Archive for the 'Actors' Category
GRAVITY, Part 2: Thinking inside the Box
Kristin here:
In my previous entry, I described Gravity as an experimental film. I had thought of it that way ever since seeing trailers for it online back in mid-September. I described it as reminding me “of Michael Snow’s brilliant Central Region, but with narrative.”
Last time I developed that notion in more detail and analyzed the narrative structure of the film. Now I’ll analyze the experimental aspects of the film’s style and the dazzling means by which they were created. I don’t have the technical expertise to explain the inventions and ingenuity that went into creating Gravity, so I have sought to pluck out the best quotations from the many interviews and articles on the film and organize them into a coherent layout of how its most striking aspects were achieved.
As in that entry, SPOILER ALERT. This is not a review but an analysis of the film. Gravity does depend crucially upon suspense and surprise, and I would suggest not reading further without having seen the film.
Screaming on the set
I’ve written about Cuarón’s use of long takes, a stylistic device that has drawn a huge amount of attention in the press. Here the editing is so subtly done that even someone like me, who typically notices every cut, missed a lot of them during early viewings. There are bursts of rapid editing, as when the ISS is struck by debris and is destroyed, or more conventional cutting, as when the camera follows the Chinese pod and surrounding remnants of the station as they heat up in the atmosphere.
The long takes go beyond what Cuarón has done before. In Variety, Justin Chang describes one major difference: “As the movie continues, the filmmakers even add a new wrinkle, which Lubezki calls ‘elastic shots’: Takes that go from very wide shots to medium closeups, then segue seamlessly into a point-of-view shot, so the viewer is seeing the action through the character’s eyes, right down to the glare and reflections on a helmet visor.” Such moments are rare in Gravity, but one occurs in the “drifting” portion, shortly after the segment laid out above:
As Cuarón has pointed out, his long takes eliminate the need to cut in to closer views: “The language I have been working on with Chivo in these recent films is not one based on close-ups. We include close-ups as part of a longer continuous shot. So this all becomes choreography.” Another point he makes in this and other interviews is the influence of Imax documentaries on Gravity: “My process of exploring long takes fits in with that IMAX documentary notion, because when they capture nature it isn’t like they can go back and pick up the close-up afterward. There isn’t that luxury in space either. So then it falls to us to find a way to deliver that objective view, but then transform it into a more subjective experience.” Hence the “elastic shots.”
The long takes often dictate a refusal to cut in to reveal significant action. There is the moment in the epic opening shot, for example, when Shariff is suddenly killed in the background while in the foreground Kowalski tries to help Stone detach from her mechnical arm and into the shuttle. Did you see the flying piece of debris that struck his head? I didn’t, not until the fourth time I watched the film, knowing that it was coming and determined to spot it. It’s there, a little white dot that flashes through the frame in a split second. Shariff’s abrupt movement to the side, stopped with a jerk by his tether, is what we spot, since his bright white suit moves so suddenly and quickly, ending up against the pitch black of space:
A great deal happens in such moments of action, and we are left to spot what we can.
If these long takes are dazzling on the screen, think what they must have been like to witness being made. Lubezki has suggested how complicated the long takes in Gravity and earlier films were to shoot:
There are very few director/cinematographer teams working today as well known for a certain aspect of filmmaking as you and Alfonso are, which is that long extended take, or the seamlessly edited take. What it is like actually shooting those scenes?
I’m going to tell you something, the reality is that the movie was so new that when we finished a shot we would get so excited people would scream on set—probably me before anybody else. There were moments when we were shooting and Alfonso said ‘cut’ we would all just jump and scream out of happiness because we’d achieved something that we knew was very special.
In Children of Men, we also had moments like that. When we finished the first shot inside that car [the aforementioned ambush scene], the focus puller started crying. There was so much pressure that, when he realized he had done a great job, he just started crying.
There is something breathtaking about the achievement of complex long takes that seems not to arise from any other cinematic technique. I have seen Russian Ark three times now, and each time I feel an inexplicable tension, wondering whether the camera team will make it through the entire one-shot film without a mistake. I’ve already seen it happen, and yet it still seems unbelievable that they did.
In Gravity, of course, the “long takes” were not actual lengthy runs of the camera. Nor were they, as in Children of Men, several camera takes stitched together digitally to create lengthy single shots. Rather, they were created in the special-effects animation, with the faces of the actors being jigsawed into them through a complex combination of rotoscoping and geometry builds. (See this Creative Cow article for an example.)
The choice to present the action in long takes was crucial to the look of the film. Most films set in space rely heavily on editing, since for decades the special effects needed to convey space walking were best handled in a series of shots. In Star Trek Into Darkness, Kirk flies through space toward a spaceship breaking up and surrounded by debris, a situation somewhat comparable to that in Gravity. The sequence is built up of many short shots of Kirk against shots of dark space, point-of-view shots through his helmet, and cutaways to characters inside the Enterprise conversing with him via radio. Here’s a brief sample of four contiguous shots:
The sequence conveys little sense of weightlessness, partly because the actor adopts a traditional superhero-style flying pose. With no air in space, there would be no need to compact oneself into a streamlined shape. The fast cutting keeps repeating similar compositions, as with frames 2 and 4 above, with the fast editing presumably intended to generate excitement. (Star Trek Into Darkness has at least 2200 shots in a little over two hours, while Gravity has about 200 in 83 minutes.) Gravity‘s success in creating a realistic environment in space is dramatically evident when contrasted with this film’s more traditional outer-space conventions.
But it turns out that the commitment to the long take led Cuarón toward less common choices about editing, staging, and lighting.
Follow the bouncing axis
For much of the film, there is minimal spatial stability for the characters or for our viewpoint into the diegetic world. There is no ground, so we cannot imagine the camera resting on anything. When outside the space vehicles, the camera moves nearly all the time. In an interview with ICG Magazine, director Alfonso Cuarón was asked, “So with the camera and characters in constant motion and changing perspective, how did you figure up from down?” He replied:
There is no point of departure because there is no up or down; nobody is sitting in a chair to orient your eye. It took the animators three months to learn how to think this way. They have been taught to draw based on horizon and weight, and here we stripped them of both.
Undoubtedly many scenes contain an axis of action running between the characters, but it is not of a traditional kind. Unlike in a classically edited film, in Gravity‘s action scenes in space, the axis is in constant, fleeting motion, and any given center line between two characters must in quick succession run not only left and right but also up and down, diagonally, in almost any direction. Any given screen direction set up by the axis is ephemeral and offers little to help orient us spatially. Eyeline directions mean very little, since there are few cuts to things that the characters have seen offscreen. (True, when characters look offscreen, they establish eyelines, and the camera sometimes pans from Stone or Kowalski to some object they have been looking at. But a pan from a person to an object automatically establishes the spatial relations between them, whether or not the character is looking at the object.)
As a result, the spatial cues used in continuity editing system are not so much eliminated as made irrelevant for long stretches. That system is meant, after all, to guide our understanding of the story space across cuts. There are exceptions, such as a brief shot/reverse-shot exchange: Stone, loosely attached to the International Space Station (ISS) by ropes, pleads with Kowalski not to untether himself from her and float away to die in space, and he insists that it is the only way to allow her to live. When Kowalski and Stone, tethered together, travel toward the ISS, he is always at screen left, she at screen right, with the strap joining them stretched out as a sort of visible axis of action; straight cut-ins to close views of each character, and even at one point Kowalski’s point of view, obey the 180-degree rule and create an almost conventional scene. Actions inside the spacecrafts are more oriented as well. In the ISS Stone moves weightlessly through a series of pods, all the while maintaining screen direction. Similarly, inside the vehicles, especially late in the film when Stone is strapped into seats, she is usually upright, her head oriented toward the top of the frame. Some sustained actions in space also keep her right-side up, as when she removes the bolts holding the parachute cords to the Soyuz landing vehicle.
In part because of such orienting devices, we are seldom seriously confused about where the characters are, or at least not for long. Otherwise we would not be able to comprehend the story action. Still, compared to typical classical films, Gravity conveys little sense of spatial stability. The disorienting simulation of weightlessness for characters and camera dominates the scenes outside the vehicles and creates a style that can truly be called experimental.
Take the brief segment (about 14 seconds) below, from the 13-minute opening shot. Stone has been standing at the end of a large mechanical arm which gets knocked off the space shuttle by a piece of hurtling debris. It spins rapidly, with the camera framing it from long-shot distance. The camera is not entirely static, reframing slightly, but we can see the earth in the background fairly clearly. Stark sunlight comes from offscreen left, and as Stone’s body whips through space, the shadows move accordingly around her, with the back of her body in deep shadow in the first frame and then her front shadowed in the second:
The fact that the light source, the sun, is offscreen left during this spinning segment suggests that the camera and hence our viewpoint are in a stable position. Yet that position is maintained for only a short time. At this point in the shot, the camera is essentially waiting for her to draw near in order for it to execute a change that will govern the penultimate part of the lengthy shot.
That happens when, after she has spun wildly toward and away from us several times, the camera “attaches” to her, so that we are now seeing her in medium shot and spinning with her. Instead of seeing the earth clearly, we see her while the blurred surface of the earth and the blackness of space alternate rapidly. This was the technique that led me, when I first saw the film’s trailers, to compare Gravity to Michael Snow’s Central Region:
Being closer to Stone, we can see more clearly the shadows coming and going; her face is sometimes illuminated brightly by the sun and sometimes in near darkness:
The function of the attachment to Stone, apart from allowing us to see her fear and confusion, is to show us that her hands are working to detach her from the arm, as a tilt down reveals:
As she soars off the arm and tumbles into the black depths of space, the camera leaves its “attachment” to her, and she spins away from it:
Cuarón’s commitment to the long take thus made him rely more than usual on events taking place within the frame–camera movement and figure movement in particular. Yet these movements had to occur in a microgravity environment radically different from the earthbound surroundings of Children of Men and Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban. This new constraint led to some technological innovations of remarkable originality.
