigation plot, structured around the trial of “swamp girl” Kya, who’s accused of the murder of her boyfriend Chase in the marshlands of North Carolina. Through flashbacks we learn of her desperate childhood, as she is abandoned by her family and castigated by the townfolk. She learns to live alone in the family cabin and fills her days drawing precise images of the natural life around her. A well-meaning young man teaches her to read but he too he leaves her to struggle alone. Soon she meets Chase, a charming good-for-nothing. Is his fall from a swamp tower an accident, or did someone push him? A kindly local attorney takes her case, and the plot climaxes first in the jury’s verdict and then a twist that reveals what happened at the scene of the crime.
We’re so used to plots like this that we may forget how nonlinear they are. In the Crawdads film, the court investigation probes the circumstances of Chase’s death, but the flashbacks, instead of illustrating stages of the crime, supply Kya’s life story in chronological order. They contextualize the long-range causes of her dilemma. Accordingly, they’re narrated by her in voice-over. Titles supply the relevant timeline, dating episodes from 1963 through to 1970, the year of the trial.
All of these strategies have become familiar from a century of popular storytelling. A court case as an occasion to visit the past goes back at least to Elmer Rice’s On Trial (1914), although the play dramatizes testimony in a way that Crawdads doesn’t. (Its flashbacks, more boldly, are in reverse order.) The crosscutting of past and present has become common to explain (or obfuscate) ongoing story events. Tying us to a character’s viewpoint and letting the character’s voice narrate what we see is likewise a standard device in modern media. And of course an investigation plot is inherently nonlinear. The task is for someone to uncover the “hidden story” of what occurred in the past.
Simple though it is, Where the Crawdads Sing shows just how pervasive devices associated with mystery and detective fiction have become in mainstream storytelling. Told chronologically, the story would be a biography of Kya (and would presumably have to reveal how Chase died). Instead, the film becomes what Wikipedia calls “a coming-of-age murder mystery.”
By splitting the chronological story into two parts and interweaving them, manipulating viewpoint, and rearranging temporal order, the film tries to achieve interest and suspense. We know from the start that Chase is dead, so we watch every scene with him for clues as to what could have caused it. Tension gets amplified as time passes, when the shifts between the courtroom drama and the day of Chase’s death come faster and faster. These effects couldn’t be achieved with a linear layout.
One of the major points of Perplexing Plots is to remind us just how much of popular entertainment trades on narrative strategies forged in the big genre of mystery. Once we’re reminded, we can ask: How did those strategies get implemented? How did audiences come to understand and enjoy these highly artificial ways of telling stories?
I promise not to keep plugging the book on this blog, but allow me one more notice. A Q and A with me has been published on the Columbia University Press site. It tries to inform any souls whom fate has cast my way about the argument of the book. You may find it of interest.
I’m taking the occasion to note some features of the book not advertised elsewhere. Perhaps they too would appeal to you, especially if you’re interested in some of the choices a writer has to make.
Obscure is as obscure does
First, the book draws on some unorthodox sources. Most obviously, I tried to canvass obscure novels and plays that are now forgotten but that did try some experiments with nonlinear storytelling. Who’d expect a reverse-chronology play in 1921, years before Pinter’s Betrayal (1978)? A 1919 play anticipates Rear Window by offering testimony from a deaf witness and then a blind one. The first version plays out on stage in pantomime, the second in a completely dark setting. A 1936 novel offers a string of conflicting character viewpoints on a single situation, revising and correcting previous accounts, well in advance of Herman Diaz’s recent novel Trust. A 1919 play depicts a woman in different aspects, as seen by the people who know her. These instances of what we now call “complex narrative” belong to what literary scholars have called “the great unread,” the thousands of pieces of fiction and drama that haven’t become canonical through enduring popularity or academic favor.
Other precedents are dimly recalled but seldom revisited, such as George M. Cohan’s play Seven Keys to Baldpate (1913) and W. R. Burnett’s Goodbye to the Past (1934). How many people would be aware of Kaufman and Hart’s reverse-chronology play Merrily We Roll Along (1934) if Stephen Sondheim hadn’t turned it into a musical? The very existence of these marginal works helps support the premise that a lot of what we consider innovative today has broad historical roots. They just aren’t as vivid to our memory as more recent instances. But fifty years from now, will many viewers remember contemporary experiments like Go (1999) and Shimmer Lake (2017)?
The book uses other unorthodox sources. I put craft technique at the center, and so it makes sense to look at the principles that writers of fiction and drama were using. Of necessity I review the emerging idea of the “art novel” at the end of the nineteenth century, with Henry James as spokesman for this trend. In addition, unlike most mainstream literary histories, Perplexing Plots consults contemporary manuals for aspiring writers. These books are the progenitors of all those how-to-get-published books that fill Amazon today, and they reveal a surprising sophistication. Manuals allow me to show how a new self-consciousness about linearity, particularly point of view, became central to popular writing as a craft. For example, a now-forgotten critic, Clayton Hamilton, epitomizes the willingness of ambitious writers to try out new possibilities.
So one choice I made was to search out fiction, drama, and films that have fallen into obscurity. Another was to look at the nuts and bolts of plotting, as practitioners seemed to be conceiving it. These help explain why many novels and plays, major and minor, began tinkering with innovative storytelling.
Time as space
From Karen Loves TV: “Contemplations on the Whiteboard.”
A nonlinear plot has a geometrical feel to it, so one way of thinking about it is to envision it as a table or spreadsheet. Where the Crawdads Sing could be laid out in a double-column table, with each present-time scene aligned with the past sequence that follows it.
 There are more complex possibilities as well. Griffith’s Intolerance (1916) would constitute a four-column layout displaying each different historical epoch. Perhaps this is one sense of the term that came into use in the 1940s: “spatial form” as a description of unorthodox narratives. The principle is akin to the whiteboard “season arcs” and “episode outlines” used in writers’ rooms to lay out story lines threading through a film or TV series.
There are more complex possibilities as well. Griffith’s Intolerance (1916) would constitute a four-column layout displaying each different historical epoch. Perhaps this is one sense of the term that came into use in the 1940s: “spatial form” as a description of unorthodox narratives. The principle is akin to the whiteboard “season arcs” and “episode outlines” used in writers’ rooms to lay out story lines threading through a film or TV series.
Novelists have long made use of such charts. The most famous is that prepared by James Joyce for Ulysses, where each chapter is assigned a different color, body organ, and so on. This was published in Stuart Gilbert’s 1930 book. Because the rights to reproduction are obscure, we regrettably didn’t include it my book. No surprise, though, it’s available online.
I did, however, obtain rights to a less-known but rather brilliant table included in Anthony Berkeley’s Poisoned Chocolates Case (1929). Later chapters of Perplexing Plots use tables of my own devising to clarify the complicated layout of Richard Stark’s Parker novels, the chapter structures of Tarantino films, and the alternating viewpoints and time schemes of Gone Girl. There will always be readers who complain that these tables are just academic filigree, but I believe that they help us appreciate the intricate interplay of time, segmentation, and viewpoint. They show how precise the narrative architecture of mystery fiction can be.
To spoil or not to spoil
For decades, criticism of mystery fiction has labored under the expectation that a critic must not reveal a story’s ending, or the story’s central deception. In journalistic reviews of literature and film, the writer is expected to keep such things secret, but even academic studies of crime fiction put pressure on the critic to maintain the surprise of whodunit and howdunit.
 But this limits our ability to study plot mechanics. I chose to preserve the secrets of the books, plays, and films as much as I could (as with my Crawdads sketch). Still, when the analysis demanded exposure of the “hidden story,” I did so. This doesn’t result in a lot of spoilers because some canonical texts, like The Maltese Falcon, Laura, and The Big Sleep, are very well-known. But I lay out some strategies of deception in novels by Christie and Sayers and films such as Gone Girl and The Sixth Sense. There really was no other way to show points of narrative craft at work in them, particularly the fine grain of writing or filming that shapes our response. I regret most exposing the central feint of Ira Levin’s novel A Kiss Before Dying, so readers who aren’t familiar with the book may want to read it before reading my account. Otherwise, I can only cite the title of one of Carter Dickson’s trickiest novels.
But this limits our ability to study plot mechanics. I chose to preserve the secrets of the books, plays, and films as much as I could (as with my Crawdads sketch). Still, when the analysis demanded exposure of the “hidden story,” I did so. This doesn’t result in a lot of spoilers because some canonical texts, like The Maltese Falcon, Laura, and The Big Sleep, are very well-known. But I lay out some strategies of deception in novels by Christie and Sayers and films such as Gone Girl and The Sixth Sense. There really was no other way to show points of narrative craft at work in them, particularly the fine grain of writing or filming that shapes our response. I regret most exposing the central feint of Ira Levin’s novel A Kiss Before Dying, so readers who aren’t familiar with the book may want to read it before reading my account. Otherwise, I can only cite the title of one of Carter Dickson’s trickiest novels.
Part of the justification for hiding the legerdemain is the doctrine of “fair play.” I trace how this idea emerged in the Golden Age of detective fiction, when a story was treated as a game of wits between author and reader. In principle, nothing necessary to the solution of the puzzle should be withheld, though it can be disguised or hinted at. One thing I learned in writing the book is that fair play has become a premise of most duplicitous narratives in any genre, from horror to science fiction. People don’t realize how much the maneuvers of Psycho and Arrival owe to the belief that the audience should in principle be able to go back and see how we were misled. (We can do this with the “missing clue” in Crawdads as well.)
Fair play encourages the author to be ingenious and entices the audience to appreciate artifice-driven construction. Both effects are legacies of classic detective fiction, and they still shape much mainstream entertainment.
Thanks to Maritza Herrera-Diaz of Columbia University Press for arranging for the Q & A published on the Press site.
The phrase “the great unread” is used by Margaret Cohen in The Sentimental Education of the Novel (Princeton, 1999) and cited in Franco Moretti, “The Slaughterhouse of Literature,” MLQ: Modern Language Quarterly 61, 1 (March 2000), 208.
As I’ve indicated in an earlier entry, Martin Edwards’ The Life of Crime is a vast and entertaining survey of the history of mystery fiction. It was crucial help to me in writing Perplexing Plots. Martin, an advance reader of the manuscript, has been kind enough to discuss my book on his blog.
Other early responses to the book have been encouraging. Michael Casey reviewed it for The Boulder Weekly, and Doug Holm discussed it on KBOO on his show Film at 11. My thanks to both these commenters.
Psycho (1960): Misdirection and fair play all in one shot.
GLASS ONION: Multiplying mysteries
Glass Onion (2022).
DB here:
Rian Johnson’s enthusiasm for classic mysteries made it inevitable that I’d get interested in writing about Knives Out. Although I merely allude to the film in Perplexing Plots, I devoted a blog entry to it. While thinking about a follow-up on Glass Onion, I began a rewarding correspondence with Jason Mittell, adroit blogger and author of Complex TV: The Poetics of Contemporary Television Storytelling. Today’s entry reflects my thoughts after this exchange of ideas.
Despite the near-universal acclaim received by Glass Onion, it didn’t whet my interest as much as its predecessor. It’s a little too campy and overproduced for my taste. But Johnson’s ingenuity in manipulating conventions of the Golden Age detective stories by Christie, Sayers et al. makes it ripe for the sort of analysis I try out in the book. So here we go.
Needless to say, there are spoilers for Glass Onion and Knives Out. But I bet you’ve seen both films.
Tools of the trade
Knives Out.
Plotting a story is a craft, and it has some essential tools. There is, for instance, the ordering of events. Will you present events in linear story sequence, or will you arrange them in a nonchronological pattern? You can’t avoid choosing one or the other or some combination of the two.
There’s also the matter of viewpoint. Will you attach the audience to what a single character experiences, or will you roam among several characters?
And there’s segmentation: How will you break your plot up into chunks? In literature, we have sentences, paragraphs, and chapters. In theatre, scenes and acts. In film, scenes and sequences (and sometimes reels or chapters). Even one-shot movies have moments of pause or shifts of viewpoint that mark off phases of the action.
These are forced choices that every storyteller must face. It’s these three–linearity, viewpoint, and segmentation–that Perplexing Plots relies on in order to analyze both mainstream storytelling and mystery fiction.
In addition, the craft requires the audience to be engaged–at least interested, at most emotionally moved. You must choose whether to get your audience to empathize with certain characters or to keep the characters remote and unknowable. Do you want to arouse anger, approval, or some other emotion? You must decide how the choices of linearity, viewpoint, and segmentation can trigger these responses.
For example, your plot can usually build empathy for a character by showing incidents in which that person is treated unfairly. Those actions will be more intense if they’re rendered from the character’s viewpoint. This is what Rian Johnson does in Knives Out when he shows Marta persecuted by the vindictive Thrombey family, and then exploited by Hugh. The disparity in power (David vs Goliath) heightens our sense of indignation and makes the finale seem to be poetic justice (My house/my rules).
Some emotions depend directly on choices about chronological sequence. If your plot signals that some past events are significant but then doesn’t reveal them, you’re using linearity to create curiosity. If the plot summons up anticipations about particular future story events, you create a degree of suspense. If your plot introduces an event that momentarily seems out of keeping with the linear story, you can summon up surprise.
Each of these “cognitive emotions” (“cognitive” because they rely on knowledge and belief) is shaped by perspective and segmentation. Creating curiosity, suspense, and surprise depends on viewpoint: each character will have different states of knowledge about the course of events. In Knives Out, Hugh Drysdale is not suffering curiosity about whodunit: he knows he did it. But because we’re attached to Marta and detective Benoît Blanc, we share their state of uncertainty–and suspense about what may come.
Similarly, decisions about segmentation will often be made based on the cognitive emotions in play. You might end a book chapter or a play’s act or a film’s scene on a note of curiosity (“Then whose body is in that grave?”), suspense (the stalker draws near the prey), or surprise (“I’m your father!”).
As my examples from Knives Out suggest, the three tools I’ve picked out have special purposes in a mystery story. Perhaps one reason for the enduring popularity of mystery as a narrative device is its ingenious use of linearity, viewpoint, and segmentation to build cognitive emotions, especially curiosity. But a perennial problem of the genre is to build up other emotions. So we need sympathetic detectives and victims along with unsympathetic suspects, cops, and gangsters to engage us. Some writers also vamp up the suspense factor by putting the investigator in danger, a hallmark of hardboiled stories and domestic psychological thrillers (Rinehart, Eberhart, and their modern counterparts). Perplexing Plots traces some of these creative options through the history of mystery fiction.
Hidden stories
Evil Under the Sun (1982).
The mystery plot centered on an investigation tells two partial and overlapping stories. The investigation is presented as an effort to disclose what happened in the past, an incomplete and puzzling chain of events. Writers in the 1920s started to call this “the hidden story.”