The LED Light Box
Early on it became clear that moving the actors through space on wires would not create the desired realism of weightlessness, and obviously they could not be whipped about and tumbled in ways that the film ultimately achieved. The actors would have to be relatively static, with the illusion of movement created through other means. One of the main challenges was to have the lighting on their stationery faces support that illusion. And it would have to be done perfectly in order to achieve the photorealistic depiction of space that the filmmakers were after.
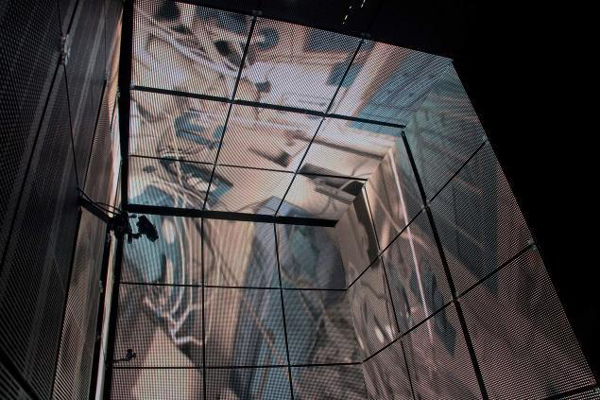
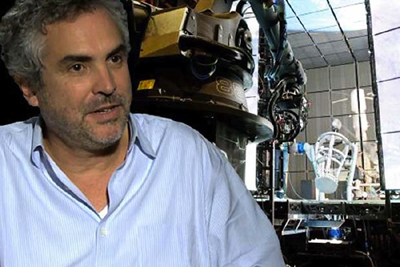
Usually in watching a film heavily dependent on CGI, one notices elements that have been assembled into a single composition but don’t quite match each other. A matte painting that isn’t lit from precisely the same angle as all the other components stands out from the rest (as, it has to be admitted, happens in the best of CGI scenes, including those in The Lord of the Rings). The problem was solved for Gravity using the LED Light Box, a device frequently mentioned in the press coverage of the film but seldom explained. (See image at the top.) The concept is truly revolutionary, although I am not sure to what extent it would work for other films that did not present such peculiar challenges.
In American Cinematographer‘s article on Gravity, “Facing the Void,” cinematographer Emmanuel Lubezki explains why consistency of lighting is crucial and how he came up with his solution:
Lubezki emphasizes that Gravity‘s blending of real faces with virtual environments posed a tremendous challenge. “The biggest conundrum in trying to integrate live action with animation has always been the lighting,” he says. “The actors are often lit differently than the animation, and if the lighting is not right, the composite doesn’t work. It can look eerie and take you to a place animators call ‘the uncanny valley,’ that place where everything is very close to real, but your subconscious knows something is wrong. That takes you out of the movie. The only way to avoid the uncanny valley was to use a naturalistic light on the faces, and to find a way to match the light between the faces and surroundings as closely as possible.”
This challenge led Lubezki to imagine a unique lighting space that was ultimately dubbed the “LED Box.” He recalls, “It was like a revelation. I had the idea to build a set out of LED panels and to light the actors’ faces inside it with the previs animation.” Lubezki conducted extensive LED tests and then turned to [special effects head Tim] Webber and his team to build the 20′ cube and generate footage of the virtual environments, as seen from the actor’s viewpoint, to display inside it. While constructing the LED Box, the crew also solved problems involving LED flicker and inconsistencies.
Inside the LED Box, the CG environment played across the walls and ceiling, simulating the bounce light from Earth on the faces of Clooney or Bullock, and providing the actors with visual references as they pretended to float through space. This elegant solution enabled the real faces to be lit by the very environments into which they would be inserted, ensuring a match between the real and virtual elements in the frame.
This ingenious approach largely did away with traditional three-point lighting in the exteriors. As Lubezki explains in the AC article,
When you put a gel on a 20K or an HMI [Hydrargyrum medium-arc iodide], you’re working with one tone, one color. Because they LEDs were showing our animation, we were projecting light onto the actors’ faces that could have darkness on one side, light on another, a hot spot in the middle and different colors. It was always complex, and that was the reason to have the Box.
The crucial point here is that the lighting was being created by playing the previs animation of the earth, space, the moon, and the large reflecting objects like the space shuttle on the sides of this 20′ by 10′ box. In other words, the moving images from the nearly finished special effects were used to light the faces of the actors, and those faces were later joined to those very same special effects, in a more polished form, to create the final images.
Lubezki gives an excellent description of the Box in his interview with Bryan Abrams, a series of responses which is worth quoting at length. Note that Lubezki refers to the Box as an LED monitor–essentially a giant television screen turned inside out and surrounding the actor:
Can you touch upon some of the pieces of technology and equipment that were created to make Gravity possible?
To make this movie we used many different methodologies. For one of them, we invented this LED box that you’ve probably read about, which is basically this very large LED monitor that is folded into a cube. So all the information and images that you input into this monitor lights the actors, and you can input all of the scenes that were pre-visualized to create the movie—all the environments that we had created—and you can input them into this large cube so space itself is moving around the actors.
So it’s not Sandra Bullock spinning around like crazy, it’s your cameras.
Yes, instead of having Sandra turning in 360s and hanging from cables, what’s happening is she’s standing in the middle of this cube and the environment and the lighting is moving around her. The lighting on the movie is very complex—it’s changing all the time from day to night, all the color temperatures are changing and the contrast is changing. There were a lot of subtleties that you can capture with the box, subtleties that make the integration of the virtual cinematography and the live-action much better than ever before.
The effects of the LED projections are visible in the changes on Stone’s face in the extended example above. Here’s a brief example of changes on Kowalski’s face in the opening shot:
The harsh light in the right frame above is a real lamp. The LEDs could not produce a local, hard light intense enough to simulate the sun. The team placed “a small dolly and jib arm alongside the actors” with a lightweight spotlight. This was moved “according to the progression of the virtual sun.” Such harsh light was necessary because outside the atmosphere there is nothing to filter bright sunlight. Several moments where the actors’ faces and suits are severely overexposed reflect this technique:
The Box also contained a large video monitor, visible to the actor, which displayed the previs animation. Lubezki explains: “This was wonderful in a couple of different ways. The actor sees the environment and how objects are moving in that environment, and at the same time we can see the interaction of that light on the actor. We capture true reflections of the environment in the actor’s eyes, which makes the face sit that much better within the animation.”
Previs as environment
The fact that almost everything in the film was created digitally–including the space suits in which the actors bob and spin in the exteriors–necessitated an extraordinary amount of planning and pre-production. “Pretty much we had to finish post-production before we could even start pre-production, because of all the programming,” Cuarón says. This was one reason why there was such a long gap between Children of Men (2006) and Gravity. Four and a half years were spent in developing the new technology and preparing to shoot.
The team started with geography:
The filmmakers began their prep by charting a precise global trajectory for the characters over the story’s time-frame, so that Webber and his team could start creating the corresponding Earth imagery. Cuarón chose to begin the story with the astronauts above his native Mexico. From there, the precise orbit provided Lubezki with specific lighting and coloring cues. The cinematographer recalls, “I would say, ‘In this scene, Stone is going to be above the African desert when the sun comes out, so the Earth is going to be warm, and the bounce on her face is going to be warm light.’ We were able to use our map to keep changing the lighting.”
Next, the filmmakers defined the camera and character positions throughout the story so that animators at Framestore could create a simple previs animation of the entire movie. [“Facing the Void”]
Lubezki was completely involved in planning the digital lighting. He recalls, “I would wake up at 4 a.m., turn on my computer, I’d say good morning to my gaffer and start working on a scene. I would say, ‘Move the sun 60,000 kilometers to the north.’ That way I could put the lighting anywhere I wanted.”
The reference material for the earth imagery came in part from NASA reference footage and photos. You can get a sense of these from the NASA films posted online, although these are mostly done in fast motion, unlike the ones the filmmakers would have used. One good example is “Earth HD.” There, at 2:25 and again at 2:41, one of the most recognizable locations on earth, the Nile Valley and Delta, are visible:
A similar image of the Nile appears on earth as Kowalski and Stone slowly make their way from the space shuttle to the ISS, with him asking her about her hometown and any family she might have waiting for her. (I was also happy to see the area of the site where I work in Egypt, Tell el-Amarna, which lies about midway between the Delta at the upper left and the large bend in the river.)
This geographical plotting included some ellipses. Although commentators have suggested that the film takes place in real time, or nearly so, there are temporal gaps. Shortly after the first pass of the speeding debris field, Kowalski tells Stone to set her watch’s timer for 90 minutes, since he calculates that is when they will encounter the orbiting debris again. That happens when she exits the Soyuz vehicle to detach its parachute. She again sets her timer for 90 minutes, and the debris field shows up at the Chinese station, battering it to the point where it sinks into the atmosphere and breaks up into chunks melting from the friction of reentry. Thus a little over three hours should be passing in the 83 minutes of screen duration.
Cuarón more or less confirms this timetable when he describes the creation of the previs: “The screenplay describes a journey that takes place mostly in real time, with only a couple of time transitions. We travel around Earth three times, so in previs we planned out visuals with specific knowledge of where we’d be in orbit at any given point in the story, whether it was in sunlight or darkness.”
In the film there are very few places where we can assume a significant ellipsis occurs. After Stone enters the ISS, sheds her helmet and suit, and drifts in a fœtal position, there is a gap. It’s probably not long, since she still holds some hope of going to rescue Kowalski, but she pauses to recover after her trying experience. Later, there is a cut from her inside the landing module, not in the suit, to her emerging from the hatch fully suited up–a gap we might assume to be ten minutes or so. Most notably, the cut from the nighttime shot of the earth that includes the aurora borealis at the right to the extreme close-up of frost on the window ellides a longer stretch of time. Stone has become hoarse in the interval as she tries to send a mayday message via radio. In other cases, such as Stone and Kowalski’s slow journey toward the ISS, time seems to be somewhat compressed though not ellided.
Staging without a stage
A lack of depth cues hampered the animators charged with creating the previs. The absence of one major depth cue, aerial perspective (the tendency of layers of space in the distance to turn successively bluer and blurrier due to the filtering quality of the atmosphere), caused problems. Visual-effects supervisor Tim Webber, of the effects house Framestore, remarks:
You can’t rely on aerial perspective because without atmosphere there is no attenuation of image due to distance. And the lack of reference points [in space] can get you into trouble, like not being able to tell if the character is coming toward you or the camera is moving toward him. Even though we played it straight with respect to science and realism, we did put in more stars than you’d be able to see in daylight, just so there’d be some frame of reference to gauge movement.