In the standard case, the detective reveals those events and makes a single continuous story out of everything. The revelation is typically saved for the climax of the present-time story line, with the detective explaining the missing events in a summing-up. Often all the suspects are gathered and the detective reviews the evidence before presenting the solution to the puzzle. In other instances, the detective may confide the results to a friend or an official.
The summing-up is often a verbal performance, with the detective recounting the hidden story. A classic example is the Christie novel Evil Under the Sun (1941), in which Hercule Poirot explains to the assembled suspects how the crime was committed. To make this scene less monotonous onscreen, filmmakers often illustrate the hidden story by brief flashbacks, as in the 1982 film adaptation of the Christie novel. Johnson employs this strategy in Knives Out, supplying quick shots of how Hugh’s scheme was enacted.
The detective’s explanation often rests on yet another hidden story line: parts of the investigation we didn’t see. Very often the detective operates backstage, pursuing clues we didn’t notice. Sherlock Holmes absents himself for a good stretch of The Hound of the Baskervilles, leaving Watson to explore the mystery of the Moors. Only later do we learn what Holmes was up to. Rex Stout’s Nero Wolfe likes to keep his assistant Archie, our narrator, ignorant of information that he asks other operatives to dig up for him.
As a result, in the final summing-up, the detective’s filling in of the plot may include telling us of his offstage busywork. Again, that may be rendered on film as flashbacks to make sure the audience appreciates the sleuth’s cunning. These might include flashbacks that replay parts of the inquiry, but from a new viewpoint. In the film version of Evil Under the Sun, we see Poirot’s first visit to the cliff’s edge.
But the replay during his summing up expands this by dwelling on the vertiginous effects he feels.
In Glass Onion, Johnson finds a fresh way to treat the detective’s offstage machinations, and that depends, as you’d expect, on exploiting the three basic tools.
A package of puzzles
The most obvious innovation involves segmentation. Johnson splits his plot into two almost exactly equal halves. The first, running about seventy minutes, is a more or less complete classic puzzle.
Tech magnate Miles Bron invites his old friends for a weekend party on his private island. Their affinities go back to their days hanging out together in a pub, the Glass Onion. A fifth friend, Cassandra “Andi” Brand, co-founded Alpha with Miles, but he cheated her out of her share when she refused to expand into questionable paths. Andi shows up at the island to join what Miles calls the Disruptors. There’s Claire, an ambitious politician; Lionel, a scientist working for Miles on a new energy source; Birdie, a scatty fashionista; and Duke, an aggrieved online spokesman for patriarchy. Famous detective Benoît Blanc joins the party, even though it’s unclear who invited him.
These characters are introduced in a rapid opening sequence that shuttles us from one to the other as each gets a puzzle box. Crosscutting and split-screen imagery yield an omniscient narration; we seem to know everything. Johnson points out the expositional advantages: “The box gave it an element of fun, a spine, and a way for all the characters to be on speaker phone solving the mystery of how to open it together, so you see the dynamics between them in real time.”
Then we see a so-far unnamed woman receive a box and break it open. Finally we find Blanc himself, stewing in boredom in his bathtub. In all, a shifting spotlight has introduced us to all but one of the major characters.
Once the group assembles on the pier to board the ship that will take them to Miles’s island, the narration narrows its range and concentrates mostly on Blanc’s reactions.
In what follows, Blanc observes the others, occasionally trailing them, and asks questions about their pasts. By and large, this half of the film will be attached to him, though sometimes the narration will stray briefly to others (chiefly to give each a motive for killing Miles). The first half assigns Blanc the conventional role of curious investigator.
Miles has planned a murder game in which he’s the victim, but that puzzle collapses the first evening when Blanc solves it instantly. A new crime emerges: Duke abruptly dies of poisoning. And soon someone shoots Andi. Blanc gathers the suspects and announces he nearly has a solution. “It’s time I finished this. . . . Only one person can tell us who killed Cassandra Brand.”
In the spirit of Golden Age whodunits, Johnson has poured out a cascade of mysteries, big and small. Who sent Blanc the extra box? Why did Andi, still smarting from her courtroom loss to Miles, show up at his party? When Duke died, he drank from Miles’s glass, so who was trying to kill Miles? Duke’s pistol mysteriously disappears; who took it? The same person who killed Andi?
Johnson’s narration can be both reliable and unreliable. During the drinking session a quick long shot reveals that Miles forced Duke to take the poisoned glass. This is a daring gesture toward Fair Play (that some of us noticed), but Johnson will try to cancel our impression. He will soon offer a lying replay to blot this out.
To further swerve suspicion from Miles, Johnson uses viewpoint. We see Miles reacting in shock to a POV image of the fallen glass with his name on it, as if he were just realizing he, not Duke, was the target.
Of course he’s faking, but by privileging his viewpoint in order to underscore his reaction Johnson suggests he’s innocent. Cheating? Not really, just misleading. Johnson gives with one hand, takes away with the other–as his mentor Agatha Christie does in prose (as I try to show in the book).
Fugue states
So Blanc has a lot to explain. But instead of continuing the traditional summing-up denouement, Johnson pauses and in effect replays the first half of the film by concentrating on the detective’s offstage activities.
Turns out, Blanc has been much busier and less naive than he seemed in the first part. A conventional assembly-of-the-suspects climax would have included explanations of his scheming, but Johnson daringly fleshes these out to forty minutes that annotate scenes that we’ve already witnessed. In this play with linearity, gaps are filled, and new information is provided.
The second part starts with a young woman delivering the wrecked puzzle box to Blanc. She is not Andi but her twin sister Helen. (Yes, Johnson unblushingly taps the convention of false identity, with twins no less.) Andi is dead, killed by carbon-dioxide fumes in her garage. Helen suspects not suicide but murder and gives Blanc an account of Andi’s career through flashbacks. These bursts of nonlinearity skip freely from the gang’s youthful days to Miles’s cheating of Andi.
Moved, Blanc coaxes Helen to impersonate Andi and go to the party, as if accepting Miles’s invitation. (Blanc will convince the authorities to suppress news of Andi’s death for a time.) The two of them form a team to investigate Miles’s posse and find Andi’s killer. So now two puzzles–who sent Blanc the box? why did Andi, or rather “Andi,” show up at the island?–are set to rest. Just as important, as Knives Out focused our empathy on Marta, this second half gives us Helen as a sympathetic figure, so the puzzle element is enhanced by emotion.
Blanc’s saunters around the compound are now replayed as more purposeful, while “Andi” stands revealed not simply as an intruder but a snoop. Some scenes are only sampled, while others are fleshed out through viewpoint shifts. In addition, the narration offers hypothetical flashbacks when Helen and Blanc play with the possibilities of who might have killed Andi.
Driving the second part is the search for a crucial piece of evidence that would have won Andi the court case: the Glass Onion napkin on which she jotted down a plan for the company. After the trial she found it and told Miles’s circle; her murder was triggered by the killer’s plan to recover the napkin. When Helen finds it, she can confront Miles. In a final twist, it’s revealed that the bullet that apparently killed Helen was blocked by Andi’s diary. At her return to the group, Blanc can launch a proper summing-up and denunciation of the guilty.
The annotated replays run about 37 minutes. These incidents could have been much more concisely presented as part of Blanc’s explanation, but as Jason Mittell pointed out to me, this new plot structure gives the second part a dynamic we associate with another genre: a film tracing a big con, like The Sting. There’s a pleasure in seeing how scenes we interpreted one way now stand out as manipulated by Blanc and Helen.
Blanc’s explanations, and Miles’s efforts to block it, take another sixteen minutes. Eventually the Disruptors unite to support Andi, and Miles is facing murder charges. The film ends not with a shot of the complacent Blanc but of the righteous Helen/Andi, the co-protagonist of the second part, a figure of vengeance and vindication.
Replays that amplify and contextualize scenes we’ve already seen are common in mysteries and other genres. Johnson’s originality comes in building one long segment out of such replays. To make it work he relies on our memory of the chronological order of previous scenes to create a double-entry plot structure in which the detective’s backstage scheming revises and corrects our perception of the core action. You could lay out the action on a table of the sort I occasionally resort to in Perplexing Plots.
Johnson’s pride in folding the second half of the film back over the first part is teased when a guest at Birdie’s party explains the fugue that Miles has embedded in the puzzle box. “A fugue is a beautiful musical puzzle based on just one tune. If you layer this tune on top of itself, it starts to change and turns into a beautiful new structure.”
Johnson’s virtuoso play with segmentation has a place in the mystery story tradition; Perplexing Plots reviews several Golden Age examples. (One somewhat similar novel is Richard Hull’s Excellent Intentions of 1938.) You can imagine a version of Glass Onion that attaches its viewpoint to Blanc and Andi from the start, with the “infiltration” strategy of something like Notorious (1946) or Mission: Impossible II (2000). But that wouldn’t engage us through its gamelike, self-consciously artificiality. No film I can recall has so thoroughly routed the offstage activities of the detective onto a track parallel to that of the unfolding crime. Creating a double-column plot like this shows not only the cleverness of design demanded by mystery stories but something I stress throughout the book: the eager drive of popular storytelling toward innovation and novelty–within familiar boundaries.
Thanks to Jason Mittell for a stimulating correspondence and to Erik Gunneson and Peter Sengstock for further suggestions.
Johnson discusses how he shaped the guest assembly on the pier around Blanc’s viewpoint in “Notes on a Scene” in Vanity Fair. A lengthy piece in Vulture explains some of the citations and in-jokes in the film.
P.S. 13 January: Thanks to Antti Alanen and Fiona Pleasance for correction of two names!
Glass Onion.
The ten best films of … 1932
Shanghai Express.
Kristin here–
The year draws to a close, and the internet abounds with lists by professional critics, educated fans, and clueless people proffering opinions on the ten best films of 2022. David and I avoid this custom, but fifteen years ago I stumbled into a habit of listing the ten best films of ninety years ago. Such films have by now stood the test of time, and they have one enormous advantage: no one is speculating about many Oscar nominations each will get.
Back in the day, only two of the films on my list got nominated at all, and those two collected a total of three Oscars. (For a hint at one winner, see the image at the top. He will feature prominently in this year’s list.)
These ten films are of course my own choices, and for those who disagree, they are quite welcome to make their own lists.
As usual, my list is a mix of very familiar titles and some not so familiar ones. My hope is to call attention to unfamiliar films that are well worth a look. Actually this year nine of the films should be familiar to any serious film student or fan, but the tenth is a masterpiece that deserves to be rescued from obscurity.
Most historians seem to agree that 1932 was the year when Hollywood emerged from the difficult transition to sound and made polished movies that regained the fluidity of cinematography, staging, and editing that had been lost to some extent. In The Classical Hollywood Cinema, Janet Staiger, David, and I proposed that the transitional period lasted from 1928 to 1931.
The same was not internationally true, however. My list contains one silent film, since the Japanese industry went through a considerably longer transition. No wonder that half of this year’s list atypically consists of Hollywood movies.
Previous entries can be found here: 1917, 1918, 1919, 1920, 1921, 1922, 1923, 1924, 1925, 1926, 1927, 1928, 1929, 1930, and 1931.
As usual, I’ll try to point readers toward the best available Blu-rays or DVDs. Those who prefer streaming should be able to find these titles for themselves. David and I prefer discs, at least for important films. With the decline of access t0 35mm and 16mm prints, studying films closely has become more dependent on discs (which also still have better quality images than streaming). Eventually, with streaming the only option obtaining frame grabs of the sort that illustrate these entries, close film analysis will become extremely difficult.
Hooray for Hollywood!
Trouble in Paradise
Ernst Lubitsch is one of the best-loved of film directors, both within the film industry and among cinephiles. I was lucky enough to be invited to teach a one-month summer course at the University of Stockholm on any topic related to silent cinema. I jumped at the chance to follow up on a vaguely planned project on Lubitsch, specifically a comparison of his German and American silent films. The course became a book, Herr Lubitsch Goes to Hollywood, now out of print but available through open access.
Trouble in Paradise is widely considered his best film, though I would say that at least Lady Windermere’s Fan and The Shop around the Corner are equal to it and others are not far behind.
The witty script is a model of sophisticated humor, and the casting is perfect. Herbert Marshall for a change got to play the suave hero, a dazzlingly expert crook who teams up romantically with Miriam Hopkins, his match as a wily pickpocket. In this 82-minute film, their hilarious courtship in a Venice hotel runs for a remarkable 17 minutes as they top each other in stealing things from each other, with her returning his watch and his flaunting her garter:
It doesn’t seem a minute too long. Essence of Lubitsch.
Kay Francis provides the potential trouble that threatens their idyllic life of thievery; she’s a beyond-wealthy owner of perfumery Colet & Cie. (see bottom)–so wealthy that she doesn’t really mind that her “secretary” may be a famous criminal worming his way into her confidence. Charles Ruggles and especially Edward Everett Horton provide hilarity as hopeless suitors wooing Madame Colet.
The comedy is played out in shining art-deco sets (above), lit with perfect three-point Hollywood lighting. As I demonstrate in my book, Lubitsch moved effortlessly from being the master of German silent film style to being the master of Hollywood style. It shows in every aspect of Trouble in Paradise.
The Criterion Collection DVD is still available.
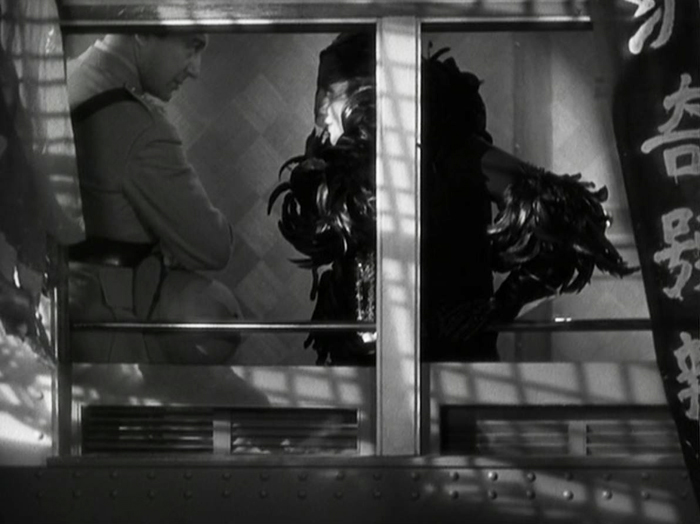
Shanghai Express
The Josef von Sternberg/Marlene Dietrich teaming. The Blue Angel, featured on my list in 1930. The pair famously made a series of Hollywood films together, all built around the glamor of Dietrich. For me, the best of the bunch is Shanghai Express. It has a stronger script than the others, being set on a train traveling from Beijing to Shanghai during the Chinese Civil War (which had started in 1927). The device of a group on a journey lends the film both unity and suspense. It’s basically a thriller with a romance included. There are more characters than in some of the other Dietrich films, the typical bunch of eccentrics for such journey-plots lending interest, humor, and pathos along the way. Dietrich’s character is strong and likeable. She pursues the man she loves, but on her own terms while he stands around cluelessly keeping his upper lip stiff.