Presumably Webber is referring here to the movement of the characters and objects through space, not the camera movement. (The lack of any “frame of reference” against which to sense movement is part of what makes the Star Trek scene illustrated above seem so unsophisticated.)
Naturally, since the actors were not standing on a floor or solid ground, the blocking was difficult, but it also had to be planned completely in advance:
Cuarón laughs as he recalls the surprises inherent in blocking characters in a zero-gravity environment. “The complications are really something because you have characters that are spinning. Say you want o start your shot with George’s face and move the camera to Sandra, who is spinning at a different rate. You start moving around her, and then you start to go back to George, only to realize that if you go back to George at that moment, you will be shooting his feet! So then you have to start from scratch. Sometimes you find amazing things accidentally, but sometimes you have to reconceive the whole scene.” [“Facing the Void”]
Finally, after all the planning, the previs animations were made. These had to be refined considerably so that they could adequately serve in the Light Box to illuminate the actors’ faces. According to Bill Desowitz, “The previs was so good, in fact, that the daughter of cinematographer Emmanuel (“Chivo”) Lubezki thought it was the real movie.”
The previs became so sophisticated because it evolved during preproduction. Cuarón recalled that Lubezki’s inspiration to create the LED Light Box changed the planning tactics:
Then that kind of had a ripple effect back into the previz, because originally they were going to just be a model that we could look back at, but we realized that the previz was more than that. That was something that [James] Cameron kept on talking about. He would say “I don’t use previz anymore, I use it as if it is the first painting on a canvas.” In other words it was the stuff that you kept on painting on top of and the thing with that is that it became very clear that in order to use these technologies, we needed to program stuff and the previz was going to have to be precise in terms of camera movements, choreography, timing and light.
As a result, the movie changed very little during principal photography. Senior visual-effects producer Charles Howell told American Cinematographer: “I think there were only about 200 cuts in the previs animation, [whereas] an average film has about 2,000 cuts. Because these shots had to be mapped out from day one, many of the lengthy shots didn’t really change in the three years of shot production. Because we did a virtual prelight of the entire film with, the whole film was essentially locked before we even started shooting.” [“Facing the Void”]
David counted 206 shots in Gravity, not including the two opening titles about life in space being impossible. This suggests that Howell is right, and that the film underwent little revision after the planning phase.
Several years ago I suggested on this blog that animated films, notably those of Pixar and Aardman, were on average better than mainstream live-action films because they had to be planned so carefully and thoughtfully. Gravity, being very close to an animated film, provides more evidence for that claim. Not that thought, time, and money can guarantee quality, but they certainly narrow the odds.
Iris in
The Light Box technology is astonishing enough, but within its confined space there also had to be a way to photograph the actors. In Lubezki’s interview with Bryan Abrams, he explains:
So we built the box, but that wasn’t it. To be able to shoot inside the box, we had to build a special rig that holds the camera and moves with motion control. So we had people build a very narrow, lightweight but sturdy rig to control the camera. If you imagine the big box of LEDs, it has a gap that is almost a foot and a half or two feet wide, and the camera has to go into the box and make all these moves to make the audience believe that Sandra is turning and turning, but it’s really the camera and the environment in the box that is moving. So we built the box, the rig, and then used a company called Bot & Dolly. These guys are from San Francisco, and they use robots from the automotive industry. They redid all the software for us, so we were able to use these robots to move the cameras and the lights around the actors. It was just a big ballet of gadgets and new technology for the film.
Bot & Dolly is a San Francisco company specializing in robots for the automobile industry. It built or perhaps modified an elaborate rolling, multiply-jointed camera mount called Iris especially for Gravity. It has been used in other features and in ads since then. (See image at the bottom.) An impressive demo film shows the Iris gracefully writhing about, quickly pointing the camera in many directions. (The camera in the film is a Red, though Gravity used an Alexa.) According to ICG Magazine, “The firm devised a Maya-based series of commands that allowed Framestore animators to direct the robots in ways that matched previs action in precise detail.” (Maya is the industry standard computer animation program.)
Typically this camera was inserted through an opening in the Light Box and swooped around the actor, who stood in a gyroscopic basket, seen in the production photo below. The photo shows one side of the Box open, though this would not be the case during shooting:
The combination of the Light Box and Iris made it possible to blend the special-effects shots and the live-action photography of the actors so smoothly that there is no “uncanny valley” effect, no sense of an obvious matte painting stuck into the middle of an image. The shots in Gravity are all photorealistic to a degree that is rare, if not unique, in recent effects-heavy films.
Iris brings us back to the comparison with Central Region. Snow built a special camera mount (below) designed to allow his images to rotate freely in almost any direction. During the three-hour film the camera never repeated any of its trajectories. Some images were close views of the pebbles on the ground; others were upside views of the bleak Canadian mountains in the distance. A nighttime segment was completely black except when the moon occasionally swept through the frame. The one area that the camera didn’t survey was the camera support itself, the “central region” of the title.
The vital difference between Snow’s machine and Iris is that the new system has no fixed anchor. Not only does it slide on a track, but everything it photographs can be digitally altered to erase any traces of the machine. It moves with entire freedom through a constructed space that has no central region, no fixed point around which everything else revolves.
Puppeteers and eyes
Gravity‘s utterly spherical space, beyond anything we normally find in commercial cinema, placed unusual demands not only on camera movement but also upon the actors’ blocking and performances. Our first entry on Gravity begins with a quotation from Sandra Bullock, which included the statement, “No character was like Stone, no film set was ever like these sets, not one member of this crew had ever done this before.” That may seem an exaggeration until one grasps how Bullock and Cuarón’s team built her character.
We all know from infotainment coverage that Bullock was isolated in the Light Box through entire days and that it was a trying experience. What doesn’t come through in such accounts is that she was often enclosed in the gyroscopic basket, visible in the photo of the Iris rig and Light Box above, as well as in the same setup visible behind Cuarón in this photo:
That was only the start of it. Anne Thompson’s interview with Cuarón and producer David Heyman reveals some of the details of blocking a character who is unrestricted by gravity:
AC: The physical aspect, not anybody can do what she did. On the one hand the physical discipline she went through to make this film, the training and the workouts. She also has an amazing capability for abstraction. Those emotional performances, it was as if they were an exercise in abstraction, like she was bonded to very precise cues. And physically that was very difficult: she trained and practiced like crazy, together with the stunt people and special effects. And the puppeteers from “War Horse” were helping her, supporting a leg or an arm, all the floating elements, they were creating approaching objects toward her in perfect timing. Then after she practiced so much her whole concern was only about emotions and performance.
Imagine a ballet dancer with really strict physical discipline in terms of what a body has to do, positions and precise choreography, who goes through months of training for one choreography so when they are performing they have expressiveness and emotion.
What was the most challenging scene to realize?
David Heyman: When Sandy comes into the ISS for the first time. She takes off her suit, then goes into fetal position, all in one shot. It was the most difficult. All the objects, getting the suit off, and into fetal position in such a way that it felt effortless, not as it was–she was sitting on a bicycle with one leg tied down leaning back in a 12-wire rig, with puppeteers. One of the things you forget about Sandy’s performance, which seems so truthful, is all the effort and physical exertion that went into making it, the precision of the technical aspects. She had to move her hands at a third of speed — zero G –while talking. Each shot connects with the next at very precise points where her head began and end and begin and end. She’s on a bicycle stringing uncomfortable with people moving around on 12 wires, through it all, with no gravity. Physically the body must not show the tension, so it looks effortless. What I loved about it is the performance behind the visor shines through, her eyes. You can’t slouch your shoulders to show sadness or weight, it’s just the eyes.
Bullock did all this with four 10′ by 20′ walls of LEDs projecting moving images of the earth and of exploding space stations around her. I think it is safe to say that this was a unique kind of performance.
The sounds of silence
As the film’s ominous opening titles point out, there is no sound in space. In keeping with the overall attempt to duplicate the effects of weightlessness immersively, Cuarón’s team limited the track to two types of sound: diegetic sounds heard by the characters and a non-diegetic, modernist musical track. In an interview with Cuarón, Wired‘s Caitlin Roper pointed out that there was an explosion in one of the trailers. Cuarón replied:
Yes, but that’s just the trailer. I honor silence. The only sound you hear in space in the film is if, say, one of the characters is using a drill. Sandra’s character would hear the drill through the vibrations through her hand. But vibration itself doesn’t transmit in space—you can only hear what our characters are interacting with. I thought about keeping everything in absolute silence. And then I realized I was just going to annoy the audience. I knew we needed music to convey a certain energy, and while I’m sure there would be five people that would love nothingness, I want the film to be enjoyed by the entire audience.
As in other areas of the film, we see the compromise between an experimental technique–an attempt to suggest the silence of space–and the desire to provide something more familiar for the broad audience. In this case, music acquires an expanded role, substituting for sound effects and conveying the rapidly shifting emotions of the scenes.
Sound effects are not entirely eliminated. Many sounds that the astronauts would hear via vibrations of things they come into contact with are included. In some cases these are fairly clear, as with the voices heard within their helmets–their own voices or others’ via radio. Other effects are heard in a distorted fashion. Glenn Freemantle, the supervising sound designer and editor, describes the process:
“When [Bullock] is in the suit, you hear her voice and her breathing, and you hear through her suit when she is in contact with things,” he explains. His team captured sounds by recording with contact mics at car plants and hospitals. “We even recorded through water with a [submerged] guitar,” he recalls.
One obvious example of distortion comes in the opening scene, when Stone is unscrewing bolts and sliding a panel out of the transmitting device she is working on. The sounds of the bolts and the sliding metal are audible but muffled, as though they were recorded under water or electronically manipulated.