Then there are the incredible visuals. The set design is even more dense than usual for a von Sternberg film. The train windows, both exterior (top) and interior (above) are used brilliantly, and the rebel headquarters where the group is trapped for much of the second half has hanging gauze and stairways that create a complete contrast with the train scenes.
And the Oscar mentioned above went to … Lee Garmes, whose five films in 1932 also included Scarface (see below). Apart from his photography of the settings, he shows off with with other dazzling moments, including an extraordinary tracking shot following an official along the crowded platform for nearly the entire length of the train.
Needless to say, the glamor shots of Dietrich are among the most beautiful ever (Garmes also shot Morocco and Dishonored).
In general, the train station scenes are spectacular and give a remarkable sense of authenticity. Speaking of which, all the extras and minor characters seem to be played by Chinese, or at least Asian people. Anna May Wong has a prominent role as Hui Fei. Whether casting Warner Oland as the rebel leader Henry Chang would count today as “whitewashing” is up for debate. He was born in Sweden but claimed some Mongolian ancestry (so far unproven).
The Criterion Collection has the set of six Dietrich/von Sternberg films on Blu-ray and DVD. (My frames were pulled from an old TCM DVD pairing the film with Dishonored. TCM now offers Shanghai Express by itself on DVD or Blu-ray.)
A Farewell to Arms
The second Oscar-winner of the three mentioned above was Charles Lang, for his cinematography of A Farewell to Arms. (The film also won the third Oscar, for sound recording.)
Frank Borzage has been a staple of these ten-best lists, with Lazybones (1925), 7th Heaven (1927), and Lucky Star (1929). This may be his final appearance in these year-end lists, with growing competition internationally.
A Farewell to Arms adapts Hemingway’s novel of World War I. Gary Cooper plays Frederic, an ambulance medic who spends his spare time drinking and visiting brothels with his friend, Italian Dr. Rinaldi (Adophe Menjou). He meets Catherine, a nurse, at a party, and they fall immediately in love, succumbing to passion under the assumption that war’s uncertainties may not give them another chance. Becoming pregnant, Catherine departs for Switzerland to have the baby, but her letters to Frederic and his to her, are returned to sender. Frederic risks a firing squad by deserting and desperately trying to find her.
Like Trouble in Paradise and other 1932 films, A Farewell to Arms benefited from the fact that the self-censorship Hollywood studios instituted under the Production Code (aka the “Hays code”) in 1933 was not yet in force. The result is a grittier and more honest look at life in wartime than would be possible in later years. Apart from the quite restrained brothel scene (above), there is considerable emphasis on the forbidden unwed motherhood rife among the nurses Catherine works with.
The two stars make a convincing romantic couple of the kind Borzage had become famous for, and the cinematography is lovely. Lang, too, was an expert at creating glamorous images.
Amazon would very much like you to watch the film for free with ads or with a subscription to Paramount+ or with a free Fandor trial or by paying $2.99. Once you scroll past those enticements, you can find Kino Classics release of a Blu-ray or DVD in a remastered version by George Eastman House. It seems a bit overly dark to me, but maybe the original nitrate copy was, too.
Scarface
I have to admit that gangster films are not my favorites. Still, there are outstanding films in the genre, as the presence of von Sternberg’s Underworld on my 1927 list indicates. The early 1930s established the genre solidly, and Scarface stands out among the other classics examples of the time. I have not seen the two other such classics still commonly watched, Public Enemy or Little Caesar, for a very long time, but I recall not being very impressed.
Scarface marks Howard Hawks’s first appearance on one of my lists. It’s not up to his greatest films of the 1930s, Twentieth Century and Only Angels Have Wings (and some would say Bringing Up Baby).
One thing that makes Scarface stand out for me is its considerable use of humor, which seems unusual for a gangster film. Paul Muni, so dignified in his prestigious bio-pics of this same period, lets go and struts with aggressive arrogance, lets go in fits of rage, and makes Tony Camonte a figure of fun with his accent (“That’s putty nice”) and flaunted ignorance. When the woman he’s trying to impress and seduce remarks sarcastically that his clothes are gaudy, he delightedly takes it as a compliment.
The comic relief flirts with slapstick in the figure of Camonte’s “secretary,” who is illiterate, inept, and downright stupid. According to the AFI Catalog, his character name is Angelo, though Camonte addresses him as Dope. There’s a running gag of him being unable to get basic information from callers. At one point during a raging gunfight in a restaurant, he struggles to hear a caller’s name, unaware that a tank behind him has been pierced and is dousing him.
The film also has its visual pleasures. It was one of five films, along with Shanghai Express, that Lee Garmes lensed in 1932. The cinematography is appropriately less glamorous than in Shanghai Express, but it’s dark and occasionally beautiful, as in the hospital-invasion scene at the top of this section.
Many films of the early 1930s start off with an impressive moving-camera shot, presumably to show off before settling down into scenes with standard continuity cutting. Scarface has quite an impressive opening, with a plan sequence leading up to the first act of violence.
It begins with a low angle of a streetlight going out, and then tilts down and tracks rightward past a milk delivery cart and a sign that establishes the locale.
Continuing rightward, it reaches a tired janitor who removes a sign informing us that a stag party had been held there the night before. The camera tracks rights as he starts to clean up.
The camera follows through the wall and continues as he tackles the job in a room festooned with streamers–possibly an homage to the big party scene in Underworld. One artifact of the party that he finds is a brassiere that has lost its owner.
As he pauses, the camera leaves him to pan right and track in on a gang boss and two of his men talking about a potential danger from a rival gangster. He declares that he doesn’t want war and is satisfied with the money he’s making.
The men stand, and the boss promises an even bigger party in a week. Thus for a gangster, he seems a decent sort, not willing to stir up violence against those seeking to invade his territory.
The men leave, and the camera follows the boss across the room and into a phone booth. He starts to make a call.
The camera glides past him and away off to the right, where it picks up a menacing shadow in the next room.
It follows the silhouette as the unknown man walks toward the corridor where the phone booth is. Silhouetted against a translucent window, he pulls a gun, fires it, polishes it with a handkerchief, and throws it on the floor. (This sort of offscreen or partially offscreen treatment allows the violence to be less explicit, a ploy that continues throughout the film.)
As the killer disappears, the camera tracks back to the left, revealing the boss’s body. The janitor enters, sees it, takes off his work clothes, and tosses them in the phone booth.
The scene ends with a pan left to follow the janitor as he hurriedly moves through the mess and leaves.
My frames were pulled from the Universal Cinema Classics DVD, a release which has since come out on Blu-ray. (Amazon still has the same edition on VHS!)
Love Me Tonight
So many of the early 1930s musicals were stagey. The review musicals were series of numbers without a connective narrative (convenient because they could be popular abroad without dubbing or subtitling) or backstage musicals where a “put on a show” premise also led to numbers on a stage. But with the growing freedom of the camera and editing, the musical could become something more.
Love Me Tonight feels like a wildly enthusiastic celebration of that new freedom. The story is a modern Ruritanian romance. A Parisian tailor, played by Maurice Chevalier, travels to a country chateau to collect money owed him by a client, who is a member of the aristocracy. While on his way, Maurice bumps into the debtor’s sister, Princess Jeanette, and falls in love with her without realizing who she is. Once at the chateau, he is mistaken for a Baron and proceeds to charm the Princess’ entire family and gain her love–until his lowly birth is discovered. Throughout, the dialogue is witty and the music and songs, by Richard Rodgers and Lorenz Hart.
Much of the high spirits of the film arise from the fact that the songs are not sung by one or two people in a single locale. Instead, the music starts out in this limited way but passes along to other characters, spreading infectiously through a household or across a countryside. The process begins on a morning in Paris, as the city wakes up and goes to work. Gradually the rhythmic sounds of various activities build up to a symphony made of sound effects: a woman’s broom against a pavement or two cobblers’ hammers striking in counterpoint.
The first actual music when a man getting married that day picks up his formal outfit and Maurice sings about his work in “Isn’t It Romantic?” The groom goes out singing it, and it passes to a taxi-driver and then his fare–who happens to be a composer. Cut to a train, where he hums the music and writes it down (top of section), overheard by a group of soldiers; cut to a field where they march along singing it, and so on, until we reach the chateau and are introduced to the Princess, also bursting into “Isn’t It Romantic?”
Upon meeting Jeanette, Maurice woos her by singing “Mimi” to her. Here it’s a straightforward solo, though one that is filmed in an unusual fashion with Maurice singing and Jeanette reacting in shot/reverse shot directly into the camera.
Once at the chateau, Maurice apparently sings the infectious “Mimi” for the family and guests since there is a montage moving among them as they all cheerfully warble the song in their respective rooms. The same thing happens still later, when Maurice’s low birth is discovered; the song “The Son of a Gun Is Nothing but a Tailor,” similarly spreads throughout the building, including to the servants, who show a snobbery equal to that of their masters. Who can resist lyrics like those sung by a washerwoman?
Down upon my hand and knees/Washing out his BVDs/Is a job that hardly please me./If I had known I would have tore/The buttons off his panties for/The son of a gun is nothing but a tailor!
Overall one gets a sense that music and singing are irrepressible and ripple outward from the soloists to infect everyone within hearing distance.
Of course once Maurice has been thrown out, Jeanette decides to defy her family and races after his train on horseback. Mamoulian throws in some Soviet-style compositions as she heroically stands on the tracks and forces the train to stop.
Apart from its infectious style and music, Love Me Tonight has a wonderful cast, with Charles Butterworth as Jeanette’s wimpy but titled suitor, Charles Ruggles as the debtor son, Myna Loy as the man-hungry younger sister, and C. Aubrey Smith as the curmudgeonly father who becomes downright jolly under Maurice’s influence. Sheer entertainment.
Love Me Tonight is available from Kino Lorber on DVD or Blu-ray.
Hooray for the Rest of the World!
Vampyr
Two masters of cinema made vampire films a decade apart. I dealt with Murnau’s Nosferatu in the 1922 entry.
The two films could hardly be more different from each other. Murnau’s film was a plagiarized version of Bram Stoker’s 1897 novel, Dracula. He followed the original very loosely, cutting out most of the characters, including Van Helsing and hence the entire lengthy investigation process. Dreyer may well have known Murnau’s film, but it is hard to detect any influence or inspiration apart from the use of a book as exposition. The Universal version starring Bela Legosi was still in production when Dreyer finished shooting Vampyr. Instead, Dreyer drew even more loosely from the collection of horror-fantasy series short stories by Sheridan Le Fanu, published as In a Glass Darkly (1872).
Dreyer seems to have taken a few ideas from the stories, but does not use the narratives associated with those ideas. The notion of a female vampire is probably derived from one of the stories, “Carmilla,” though Le Fanu’s vampire is young and beautiful, while Dreyer’s is an elderly woman, Marguerite Chopin. The collection of stories is presented as having been case studies collected by a Dr. Hesselius, a researcher of the arcane. Allan Gray may be inspired by Hesselius, though he does no evident research and reacts in fear in most cases where he encounters anything strange and grotesque. Gray’s dream of being trapped in a coffin and carried off to be buried comes from “The Room in the Dragon Volant.”
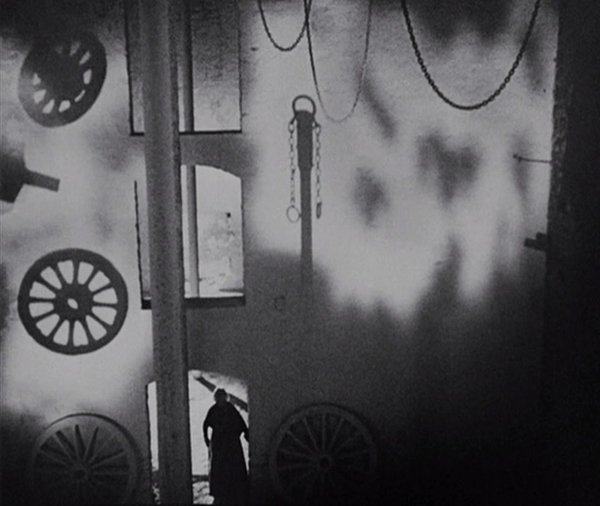
On the whole, though, one of the most striking things about Vampyr is how little it adheres to the conventions of the vampire tale. It is not told as a collection of documents, as are Le Fanu’s stories (“Carmilla”is told in first person by Laura, the heroine and victim of the vampire) and Dracula (a collection of documentation by gathered by several characters). As in Nosferatu, a book is included to help present the “rules” of vampire stories, but the book is not written by Gray. It is given to him by the old Chatelain. The premises that vampires must travel in coffins full of dirt or will be killed if exposed to sunlight, so important in Nosferatu, are ignored here. Actually, the intention seems to be that Chopin is active mainly at night, but since the entire film was shot in murky daylight, it’s difficult to to tell night from day. Vampires also tend to be of noble birth, and we usually find out something about their family history. Chopin seems to be a local woman who somehow became a vampire.
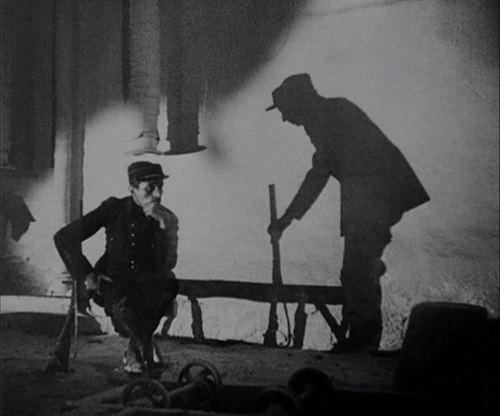
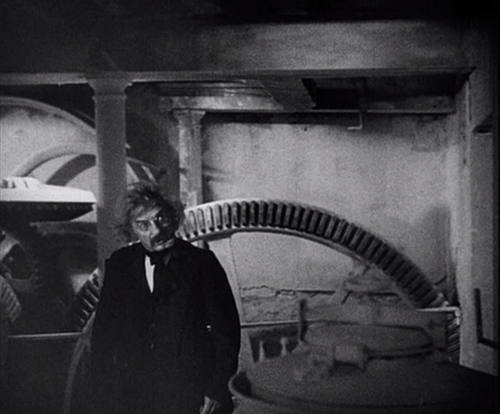
To create a creepy atmosphere, Dreyer has Gray wander about observing menacing, unnatural, or unexplained phenomena in the neighborhood of the village of Courtempierre. These are not phenomena conventional to vampire stories, so they seem as mysterious to us as to Gray. Much of what Gray observes is never explains. Gray sees numerous shadows and reflections of beings who are not visible. He follows the shadow of a peg-leg man until it finally rejoins the soldier who should be casting it. Most vampires live in crumbling Gothic castles, but Chopin seems to have made her headquarters in a dilapidated factory of some sort. (Dreyer chose a deserted plaster factory whose white walls would show off the shadows cast on them.) Her main minions, a sinister doctor and the one-legged military man apparently do whatever they do there, waiting to do her bidding. As the images above and on the right below show, Dreyer creates a mysterious air to the building through the circles and curves of large gears, wheels, and hanging chains.