Yet other sound effects not heard by the characters were relegated to musical expression. As Angela Watercutter put it in a Wired article based on interviews with Cuarón and composer Steven Price,
Every time there’s a collision in the movie the audience doesn’t hear a bang – they hear a sonic boom. The same goes for the characters’ — and, by extension, the audience’s — feelings of anxiety, claustrophobia, and agoraphobia. Much of what is seen in Gravity is terrifying, and when the audience can’t hear the horror of a space shuttle breaking apart or an airlock flying open, Price had to fill the void with his nerve-wracking score.
Cuarón dictated that one of the rules for the film’s score was the eliminating of percussion, to avoid the “cliché of action scoring.” Watercutter continues:
As a result the score for Gravity serves as more than just musical accompaniment – it also provides the movie’s sound effects. There are some non-music sounds that would be space audible, like the ones transmitted by vibrations characters feel in their spacesuits, but for the most part everything that happens in open space is accompanied only by Price’s music and the voices of Stone and astronaut Matt Kowalski (George Clooney), which “freed up the rest of the frequency spectrum for me,” Price noted.
Price used a mix of organic and electronic sounds to meld the natural world of space with the mechanical world one of the space exploration. There are also moments where he took an analog instrument – a cello, for example, or even a human voice – and ran its notes through a synthesizer or processor in order to create a whole new sound. And for the opening song on the score, “Above Earth,” Price took a track he was already working on and slowed it to about 1/60th its original speed. “Basically,” Price said, “what you’re hearing is the space between the notes.”
In an interview with Rolling Stone, Price discussed some of the aesthetic principles and functions he aimed for with his score:
Really it was all very much led by the character of Ryan. I tried to be with her all the time. The idea was that the music was up there in space and we made it very immersive and used a lot of elements and a lot of layering so that things would move around you all the time. The writing of those elements and what they were, were always influenced by what Ryan was feeling and where she was emotionally in the whole thing. And also where the camera was, where things were moving and what point of view the camera was facing, whether it was looking at them or kind of looking through their eyes. Some of it was melodic and some of it was intended to underscore a kind of emotional journey, and then there were a lot of sounds that were there to express real terror. It was those two extremes, really, expressing the beautiful nature of where they were but also absolutely a massively terrifying situation.
With little expertise in musical analysis, I can simply say that I hear the score as a combination of traditional instrumental music and electronically synthesized instrumental music. Under this, typically in tense passages, there are abrupt or charging percussive emphases, not using percussion instruments but, in some cases, deep string chords. Scenes of damage or tension are sometimes accompanied by sounds like stressed, grinding metal. Other sounds like distorted, high-pitched radio waves (in the “ISS” and “Fire” tracks) are included, reminiscent of electronic music of the 1960s.
Other critics have offered suggestive descriptions. Justin Chang’s review refers to “Steven Price’s richly ominous score, playing like an extension of the jolts and tremors that accompany the action onscreen.” David S. Cohen and Dave McNary’s Venice festival coverage characterizes the track: “Much of the action, even the debris storms, plays out against eerie silence, broken only by the score. The silence is more startling after the score builds to deafening crescendos, then stops abruptly. But during the interior scenes, the rumbles and groans of failing space gear are as frightening as the roars of any classic movie monster — even more so because their source is unseen.”
Price has contributed a remarkable score, one which is highly original and yet completely motivated by the story situation it accompanies.
The space between
The immersive, 360-degree surrounding and sound fields made Gravity a natural for 3D exhibition, but they also posed unique problems. Given the long takes, the need for complex camera movements, the demands of the LED Box, and the complicated acting conditions, it would have been very difficult to shoot the film in 3D. In most scenes, of course, there were no real objects juxtaposed in different layers of depth in front of the camera. Even the actors’ placements in long shots would have be created digitally. So the project had to be converted to 3D. But this forced choice actually yielded strong results.
The press coverage of popular cinema has come to treat films shot in 3D (“native” 3D) as pure and admirable and films converted to 3D after shooting as crass and compromised. But is there all that much difference? Even Avatar, the film made with an intention of promoting the universal use of 3D, had some converted footage. With conversion technology improving, the notion of waiting until after filming to create a movie’s 3D is becoming less onerous. As Variety‘s David S. Cohen pointed out earlier this year, Iron Man 3, Man of Steel, Star Trek into Darkness, and Pacific Rim have been post-converted with little objection from the public or press.
That conversion techniques for generating 3D images are not inferior became much more evident during the early decision-making process for shooting Gravity. Nikki Penny, the film’s executive producer, took some test footage shot by in 3D to Prime Focus World, a conversion house that ended up doing 27 minutes of Gravity. The filmmakers were trying to decide whether to shoot the live action portions in 3D or use conversion. In an article on Creative Cow, Debra Kaufman explains what happened:
The production had done a test shoot in 3D, which involved placing the cumbersome 3D rigs inside the cramped space capsule. When Penny brought the 3D live action footage to Prime Focus World, she asked that they test 3D conversion by utilizing a single eye from the same footage. The results convinced Cuarón and producer David Heyman that conversion would not only look as good as shooting in native 3D, and would be much easier and more efficient to accomplish.
That is, the footage shot by one of the two lenses in the 3D setup was separated out. It was then treated as if it were native 2D footage and put through a conversion process to create a 3D image. The result resulted in 3D that was not inferior to the original native-shot 3D. The lesson, I think, is that the question is not usually whether a film is shot in 2D and converted; it’s whether it was planned to be completed as a 3D film (and has sufficient budgets and skills invested in it) .
Gravity couldn’t be shot in native 3D, since in most scenes there were not real objects juxtaposed in different layers of depth in front of the camera. Also, the camera was too cumbersome to fit into the space-capsule sets. With so much of the characters’ surroundings done as CGI, however, the conversion to 3D could be done concurrently with the filming. Kaufman describes the process at Prime Focus World, one of the firms that handled the conversion:
Unlike the more typical post-production 3D conversion, Gravity involved PFW working on the 3D conversion during production. The work on 3D conversion began with six months of pre-production, during which the production’s Stereo Supervisor Chris Parks worked closely with the PFW team to explain his carefully plotted depth map, which contrasted the vast emptiness of space with the tight, nearly claustrophobic quarters of the space capsules.
From the beginning, the challenge for Prime Focus World would be to make sure that the 3D converted footage integrated seamlessly with the extensive 3D CGI. Both the live action footage and CGI would be 3D, but 3D from two different worlds, conversion and visual effects – and they would both be active or “live” during the production process. At the same time, the PFW team wanted to retain the creative flexibility of its View-D conversion process, while integrating the stereo VFX universe. What made it trickier was that, unlike a completed film, Prime Focus would be working with work-in-progress shots and an open edit.
For more on the technical aspects of the integration of converted footage and CGI, along with an example of the stages that went into creating a single shot, see the Kaufman article.
In an essay on ICG Magazine, Vision3 stereo supervisor Chris Parks describes some of the narrative functions of the film’s 3D:
We had a virtual camera at Framestore that let us control depth functions. When Sandra floated off in space, we separated her slightly from the starfield, using 3D to make her feel very small. At another point we went very deep, when we see her POV as her hands reach out to those of another astronaut coming to camera. At the point when they make contact, we increased the interaxial to five times normal, then scaled it back down as they separate and drift apart.
Parks also comments on the scene where Stone and Kowalski look through the shattered windows of the space shuttle and a crew member’s dead body suddenly falls into the shot:
Alfonso asked how the 3D could make this more powerful, but without just throwing something out into the audience to make them duck. We decided to float a little Marvin the Martian doll out into the audience, which is a kind of fun, lighthearted tension-breaker, and then we whip-pan right off that to the dead astronaut, which makes the emotional revelation more jarring.
In fact the Marvin doll (derived from Chuck Jones’s Warner Bros. cartoons) comes diagonally forward from the depths of the shuttle interior, and the camera pans with it as it moves out of the ship past Stone, who watches it and then turns back to look inside again. The corpse falls into the shot from above left, but not out toward the audience. It bumps Stone’s helmet, and the camera pans to reveal it more fully and continue almost nonchalantly onward to show another dead astronaut further back in the shuttle interior.
Finally, Parks points out an expressionist distortion of space for subjective purposes in the dream sequence where Kowalski joins Stone in the Soyuz landing vehicle:
It’s a dream sequence that doesn’t reveal itself as such right away. To give a subconscious impression that something different was happening, we pushed the top right corner into the set while pulling the bottom left corner ahead, skewing the whole view. That sense of unease represents, to me, how 3D can be expanded beyond just giant VFX movies. It’s a tool that can be most effective in very small spaces, as this one shot reveals.
Outside the dream scene, we see the wall panel of instrument controls at an angle to the camera, with Stone in her seat at the left. During the dream, the panel is suddenly turned so that it is almost straight into depth, so that we are pressed up obliquely against it. Stone’s seat at the left is further away from it. The result is that the space is strangely skewed during the dream.
In all, shooting in long takes, building each shot with CGI yet including complex camera and figure movement, canceling the sense of horizons and ground planes, and enhancing all these choices through 3D, has resulted in a film in which stylistic patterning becomes an object of fascination in its own right.
Despite the occasional joke about a Gravity sequel, it seems unlikely that Cuarón will tackle similar subject matter and formal strategies in his next film. Dealing with space without horizons and characters without weight was a formidable task. At the end of his Wired interview, asked what his next film will be, he replied, “Any movie in which the characters walk on the floor.” Welcome back, axis of action.
Most of the frames used here and in Part 1 were taken from a New York Times article containing a clip from the opening shot with commentary by Cuarón.
Thanks to Stewart Fyfe, who shared links to some of the sources cited in this entry.
Bette Davis eyelids
Bette Davis, ca. 1950; caricaturist unknown. From Miguel Andrade’s site.
DB here:
Janet Frobisher, mystery writer, has murdered her husband. Naturally, she telephones her lover and asks him to come over. But before he arrives, Janet finds that the runaway George Bates has come calling. George has been her husband’s partner in bank fraud, and now they’ve gone further. They robbed the bank at gunpoint, and a policeman was shot. George faces Janet and demands to know where her husband is.
Nobody is likely to call Another Man’s Poison (1952) a masterpiece, or an undiscovered auteur gem. (Irving Rapper has, however, signed some better-than-average pictures.) Like many ordinary movies, though, it can tell us some interesting things about cinema if we look closely. Especially when that look takes in Bette Davis.