Beyond such motifs, there are the actors’ unpredictable exits and entrances into the frame during camera movement and the eerie offscreen sounds that hint at something disturbing happening nearby. David has analyzed all this in detail in his book, The Films of Carl-Theodor Dreyer (out of print but available from second-hand book dealers).
For the ending, Dreyer draws upon the convention of a stake through the heart as the way to kill a vampire. It isn’t Gray that figures this out. A remarkably passive protagonist, he sits dreaming of being buried alive while the old servant, initially a minor character, reads the Chatelain’s book, gathers the needed equipment, and initiates the task of the staking of the vampire in her grave.
The 1998 restored version of the film is available from The Criterion Collection on DVD or Blu-ray, with a particularly good set of supplements. These include a visual essay by Danish expert Caspar Tybjerg that deals in more detail with the influences of previous vampire literature and films on Dreyer’s work; I have drawn upon it for some of the information above. Vampyr also streams on The Criterion Channel, accompanied by some of these supplements as well as a video essay by David, “Vampyr: The Genre Film as Experimental Film.”
Boudu Saved from Drowning
Jean Renoir entered this list in 1931 with La Chienne. Although a grim melodrama for the most part, the film provides put-upon accountant Maurice Legrand with a happy ending as he leaves home and becomes a jovial tramp.
Boudu, the self-centered, careless tramp at the center of this film, is presumably not Legrand, despite being played by the same actor, Michael Simon, and Boudu Saved from Drowning is not a sequel. It almost could be, but this time the genre is comedy.
The opening sets Boudu up as an unusual tramp. He is not begging, and when a little girl offers him a small bill, he asks what it is for. “To buy bread,” she replies. Soon Boudu does beg by opening a car door for a rich man, and when the man can’t find any money in his pockets to tip him, Boudu hands him the small bill “To buy bread” and walks away.
Unexpectedly, Boudu jumps into the river in a suicide attempt. Lestingois, a prosperous bookseller whose shop and apartment are across the street, witnesses this and rushes out to dive in and save Boudu. He succeeds, receiving praise from the onlookers as a bourgeois who would take this trouble for a mere tramp. Lestingois is fascinated and amused by this “perfect tramp” and takes him in, offering him dry clothes, food, and a sofa to sleep on for the night, much to the disgust of his wife.
Boudu’s antics delight Lestingois, who treats him somewhat like a pet dog (top of section). He also gives Boudu a lottery ticket, which predictably will become a vital plot device later on. The tramp, however, disrupts the routine of the household–in particular sleeping in a spot that prevents Lestingois from making his nightly visits to the maid Anne-Marie.
Boudu lingers on, seeing this cushy home as a good setup; he tries to fit in by shaving his bushy beard and trying to dress respectably. He is utterly uncouth, however, shining his shoes on the wife’s bedspread, and knocking things off shelves, and causing a flood by leaving water running in the kitchen. Lestingois ultimately gets fed up with him–but in the nick of time Boudu wins the lottery and the attitude of the household changes. Anne-Marie, who supposedly loves Lestingois, suddenly becomes engaged to him.
On the wedding day, however, as the happy couple are in a rowboat on the river, Boudu upsets the boat and floats away to resume his old life as a tramp.
Stylistically the film is distinctly Renoirian. He shot his exteriors in Paris streets and parks, seemingly concealing the camera in some cases. A telephoto lens captures Boudu wandering along the bookstalls on the banks of the Seine, with the other people presumably ignoring him as a real tramp.
In a modest way, Renoir used the sort of roving camera movement that he would later develop into a major feature his late-1930s masterpieces. One scene starts with Lestingois and his wife eating a meal along with Boudu, seen from a distance down a hallway. As Anne Marie finishes serving, she exits left, and the camera moves left into the next room, where she is glimpsed walking toward the kitchen. It continues moving and stops briefly as Anna Marie enters the kitchen and puts down her tray. As she comes forward to the kitchen window, the camera tracks closer to the foreground window and stops, still at a distance as she talks with an unseen neighbor.
Boudu Saved from Drowning is available on DVD from The Criterion Collection and streams on The Criterion Channel (along with some supplements).
Wooden Crosses
Raymond Bernard’s Wooden Crosses is this year’s masterpiece unknown to most modern viewers, and I cannot recommend it highly enough. I discovered the film through The Criterion Channel. David and I were relatively early in our “Observations on Film Art” series of supplements–early enough that the service was still called Filmstruck. In picking a film for a video essay, I thought it would be helpful to choose titles that were obscure but very much worth calling attention to.
One such film on the Criteron list was Wooden Crosses. I was dubious about it, since my only association with Bernard’s work was the 1924 historical epic, The Miracle of the Wolves, which I had seen back in my post-graduate days and found pretty turgid. Nevertheless, I gave Wooden Crosses a try and was bowled over by it. My video essay, “The Darkness of War in Wooden Crosses,” became number 16 and is available to subscribers.
In some ways Wooden Crosses is France’s great anti-war film of the early 1930s, following Hollywood’s All Quiet on the Western Front and Germany’s Westfront 1918, both of which were in my top ten for 1930. For me, it’s the best of the three.
The film begins with stock footage of Parisian crowds cheering the young men signing up to fight and marching off to war. Like The Big Parade, it introduces the war from well behind the lines, as new recruits arrive at a farmyard where the more experienced troops are billeted. The action takes place shortly after the Battle of the Marne in autumn of 1914; it was won by the French, but did not succeed in achieving ultimate victory. In Wooden Crosses, the experienced men scoff at the recruits for having arrived too late to experience any fighting.
Their optimistic assessment proves wrong, and the group is ordered to march to the front-line trenches. The result is an impressive sequence shot at night as the group goes through open areas, woods, and finally ends neck-deep in the trenches looking out across no man’s land in the darkness. As my video-essay title suggests, there is a considerable amount of night footage in the film. One point I make in that essay is that the epic footage in the film made an impression in Hollywood:
In 1935, the head of the newly merged 20th Century-Fox studio, Darryl Zanuck, bought the North American rights for Bernard’s film. He didn’t intend to release it theatrically. Instead, he realized that the spectacular battle footage was beyond anything that the studio could afford, and he wanted to reuse it.
The film it was to be used in was Howard Hawks’s The Road to Glory, released in 1936. Hawks, however, wasn’t just keen to use the battle footage. Like me, he seems to have admired the many night scenes. He said of Wooden Crosses that it had “Some fabulous film in it, marvelous scenes of great masses of people moving up to the front and through trenches—wonderful night stuff.”
The group of soldiers are quickly and marvelously characterized, notably by Charles Vanel as the group’s quiet, sensible Corporal and Gabriel Gabrio (Javert in Bernard’s Les Misérables) as the sarcastic, boastful Sulphart–a key source of comic relief in the film. Graduallynew volunteer Gilbert Demachy emerges as our main point-of-view character, though the others are kept prominent. There is a suspenseful series of scenes as they hear the sounds of German sappers tunneling below their dugout to lay mines. They are ordered to stay put, as there is plenty of time before the explosions, but as we discover, this is an example of a common motif in these films: the incompetence of the leadership.