I had to restrain myself from adding a soundtrack link for this entry. You know the one. The earworm may be at work already. But having you listen while you read would probably only distract from my point.
Eyeball to eyeball
That point is one I’ve made before. We humans are very good at watching each others’ eyes. Evolutionary psychologists debate how that skill might have evolved, but there’s little doubt that we can “mind-read” on the basis of others’ gaze direction and other eye-related cues. Of all the arts, cinema probably has the most powerful ability to galvanize and channel our reactions solely through the way people use their eyes.
But what’s an eye? I argued in an earlier entry on The Social Network that eyeballs as such aren’t very expressive, despite poets’ claims to see the soul there. Dilations are about all you get. The real expressive work gets done by gaze direction, the brows, and the lids. Blinks help too. Lately, watching films from the 1940s and early 1950s for a book I’m planning, I was struck by how the great divas of that era used their eyes.
Consider for example Barbara Stanwyck in the Mitchell Leisen weeper No Man of Her Own (1951). Helen Ferguson has innocently assumed the identity of the dead daughter-in-law of a wealthy family, and she’s torn between revealing her lie and protecting her baby. So in most scenes her look is intent and direct. She uses the screen actor’s usual tactics of steady gaze and motivated blinks, with brows and mouth carrying the emotional impact (below, shocked anxiety; then distress).
Even when she’s thinking, her eyeline remains steady and she doesn’t play much with her eyelids.
What about when Stanwyck is much less innocent, as in Double Indemnity (1944)? Devious as she is, Phyllis Dietrichson meets Walter Neff’s eyes squarely. “There’s a speed limit in this state, Mr. Neff.”
When Phillis isn’t looking straight at Neff, it’s when she’s pretending to be demure and concerned about her husband’s safety—and acting as coy as Brigid O’Shaughnessy in The Maltese Falcon. But once Neff sees through her effort to insure her husband, she glares at him unwaveringly.
Part of Stanwyck’s star persona is the bold woman who responds frankly to whatever is put before her. When it comes to evasive maneuvers, though, there’s Bette.
Putting a lid on it
Publicity photo for Jezebel.
Her eyes are big and can be quite round, of course. They also sit remarkably centrally on her face, thanks to her high forehead; this quality is accentuated when her hair is brushed back, as it often is. What especially interests me today, though, is her eyelids. If Bette rolls her eyes at us in those Warners publicity shots, she can also create hooded eyes that suggest she’s harboring secrets.
Bette has remarkable control of those eyelids; she can close them to a very exact degree. In performance, the slight drooping of the upper lid, combined with a small shift in her gaze and a turn of her head, can shade the line or word she speaks. Add that sullen mouth and her vocal tone and rhythm, and you get a nuanced suite of micro-emotions.
Take the moment in Another Man’s Poison after Janet Frobisher tells George that she’s killed her husband. She rushes into a two shot favoring her as George says: “You could’ve divorced him.” Her reaction is an eye-flick, evading his look but still radiating defiance.
Now begins a series of micro-movements that shift Janet’s reaction away from George. She explains how her husband kept her tied to him. “He/ was/clever”: On each word, her expression, eyelines, and eyelids change minutely. Then she pauses.
“He saw/ to that/ too” gets mapped onto three more changes, with traces of a smirk accompanying an eye-shift on the word “too.”
But Janet isn’t looking straight at George yet. She’s got more to say by way of explaining why divorce wouldn’t work: She and her husband continued to have sex. She puts it more indirectly: “He paid me”—pause when she lifts her eyes to look back at George—“visits.”
This instant of looking sharply back at George, as she had at the start of the shot, drives the point home and becomes the climax of this phase of the exchange. Eyelids, brows, chin, mouth, and gaze have all cooperated in creating an emotional detour away from and back to her questioner. Bette’s tiny side-glances show us a woman thinking and reacting to what she’s thinking, relishing what she’s going to say and then watching the effect of what she says. It all takes eight seconds.
Don’t be the wide-eyed ingenue
You can see the two stars’ technique operating very early in their careers. Stanwyck is the name star of So Big! (1932) and Davis is fifth-billed. Above, we find Stanwyck, playing the nobly suffering mother Selina, using her direct-gaze strategy (though as she ages, the eyes get a little pinched). By contrast, we have Davis as the saucy young illustrator Dallas O’Mara. Selina’s son Dirk asks Dallas why she doesn’t love him. When she answers, William Wellman’s staging gives Davis a little aria of face-time at the piano.
Dallas explains that she’s attracted to men who have confronted the rough side of life. I can provide only excerpts of what is a forty-second shot, full of shifts of head position, facial expressions, and eye movements, complete with finely calibrated eyelid work. The passage reminds us that Davis’ dynamic expressions and eye movements are often motivated by her playing characters full of jittery pep, talking fast and thinking faster. She will even deliver phrases with her eyes closed—here, speaking of men with hands scarred from work and struggle.
As she says, “You haven’t a mark on you, Dirk,” Dallas reaches across to grip his forearm. A new phase of the scene begins, but still with the suite of slight head turns and eyelid action.
Dallas says that if he’d kept on as an architect instead of taking refuge in a safe business job, his face would show it. As in Another Man’s Poison, Davis concludes her monologue by turning to face the man and deliver the final line directly. From early in the scene, however, Dirk has turned his face aside in shame.
Where would his marks of character show? “In your eyes, in your whole being.” She peers up at him, her face closer than at any other point in the scene, and her hand lifts from his arm to accentuate her frank but brutal blow to his pride.
Which makes our last view of her all the more arresting. In the final scene, Dallas meets Dirk’s mother and imagines her as an ideal subject for a portrait. Now the flighty young artist is riveted on the steady, serene gaze of the older woman.
In this climax, Dallas becomes what Dirk has called her—“a wide-eyed ingenue”—but in her rapt admiration she proves herself worthy to be Selina’s daughter-in-law.
Bette, eyeballing us
Now that we know the role Bette’s upper eyelids play, we can appreciate other moments when she milks their effects virtuosically. Go back to Another Man’s Poison. George tells Janet that he has the weapon used in the bank robbery—the pistol that bears her husband’s fingerprints. As George starts his line, she’s taking a drink in the foreground. Lifting the glass, she tips her head back too so that her eyes are just visible under her lids—and they’re looking out at us.
George says, “I’ve got the gun.” Janet lowers the glass, but she keeps it poised. Now her lids and eyelines present her reaction to George’s information that the pistol bears the husband’s fingerprints. You see her thinking about evasive action.
This moment in effect spotlights Davis’ use of her eyes; she’s frozen in place, and they’re the only things that move.
Early in the film, we’re given a sort of primer that trains us to watch Janet/ Bette’s eyelids. The first scene shows Janet making her call to her lover from a phone booth. It’s staged with her in profile, so that her brows and mouth are relatively unmoving and the eyelids, centered in the frame, become quite salient. I won’t try to follow all their tiny fluctuations, in coordination with the chin’s angle and the mouth, but these samples should give you the flavor. (Note the very slight difference between the first and the third image, and the second and the fourth).
A more frontal view of La Davis would have been a more characteristic star introduction, but it’s as if the film is saving her full-face firepower for later scenes.
There’s other evidence that Bette was considered to be able to hold a scene by an eyelash. In Payment on Demand (1951), flashbacks from Joyce and David’s miserable marriage take us to happier days. One scene shows the couple embracing on a hospital bed after Joyce has given birth to their second child.
Joyce learns of David’s plans to move out of town, but she resists and sits upright. This brings her distraught reaction home to us with the now familiar coordination of eyeline, eyebrows, and eyelids with the mouth and shakes of the head—another suite of micro-behaviors I can merely sample here.
But then Joyce relaxes and falls back, hiding her face as the camera cranes up slightly.
Director Curtis Bernhardt has reframed the shot so that as Joyce curls up on the pillow, one eye peeps out. We don’t see her mouth replying to David’s lines, but we get the customary fractional eyelid changes, as in the phone booth scene above.
Eventually Davis moves her shoulder and reveals Joyce’s mouth, but for several seconds we’ve been obliged to follow the small movements of her lids as the only clue to her calming down—and getting her way with David. This is, needless to say, all done without a close-up.
Hollywood cinema is a highly formal cinema, as conventional in some ways as commedia dell’arte. Yet that doesn’t mean it must trade only in gross effects. Admittedly, much of today’s cinema has sacrificed nuance for brute force. All the better, then, that returning to even minor films from the studio era can remind us of how many opportunities the medium affords.
Bette Davis isn’t the only virtuoso performer, of course, and many of her contemporaries show the same kind of gifts, sometimes put to different ends. She offers a convenient illustration of how film actors can cultivate meticulous control over facial regions we don’t normally think about. She makes up for being short and rather slight by playing her face like a chamber ensemble, with every “voice,” eyelids included, contributing to the restless dramatic flow.
Okay, I know: The song was running through your head all the way through. You deserve a break. Go ahead, but you might as well watch something too.
On the evolutionary implications of our eye behavior, see Michael Tomasello et al., Why We Cooperate (Cambridge: MIT Press, 2009). Tomasello argues that the need for social cooperation favored signals of shared attention; to work together, we need to notice things that other people are looking at. He also points out:
All 200-plus species of nonhuman primates have basically dark eyes, with the sclera—commonly called the “white of the eye”—barely visible. The sclera of humans (i.e., the visible part) is about thee times larger, making the direction of human gaze much more easily detectable by others. A recent experiment showed that in following the gaze direction of others, chimpanzees rely almost exclusively on head direction—they follow an experimenter’s head direction up even if the experimenter’s eyes are closed—whereas human infants rely mainly on eye direction—they follow an experimenter’s eyes, even if the head stays stationary (pp. 75-76).
But tracking my eye direction helps you, not me; how could it have evolved? Tomasello hypothesizes that making eye direction salient developed in a cooperative social environment. It’s part of social intelligence, in which mind-reading works to everyone’s benefit in shared tasks.
A vast resource on all things Bette is this site. Some perceptive remarks on her acting style are at Uncle Eddie’s Theory Corner. Jim Emerson offers an interview with Miss Davis in a smoke-filled room, while Roger Ebert presents an admiring appreciation of All About Eve.
An earlier blog entry here reflects on the performance of another sacred diva of the period, Joan Crawford. If you’re interested in a wider account that fits such matters into a broader theoretical perspective, including folk psychology, try this essay.
Hand jive
The Magnificent Seven.
DB here:
In the long trailer for The Girl with the Dragon Tattoo, Rooney Mara as Lisbeth Salander makes a gesture to show that her fabulous memory has recorded the documents Blomkvist wants her to read over. She raises her hand toward her head and flicks her spindly forefinger.
It reminded me of how important gestures are to film performances, and how comparatively rare they are today. One feature of what I’ve called the contemporary intensified continuity style is a reliance on tight facial shots, so that actors work more with their eyes, eyebrows, and mouths than with other body parts. This solves one perennial problem actors have: What do I do with my hands? But it does cut off a lot of expressive possibilities. When filmmakers used more medium and long shots, actors could use all their equipment—stance, bearing, knees (as in The Cary Grant Crouch), elbows (The Cagney Cocked Elbows), shoulders. And arms, and hands. Nowadays if actors want to activate their hands in a dialogue, they usually have to lift them to their faces because the director hasn’t provided a looser, more distant framing.
I’ve already shared some thoughts on eyes (and argued that they aren’t as expressive as we usually think), eyeblinks, and sleeves. I’ve written about hands before, and Tim Smith has tested some of the things I discussed. Now I’d like to write about two of the best hands in the business. Before I do, though, let’s look at some simpler cases.
Handiwork
Rooney/Salander’s finger flip is a one-off, a staccato gesture that communicates instantly. It reminds us that she is, for all her cybernetic genius, rather nonverbal. Her dialogue is laconic, her face impassive. The gesture comes and goes like a keystroke. If there are air-quotes, this is an air-period.
Something more emphatic happens in Wuthering Heights, as you’d expect from (a) the more extroverted emotion of the tale and (b) the fact that the owner of the hand is matinee idol and occasional ham Laurence Olivier. Early in the film, Lockwood is staying the night in Heathcliff’s dismal mansion. He tries to close a shutter, and finds the windowpane already broken. He’s startled by what he hears (“Heathcliff! It’s Cathy!”) in the stormy night. He also thinks he sees a phantom woman. Unnerved, he pulls his hand back through the pane and stares at his trembling fingers.
This occurs in the frame story. Later that evening Lockwood is told of the tragic romance of Heathcliff and Cathy, and we get an extended flashback. Cathy yearns to join the high-flown elite in the neighborhood and is about to go out with Edgar Linton. In her petulance Cathy calls Heathcliff a stable boy and a beggar with dirty hands. Heathcliff stares down at those hands (“That’s all I’ve become to you, a pair of dirty hands”), before he slaps Cathy with one, then the other, crying, “Well, have them, then—have them where they belong!”
He stumbles from the room in a mixture of anger, shame, and confusion. Coming down the stairs he confronts Linton, who has just arrived to pick up Cathy for the party. Heathcliff stands awkwardly on the stair, his hand held at an angle, as if it’s something he’d like to slough off.
Back in his stable loft, Heathcliff smashes his fists through a window, in the manner of the broken pane that Lockwood will discover in the frame story.
Later Heathcliff, now wealthy, returns to the neighborhood. When he visits Cathy, who’s now married to Linton, he initially hesitates to shake hands with his old rival. It’s a beat long enough to remind us of the class difference marked in a pair of hands.
For a more unstressed example, consider The Magnificent Seven. Throughout the movie Steve McQueen invents hand business with the apparent aim of stealing every shot he’s in. At the very start, poor Yul Brynner is trying to be the brooding main attraction, ominously lighting a cigar. But Steve is making us watch him by shaking shotgun shells against his ear and then holding his hat up against the sun.
Soon afterward Steve sets a whisky bottle precariously on a fence post while Yul is acting seriously serious. Then McQueen has the nerve to fiddle with his hat so that Yul can no longer ignore him.
Much later Steve faces down Calvera’s outlaw band and strides into the foreground, back to us.
In such a setup, the actor who turns away is traditionally ceding the audience’s attention to the frontal players in the distance. Not Steve. Once he gets into place, he swivels just a bit and swings his hand behind his gun belt. (That instant surmounts this entry.) Then he tucks one finger in his hip pocket in the lower right corner of the shot.
If Tim Smith ran an eye-scanning experiment on this shot, my hunch is that a fair number of his subjects would watch Steve’s digits.
Hands down
McQueen’s scene-grabbing reminds us that once a filmmaker has framed the performer from fairly far back, judicious use of the hands can activate areas of the frame we normally don’t watch. After all, in most shots the upper half carries the most information, especially with respect to the actors’ bodies. My favorite example of highlighting a lower corner remains a shot from Kriemhilde’s Revenge (above). The director, Fritz Lang, laid out his frames with the precision of an engineer.
Even in a less exactly composed shot, slight hand movements down the frame can add gradation of emphasis. Smash-Up: The Story of a Woman presents some hard-boiled poker players forced to listen to a radio song that interrupts their game. They sit still, but their fingers stir a little, suggesting their impatience to get on with playing.
Now we’re moving into the area I described earlier this fall as scenic density. Several of my examples there involve small gestures. To take another instance, here’s Mercedes McCambridge in her Oscar-winning performance in Robert Rossen’s All the King’s Men. As tough campaign strategist Sadie Burke, she’s trying to explain to Willie Stark (Broderick Crawford) that he’s running as a dummy candidate for the very men he opposed at the start of his political career. (The whole movie will remind any Wisconsiner of what our Governor and his pals have been up to lately.) The scene pivots around drinking, and the saliency of Sadie’s hands is heightened by the fact that the men’s hands aren’t used at all.
After she pours herself a drink, Sadie tells Willie he’s been framed, holding her glass at her waist.
She walks away to the right, then turns and says that Willie is “the goat.” She sets her glass down at the far right of the shot.
She steps toward him and leans on the chair, tipping forward.
Jack Burden (John Ireland) steps to center frame and says that’s enough. But she presses in on Willie, saying his egotism has made him blind. There’s a cut to a tighter framing as Sadie faces Willie in profile.
She turns away, mocking Willie, and yanks the speech out of Jack’s typewriter.
She steps left to the foreground and pauses, momentarily abashed by her attack on the man she loves. Her hands do something below the frame line.
Stepping back and turning away from us, she lets us concentrate on Willie. He quietly asks Jack, “Is it true?” As Sadie shifts her position, she raises her arm and we see she’s pouring another drink.
Jack replies after a pause: “That’s what they tell me.” As Willie hangs his head, Sadie’s hand emerges at the bottom of the shot to offer him the drink she’s poured. A more assertive director would have cut to a big close-up of Willie and the proffered glass, but here the information slides into a rarely used area of the frame. The Kriemhilde trick, we might call it.
Willie takes it, and Rossen cuts to a low angle on all three, with Jack and Sadie watching the key gesture: Willie, a teetotaler, downs the drink.
Now the only hand visible is his, and the narrative momentum has passed to him. He’ll change his tactics and crush his handlers.
I can’t resist a more recent example of a similar strategy. In Mysteries of Lisbon, Raúl Ruiz keeps fairly far back from his players, filming many scenes in a single distant shot. Even when he breaks the scene into shot/ reverse-shot, he can isolate gestures in the full frame in ways that echo the handwork in Kazan (and in the work of other directors, particularly in the 1910s). Elisa de Monfort, quietly mad with vengeance, calls on Eugénia, the wife of her hate/love object Alberto de Magalhães. In the opening setup, Elisa sweeps in to wait for Eugénia, setting a purse on a distant end table. (The action is quite marked on the big screen, but might be missed on video; this is the price the modern director pays for using long-shots, I guess.)
At the end of the conversation, Ruiz cuts back to the main set-up. Because of Eugénia’s position, the purse nestles in the sort of slot that we find at the bottom of the frame in All the King’s Men above. Elisa rises and goes to pick it up, her gesture highlighting it.
It contains the eighty thousand francs she is trying to return to Alberto, a love pledge he has been refusing. Elisa picks it up, then drops it back to the table, defiantly leaving it for him.
By now I’d again bet that Tim Smith would find our eyes fastened on this tiny bit of the screen. Hands point us to props, and close-ups may not be necessary.
All hands on deck
I’ve praised Henry Fonda’s handicraft earlier on this site (and in Film Art: An Introduction). Maureen O’Hara said of him: “All he had to do was wag his little finger and he could steal a scene from anybody.” But to see his long fingers and fluid wrists at full stretch, put him in a combo. There’s a remarkable six-minute scene in Mister Roberts that lets Fonda (playing Roberts), William Powell (as the ship’s doctor), and Jack Lemmon (as Ensign Pulver) make beautiful music. I can’t go through it all, but let me mention some high notes.
Roberts wants to give the crew a day’s liberty, and to that end he’s bribed a port officer with a bottle of whisky he’s been saving. But Pulver, a lecherous layabout, has convinced a nurse to come to the cabin he shares with Roberts, and he’d planned to seduce her with the Scotch. So to help Pulver out, Roberts and Doc will concoct fake Scotch with ingredients they have at hand.
As I work it out, Powell supplies gravitas, a steady ground bass of minimal, exact gestures. Lemmon, playing Pulver as wound much too tight, punctuates his passive role with nervous head movements and stabbing arms. He supplies percussive accents. Fonda’s relaxed but severe playing, neither stolid nor spiky, is the melody that floats through it all.
At the start, after the older men have entered, Pulver is slouching, Doc is wiping off sweat, and Roberts is looking for his monthly letter requesting transfer.
As Doc replaces his hat, Roberts stresses his explanation about the whisky with a quietly tapping forefinger, a gesture you can hear on the soundtrack.
When Pulver realizes that the sacred bottle is gone, he jolts into activity, frantically pointing, as if in amplified imitation of Roberts.
Throughout the scene, Pulver will echo Roberts’ gestures, as when the senior officer lays his arm across his belly.