One of the film’s most impressive aspects is the epic recreation of battle scenes. There’s no stock footage here, and there are shots over vast areas of no man’s land with explosions going off among the actors.
The climactic battle goes on and on–ten days, as repeated superimposed titles inform us–and conveys the relentlessness of the struggle that the group undergoes.
The battle ends in a long, tense scene, ironically set in a cemetery where many of the graves have been blasted open. These substitute for trenches as the men hunker down under German attack.
As with some of the other films on this year’s list, the cinematography of Wooden Crosses is extraordinary. It was shot by Jules Kruger, who had worked with major French Impressionist directors, notably Marcel L’Herbier on L’Argent and Abel Gance’s Napoléon, the latter of which no doubt gave him considerable experience with epic battle scenes. His most famous films after Wooden Crosses were La belle équipe and Pépé le Moko.
The Criterion Collection did a great service by releasing Wooden Crosses paired with Bernard’s Les Misérables in their Eclipse series. It also streams permanently on The Criterion Channel along with my video essay linked above. (New Year’s resolution: watch more Bernard films. I should give The Miracle of the Wolves another chance and set aside plenty of time to watch Les Misérables, a three-feature serial adaptation of the novel that clocks in at 281 minutes.)
I Was Born, But …
Yasujiro Ozu makes his third appearance in a row on these lists (see here and here for the first two). If I were to live to 102 and if I were still posting these lists, his last film would be on the 2052 list. That’s unlikely, but even so, he will probably be the director most represented on these lists as long as this series continues. I am still pondering whether to give him three spots on the 2023 list or just group his three masterpieces from that year as tied for a single spot.
I Was Born, But … was the first of Ozu’s silent films to become available in the West, and it is still probably the best known. So many of his early films are lost, but this may be the one where he achieved the perfect balance of humor and poignancy that characterizes so many of his best films.
Ozu is known for creating stories centered around the stages of life, often expressed as seasons in their titles, such as Late Spring‘s focusing on a daughter pushing the limits of marriageable age to care for her elderly father. His surviving early films often dealt with students or recent graduates struggling as “salarymen” in the job market of the Depression. In this film for the first time he shows the woes of the salaryman largely from the viewpoint of his children. Many of Ozu’s films are based on relations between parents and children young or grown. Those that dealt with young children were among his masterpieces: Passing Fancy, The Only Son, There Was a Father, Record of a Tenement Gentleman, and Ohayu.
The salaryman films deal with the difficulties of getting jobs, competing with colleagues, and surviving on meager wages. I Was Born, But … adds the problem of the subservience and even humiliation a salaryman sometimes undergoes and how it affects his family.
The story unfolds in parts that to some extent echo each other. Early in the film the two sons are bullied at school by the son of their father’s boss. They manage to defeat the bully and in a show of bravado boast that their father is the best in the world.
Later the family is invited to a gathering at the home of Yoshii’s boss, who shows some home movies of his employees showing off for the camera. These include Yoshii making faces and playing the fool, obviously at his boss’s insistence. The sons’ delight in seeing their father on the screen fades as they realize that their father has been humiliated and is not the great man they boasted about. Implicitly, Yoshii is being bullied as well but must submit in order to please his boss.
In an angry confrontation with their father, the sons accuse him of having proved himself not to be the man they had looked up to. The confrontation ends in their refusal to eat or speak to their parents. The parents admit to each other that their life is disappointing and not one they would wish for their children. The quarrel soon ends, with the boys accepting that their father is not the greatest.
As with That Night’s Wife (1930), Ozu is already using some of the techniques that would be part of his style for his entire career. For example, there is a transition between scenes that uses graphic values and objects in a series of images that do not behave like ordinary establishing shots.
I Was Born, But … is available in another DVD set in The Criterion Collection’s Eclipse series, “Silent Ozu: Three Family Comedies.” The other two are the charming Tokyo Chorus and the wonderful Passing Fancy (which will definitely appear on next year’s top ten). Along with a slew of other Ozu films, it also streams on The Channel. Many of you know David’s book, Ozu and the Poetics of Cinema; it’s long out of print but available through open access on the Center for Japanese Studies Publications site (with the frames from the color films in color!).
Kuhle Wampe or Who Owns the World?
Slatan Dudow’s Kuhle Wampe, scripted by Bertolt Brecht, was a bold pro-Communist film made in the year before the Nazis swept into power.
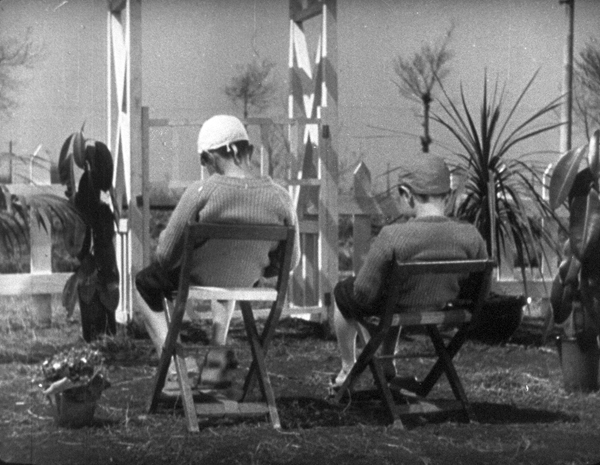
Kuhle Wampe, named for the workers’ camp in which much of it is set, starts with the dire situation for the working class in Depression Germany. A typical family is singled out, with the son returning home after one of many fruitless searches for work (below). His parents blame him for his failure to find work in a society where unemployment is rampant. Their anger drives him to suicide. A neighbor woman remarks resignedly to the camera, “One fewer unemployed.”
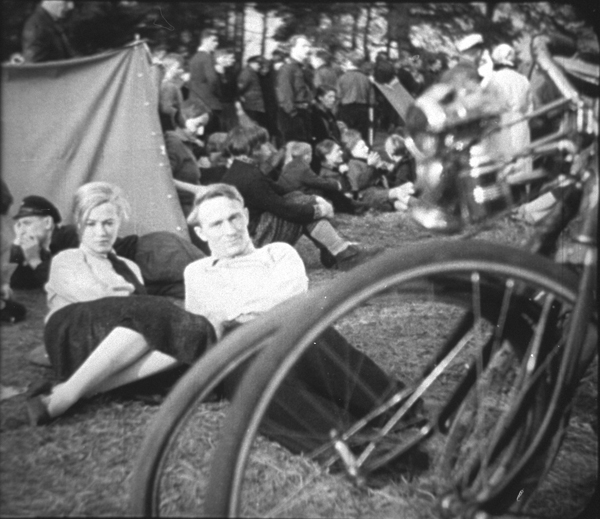
The boy’s sister Anni becomes one of the main characters. Another is Fritz, her boyfriend, a leader in the labor protests in a local factory. When Anni becomes pregnant, the pair split up but eventually reunite when her family is evicted and moves into the tent city of the title, run by a Communist group (above). Communism is portrayed as a solution to the problems presented earlier. A lengthy sequence at a Communist youth sports festival emphasizes the happy life on offer by the Party. In the final scene, directed by Brecht himself, Anni and Fritz have an argument about the world’s financial dilemma with some middle-class passengers.
In 1933, Brecht fled the country, eventually ending up in Hollywood, and Dudow was expelled from Germany, only returning after the war to help found the Communist-run East German film industry.
As far as I can tell, the only DVDs or Blu-ray discs available in the US are imports and may not play on encoded machines. (It’s not even on YouTube!) For those with region-free players, the BFI’s release in either format seems to be best source.
Trouble in Paradise.