This mirror-effect is tied to the larger dramatic dynamic: Pulver looks up to Roberts, but his selfishness keeps him from being anything like his model. In the film’s last scene, however, he will become the new Roberts.
As Roberts and Doc decide to help Pulver, they give virtually silent-film renditions of the concept, “planning and preparing.” Powell roles up his sleeves, and Roberts claps his hands and then rubs them together as if hatching a plot. Hand-rubbing will be his refrain through the rest of the scene.
No actors under age fifty today, I think, would dare this sort of straightforward stylization. Here’s something to do with your hands, cast members.
When Doc requests a Coke to add to their ethyl alcohol, Pulver yanks a bottle out from his mattress and thrusts it across the CinemaScope frame.
Doc adds the Coke with surgical precision. All eyes are on his hands, while Roberts’ hands are out of frame.
Pulver is still skeptical and sits back down on his bunk. The dramatic impetus passes to Fonda, whose long forefinger rests meditatively under his nose: Thinking personified.
Fonda has to shift his hand in order to remark that Scotch has always reminded him of iodine. But what other actor would rotate his wrist and stick his thumb under his eye as he says that line? Try it yourself, and I bet you find it awkward. He executes it smoothly.
Without having to get up, Roberts reaches back into the medicine chest and pulls down a bottle of iodine. He passes it to Doc and signals the handoff with a little flourish.
Earlier we’ve seen Doc do the mixing as a solo performer, in the over-the-shoulder shot shown above. As Doc blended the stuff in other framings, Fonda kept his hands below the desk top, giving Powell the stage. But now we get two for the price of one: Powell’s meticulous adding of a drop of iodine to the brew, Fonda’s revisiting his calculating hand-rubs.
Fonda’s slightly out-thrust tongue is a grace note.
Pulver tries to sample the blend, but Doc beats him to it. “We’re on the right track!” he declares. Doc asks Roberts what else he’s got and Fonda, in a beautiful medium-shot with eye-catching colored medications arrayed before him, mimes the act of mulling over the next ingredient. His hand flits gracefully over the bottles and jars.
They settle on hair tonic for a touch of ageing. Again Doc adds the ingredient with precise pouring, and now he prepares for Roberts to test it. Into the frame come Fonda’s hands.
To accentuate the climax of the scene, Roberts rises to take the drink, forestalling Pulver.
Roberts clears his palate, then drinks it, pinky extended, as daintily as a lady at a party.
He stares at the glass, swallowing. Then Fonda’s hand lowers out of the frame so as to let us concentrate on his expression. His strangled line tops the whole comic arc: “You know, it does taste a little like Scotch.” Now his face does the work.
All three players are reintegrated into a master shot: patient Doc, frantic Pulver, and stalwart Roberts as they realize they’ve succeeded. Pulver, after lunging with his characteristic abruptness, finishes the glass in a hunched-over gulp.
“Smooth!” he yelps.
You might argue that such hand jive is rather “theatrical,” and perhaps some of the business came from Fonda’s three years in the Doug Roberts role on Broadway. Even so, it has clearly been recalibrated for the cinema. Theatre taught actors how to use their hands, but cinema gave them further lessons, and film directors learned to choreograph hands in relation to framing and shot scale.
My discussion doesn’t exhaust the scene, but I hope it suggestst how choices about staging and performance can make hands carry story information and express character. They can add nuance to a moment; they can surprise us by slipping into and out of visibility; and they can inflect a facial expression or line reading. If filmmakers today lock their framing on facial close-ups and moving lips, they’re depriving us of some beautiful music.
P. S. 18 January 2012 (from Midway, Utah and the Art House Convergence): Thanks to three alert readers. First, Adrian Martin spotted an orthographic error, now corrected. Second, David Cairns of the indispensable Shadowplay) writes of scene-stealing in The Magnificent Seven:
You do know what Yul said to Steve? “If you don’t stop playing with your hat, I’ll take off my hat, and then we’ll see who they’ll look at.”
And from James Benning, with the laconic message: “Here’s another.”
I wrote about Jim’s related project here.
P.P.S, 20 January 2012: This entry’s title, as many readers noted, referenced the great Johnny Otis song “Willie and the Hand Jive.” Today Ethan de Seife writes to tell me that Johnny died the day before my blog was posted. So take it as not only an homage but a valedictory.
Mr. Roberts.
Play it again, Joan
“The happy heart loves the cliché.”
–Myra Hudson (Joan Crawford) in Sudden Fear.
Sometimes your audience gets what you’re saying faster than you do. Years ago, after I gave a lecture in a class at Columbia University, a grad student came up and said: “What you’re doing is looking for the conventional side of unconventional films and the unconventional side of conventional films.” I’d say it’s not all I try to do, but the student’s chiasmus does capture a lot of what interests me.
It’s especially on target for Hollywood cinema. I don’t understand criticisms of Hollywood for not being realistic. It’s a highly stylized, artificial cinema, only a few notches above ballet or commedia dell’arte. Some of our best critics, like Parker Tyler and Manny Farber and Geoffrey O’Brien, have understood this. All the artifice will demand plenty of conventions, yes, but there are always filmmakers ready to treat them in fresh ways. And the churn is swift. American studio cinema is constantly finding new variations on its traditional forms, formats, and formulas.
Do-overs are allowed
Sleep, My Love
Take replays. The repeated sequence has become so common in our movies that nobody much notices it any more. We’re quite used to seeing an earlier action revisited. Often the replay simply serves to remind you of what happened, as when clues to a mystery are given in fragmentary flashbacks. The replay may also aim to get you absorbed in a character’s mental life. John, the hitman in John Woo’s The Killer, is traumatized by the fact that he blinded an innocent woman during a contract hit, and the moment of her wounding haunts him.
Sometimes, however, we get multiple-draft replays, in which the second version significantly alters the first. A common gambit is to have the second version show more of what happened, as in the money drop in Jackie Brown. Other cases show contradictions, as when conflicting testimony is dramatized in flashbacks. The most recent version I’ve seen occurs in The Debt, when the central 1966 section of the film concludes by showing what really happened when Dr. Vogel slashed Rachel and fled. In such cases the replay becomes less a true repetition and more of a revision, a new version questioning or canceling what we’ve seen before.
The idea isn’t new. You can find the replay in various forms in trial films of the 1930s, as I’ve discussed here. But the replay really came into its own during the 1940s. Directors and screenwriters experimented with the device as part of a broader initiative, burrowing into new niches in the ecosystem of classical narrative.
In those films, it’s common for replayed scenes to show an incident haunting the protagonist, as when the tormented bride of The Locket is assailed by memories as she walks down the aisle. Sometimes a flashback fills in information that was cunningly omitted from the earlier version, as in Mildred Pierce. And we also have competing accounts of what happened, as variant replays furnish multiple drafts. The most famous example is probably Crossfire.
By 1950, Joseph Mankiewicz could dream up one of the most daring experiments of the period, one that anticipated the repeated scene in Persona. For All about Eve, Mankiewicz planned to present Eve’s memorable monologue about the power of theatre twice: first through the sympathetic eyes of Karen (Celeste Holm), then from the perspective of the bitter Margo Channing (Bette Davis). What would viewers and other filmmakers have made of it? But Fox studio head Darryl F. Zanuck ordered the replay dropped, for reasons I speculate about in this entry’s codicil.
Mankiewicz’s unseen experiment with Eve’s “Audience Aria” reminds us that replays affect the soundtrack too. The most common use of replays is probably auditory, that line of dialogue that flits through a character’s consciousness—an auditory flashback, in effect. “Who knows what you may do the next time?” asks the sinister voice of the psychiatrist as Alison (Claudette Colbert) totters up the stairs in Sleep, My Love (1949). Several snatches of dialogue can flow together to recall a host of earlier scenes. In The Hard Way (1943), on another staircase, Katie (Joan Leslie) becomes distraught as bits of dialogue spoken by several characters flash through her mind.
More unusual is the audio replay in Duvivier’s wonderfully stylized Lydia (1941). A flashback to a ball is introduced by Lydia’s voice-over, recalling the splendid ballroom with its mirrorlike floors and the “divine aggregation of musicians, hundred of them, I think.”
But then her old lover corrects her memory and we get a flashback showing a more modest ballroom with a small ensemble.
Over these later shots, however, we hear bits of Lydia’s earlier description of the big ballroom and troops of musicians, in contrast to what we see. The sound flashback functions as a wry narrational commentary on Lydia’s stubborn romanticism.
Purely auditory replays tend to be subjective, but could we have an objective one? And can it promote surprise and suspense? As we say in Wisconsin, you bet. (Not you betcha.)
The replay machine
A lighthearted instance appears in The Pajama Game (1957). Sid Sorokin (John Raitt) , the new superintendant at the Sleeptite Pajama Factory, is falling in love with Babe Williams (Doris Day), the no-nonsense head of the labor union’s Grievance Committee. He sings into his Dictaphone about her in the song, “Hey, There (You with the Stars in Your Eyes).”
At the end of the song’s first section, he plays it back and then comments sourly on the lines he’s just sung. By the end, he’s joining himself in a duet, harmonizing nicely.
This instant playback wasn’t a cinematic invention, though. The same number, including the Dictaphone gimmick, was employed in the original Broadway production.
The Dictaphone, which used both wax cylinders and plastic belts for recording, was a popular device for businesses. Erle Stanley Gardner employed it for dictating many of his novels. A competitor to the Dictaphone was the SoundScriber, a late 1940s device using vinyl phonographic discs. The SoundScriber figures in a more sustained and suspenseful replay scene a few years before The Pajama Game.
In Sudden Fear (1952), Myra Hudson (Joan Crawford) is a prosperous playwright who has outfitted her office with a SoundScriber. She uses it for dictating plays and correspondence. One evening before a party, euphoric after her new marriage to the handsome actor Lester Blaine, she meets with her attorney to prepare a new will. He proffers a draft that assigns a modest sum to Lester, but she considers it insulting. She switches on the SoundScriber and dictates a new will, one leaving all her estate to Lester.
But we’ve had our suspicions about Lester, since he’s played by Jack Palance, an actor with more juts to his facial planes than a Giacometti bust. Our fears are confirmed after Lester hooks up with his old girlfriend Irene (Gloria Grahame). When they learn that Myra is making a new will, they believe she’s going to give the bulk of her estate to a foundation.
On the evening of the party, as she starts dictating her new will, the guests arrive and she descends to meet them. Irene and Lester slip away and meet in Myra’s study. Fade out on Lester closing the door.
Next morning, Myra return to her study and discovers she left her SoundScriber on all night. She hits replay and listens to herself bequeathing all her money to Lester. This is the replay that launches the big action. As she’s about to switch off the machine, she hears the conversation starting between Lester and Irene. The microphone, left on accidentally, has picked up their plotting.
The couple is still under the false impression that the new will leaves Lester penniless. We hear him declare his contempt for Myra while caressing and embracing Irene. They start planning to kill her before she can sign the new will.
The SoundScriber scene gives us two plot developments, past and present, simultaneously. The recording fills in the gap left by the fade-out: Now we know what happened behind those closed doors. On the visual track, we can watch Myra’s developing anxiety about the couple’s murder plot but, more piercingly, we register her realization that Lester has never loved her.
Across seven minutes, Joan Crawford executes a carefully modulated solo performance, for the most part with no accompanying score. Meanwhile, Palance and Grahame get to act viva voce. And David Miller’s direction scales and times things nicely. I won’t try to analyze the very end of the scene, let alone its frenzied aftermath. I just want to trace the dynamics of the double-layered time scheme the replay machine gives us.
Joanie, more than shoulders
The recorded scene develops from the lovers’ frustration with keeping up a false front, then to their suspicion that Irene will cut Lester out of her will, then to the mistaken belief that she’s just done so, and finally to their decision to kill her. Myra’s playback scene proceeds, I think, in four stages as well. Myra starts out placid and almost giddy in her love for Lester. She’s abruptly shocked and disenchanted when she learns he doesn’t love her; her stomach churns. A third phase consists of her discovery that Lester and Irene intend to kill her, and she devolves into sheer panic. The last phase, of which I’ll show only a bit, initiates a search for a way to defend herself.
Myra comes in euphoric. As she replays her dictation of the night before, she strolls around her study, going far back to the distant refrigerator for a glass of milk and then coming forward. She seems to savor hearing again her own declaration of her devotion to Lester.
Myra’s circuit around her study isn’t just filler: it etablishes the rear area for use later. But now, as she’s about to turn off the recording, she hears Lester’s voice: “What’s up?” She backs up a little, bumping the desk as she realizes that there’s more on the disc. This recoil, as a performance decision, will get magnified in the course of the scene. Then Miller cuts to a reaction shot.
The first of several optical point-of-view shots gives us a close view of the twin SoundScriber units (good for product placement too). Myra has set the milk down on the console.
As we hear Lester venting his contempt for her, Myra’s eyes fill with tears. Worse, he adds that he’d like to tell her he never loved her for a moment. “I’d like to see her face.” He can’t, but we can; in the closest shot yet, she looks right at us. Hollywood can be brutal.
She turns away and, seen from a new angle by the desk, she advances toward us. On the track, Lester is pitching woo to Irene. Myra realizes that he lusts for this other woman. She sighs. Listen closely and you can hear her emit a soft whimper as well.
Another cut to the SoundScriber as Lester says he dreams of holding Irene: “I don’t know how I stand it, not being with you.” On these last few words, cut to Irene, turning away in shame.
She rushes back, having heard enough. A low angle shows her about to switch off the horrible recording when Irene is heard noticing the attorney’s draft of the will on the desk. “It’s the will!” Myra freezes, accentuating the line, and then starts to turn when Lester begins to read the draft.
Having hidden her face from us for a little while, Miller’s direction makes the next close view all the more powerful. (Note the eyebrow work.) Lester’s reaction to the will proves it’s been about the money all along. As he curses Myra, she doubles over grabbing her stomach. This, I take it, is the high point of the scene’s second phase–a sheerly physical reaction to Lester’s cynical betrayal of her love.
Phase three starts, I think, when Irene is heard purring, “Suppose she isn’t able to sign it on Monday.” The line is heard over a shot of the machine, and not a POV at that. The visual narration cunningly delays, by just a few seconds, Myra’s reaction to Irene’s hint. The cut shows her listening, stunned. Lester agrees with Irene. “I’d get it all! Why not?”
Myra turns, as if in disbelief, and a closer view of SoundScriber underscores Irene’s response: “Lester, I have a gun.”
This triggers the scene’s big movement: Myra’s retreat from the recording. Back to the extreme long shot, low angle, as she hurls herself toward the rear wall and sidles along toward the refrigerator, taking refuge behind the chair. The lovers discuss how to arrange an apparent accident, all the while kissing and declaring their love. Lester exclaims, “I’m crazy about you! I could break your bones!” as only Jack Palance could say it.
Again we get an optical POV shot, but now from Myra’s position across the room as Lester muses on “a nice little accident.” And in the cut back to Myra, we hear Irene say, “We’ll work something out. I know a way.” The recording needle is stuck in a groove, and we hear her say it again: “I know a way.” Music comes up for the first time, shifting the action to a new pitch.
I know a way. This mechanical glitch, I think, pushes fear into panic. The tightest close-up yet of the spinning disc is a sort of mental subjectivity: It’s not what Myra sees exactly, but an expression of her being riveted by insistent, maniacal repetition of Irene’s assurance: I know a way. Myra rushes out of the shot and hurls herself into the bathroom to vomit. All the while we hear, again and again: I know a way.
The couple’s plotting has driven Myra out of the room, as the music rises and nearly suppresses Irene’s “I know a way.” In a closer view of the bathroom, Myra staggers to the sink and splashes water on her face, while the record still spins and Irene’s voice taunts her.
But now we get the start of a new phase, with Myra trying to seize the initiative. In a burst of anger she rushes back to the machine, switches it off, and fumblingly takes out the disc. By the time she does so, we’ve heard Irene’s “I know a way” thirty-one times. Talk about hammering the audience.
Myra grips the disc, proof of the criminal conversation, and….
…But my analysis has gone on too long. It’s reasonable, although mean, to stop with the end of the replay. The rest of the sequence builds on what we’ve heard and seen, developing Myra’s efforts to defend herself.
I should note, though, that there follows a hallucinatory sequence in which we get not only perceptual subjectivity, like the POV shots, but also mental imagery and sounds as well. That sequence also includes auditory flashbacks of the usual sort, Myra’s anxious memories of things that Lester and Irene said on the SoundScriber recording. They’re replays of a replay, if you want to get fancy about it.
Conventioneering
In a way this scene is just a variant of a common storytelling convention: Someone accidentally overhears a key piece of information, in an adjacent room or over the phone. But the sequence shrewdly recasts this convention in ways that pay off on many dimensions. We get the suspense attached to the lovers’ mistaken belief that Myra will cut Lester out, and we get Myra’s reaction to it. That reaction is compounded of her sense of betrayal, her disillusion, and her realization that she’s in danger. Had she been eavesdropping on their conversation, she could have burst in on them and denounced their misreading of her will. As it is, she must helplessly listen to them unfold their plans.
After more than a decade of female Gothics–aka”woman in peril” movies, aka I-think-my-husband’s-trying-to-kill-me movies–from Suspicion and Gaslight to Woman in Hiding, Miller and his colleagues found a fresh way to put a lady in a cage. Schema and revision, a key process in the history of any art form, allows ingenious artists to remake what tradition hands them. Twenty years later, Francis Ford Coppola and Walter Murch would build an entire movie, The Conversation, around the audio replay and its possibilities for objectivity and subjectivity. Over and over, the unconventional burrows inside the conventional.
After this film, Joan Crawford became a spokesperson for SoundScriber. (See below.) Who would know better than she the advantages of the gadget? Perhaps Joan even had a stake in the firm. Such fruitful synergy wouldn’t be unknown in Hollywood. Jack Webb found the Teleprompter so useful in shooting Dragnet episodes that he invested in the company.
On All About Eve and Zanuck’s purging of the replay of Eve’s monologue: I suspect that it was a forced byproduct of another decision Zanuck had taken. The film consists largely of flashbacks, and Mankiewicz had intended to move through them by shifting from one character to another. At the awards dinner the flashbacks begin with Karen, and then another block of them, grounded in Margo’s memories, was to take up later episodes in Eve’s ascent to stardom.
But the film ran very long, so Zanuck cut the framing portion at the dinner that would have introduced Margo’s flashbacks. The result is that in Karen’s flashback, we occasionally hear Margo’s narration of certain episodes Karen didn’t witness. But once we’ve lost Margo’s narrating frame, then it becomes quite difficult to justify re-hearing Eve’s ruminations on theatre from anything approximating her point of view. I suspect that consistency of this sort played a role in Zanuck’s cutting Eve’s monologue. Plus it was a pretty daring move on Mankiewicz’s part. And the film is already pretty long. The fullest account of the changes, though still not as specific as I’d like, is in Sam Staggs’ All About All About Eve (St. Martin’s Griffin, 2001), 170-172. As Staggs points out, Mankiewicz did work differential-viewpoint flashbacks into The Barefoot Contessa (1954).
Sudden Fear is available on a so-so DVD transfer from Kino Lorber.
The interplay between film and fiction in the 1940s is fascinating, and we can sometimes find rough equivalents between techniques. Here is a stream of auditory flashbacks in Steve Fisher’s novel I Wake Up Screaming (1941), ending with the protagonist’s inner monologue.
I’d remember Lanny Craig saying: “They crucified me . . . it was because of Vicky Lynn!” And the night Robin Ray said: “She’d laugh, see, and it was like Guy Lombardo’s band playing.” And Hurd Evans: “I only get two hundred and fifty a week.” Tick-tock, the faceless clock on Sunset. “It’s possible to build a case out of nothing,” the assistant district attorney said. Where was Harry Williams? If he’d been murdered, where was his body?
By the end of the thirties, of course, such montages were already heard in radio programs as well.
Joan Crawford was also a spokeswoman for Pepsi-Cola, having married the man who became the company’s CEO. This image comes from a nifty survey of her endorsements available here.