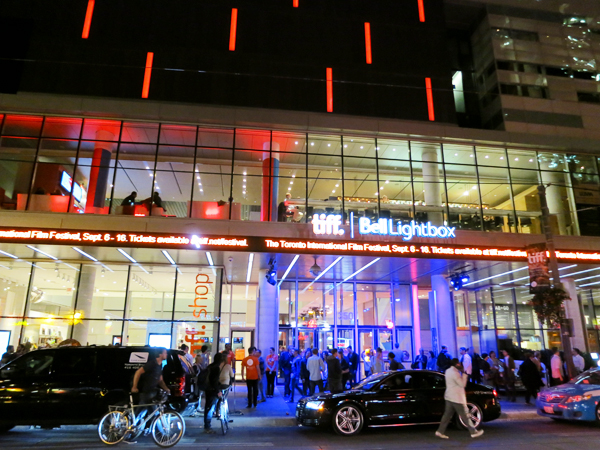
Audiences gather for screenings at the Bell Lightbox, hub of the Toronto International Film Festival.
DB here:
Around midnight tonight, the crowds packing the Toronto International Film Festival [2] will disperse, leaving the city full of memories of another extraordinary year. I’ve been back in Madison for this last week, but my few days at TIFF remain on my mind. This is partly because along with the films came a lot of ideas, opinions, and information. At any festival, fraternizing with audiences, critics, and programmers is one fine way to get that stimulation. It happened after some of the Wavelengths section’s short-film programs. Here are Raymond Phatanavirangoon and Bob Koehler outside the Art Gallery of Toronto, where their Devo retro-stylings raised our conversation to a new level.
More structured sessions delivered too. Out of my 4-plus days at the Toronto International Film Festival, I set aside about one and a half for industry panels and filmmaker Q & A’s. Let me tell you a little of what I learned.
From Assayas to Asia
TIFF: Where programmers meet stardom.
The talkfests I attended shed light on both film artistry and film business-making. Central to the first area was the master class with Olivier Assayas, hosted by Brad Deane.
Assayas, a charming fellow, talked fluently about how Something in the Air [5] (discussed here [6]) bears traces of his youth. During the 1970s, high-school kids were “footsoldiers of the cultural war of the time.” He recalled his affinities with the artistic side of the counterculture, as opposed to the extremes of the political activists, some of whom, being aligned with Maoism, refused to recognize the Cultural Revolution as “disaster on a demented level.” Yet this shouldn’t be taken as apolitical aestheticism; Assayas has been a vigorous advocate for the work of Situationist Guy Debord.
 [7]Assayas was refreshingly detailed about his working methods. He writes only one draft of his screenplay, partly because he wants to protect the “digressive” aspects of his story. (This tendency is apparent, and enjoyable, in Something in the Air.) Since his films are difficult to classify within standard genres, he needs to cobble together creative financing for each project. But the script becomes obsolete when he casts the film and visits locations. By embodying the characters, the actors create beings “more powerful than what I’ve written.” Working with them, he refuses to supply background on the characters’ psychology. “I look to them to understand the characters.” This hands-off approach yields striking results in the new film, where nearly all the cast is non-professional.
[7]Assayas was refreshingly detailed about his working methods. He writes only one draft of his screenplay, partly because he wants to protect the “digressive” aspects of his story. (This tendency is apparent, and enjoyable, in Something in the Air.) Since his films are difficult to classify within standard genres, he needs to cobble together creative financing for each project. But the script becomes obsolete when he casts the film and visits locations. By embodying the characters, the actors create beings “more powerful than what I’ve written.” Working with them, he refuses to supply background on the characters’ psychology. “I look to them to understand the characters.” This hands-off approach yields striking results in the new film, where nearly all the cast is non-professional.
Assayas doesn’t undertake elaborate rehearsals, instead coming to the set each morning and describing the shots they’ll make. He wants to take account of the evolution of the film as it’s been developing. He doesn’t fully block the shots. He sketches each one in longish takes that, as the actors expand on the action, “add layers” to what he’d initially planned. Alternatively, he cuts up the long takes and combines pieces of them. For Something in the Air, he relied on stable and wide framings, partly in reaction to trends toward handheld shots and close-ups, partly because he used the crane to create a “floating,” more lyrical circulation through the space.
 [8]Artistry, mixed with business sense, was apparent in one of the panels at the Asian Film Summit’s day of meetings. Colin Geddes hosted a session on Asian genre cinema, and several producers and directors shared thoughts on action cinema as an international genre. Fanboy blood pulsed high.
[8]Artistry, mixed with business sense, was apparent in one of the panels at the Asian Film Summit’s day of meetings. Colin Geddes hosted a session on Asian genre cinema, and several producers and directors shared thoughts on action cinema as an international genre. Fanboy blood pulsed high.
Eli Roth (left), another kid who grew up with Kung-Fu Theatre on TV, was bowled over years later by Korean and Japanese thrillers like Sympathy for Mr. Vengeance. Now Roth is producer and co-writer of The Man with the Iron Fist [9], directed by RZA–who is, according to Roth, letter-perfect on his kung-fu film knowledge. “We wanted to do a movie like we saw as kids on Saturday afternoon.” But production values in the genre have swollen since the old days. The project is using the Hengtian studio’s vast replica of the Forbidden City. RZA, Roth says, expected The Last Emperor to be a kung-fu movie, so this is his attempt to make things right.
Tom Quinn, Co-President of the Weinstein Company’s RADiUS [10] division, had similar affinities. As he pointed out, East Asian countries have strong local markets and so can build a base in genre cinema. With quantity comes quality. While working at Goldwyn and Magnolia, Quinn handled US distribution for The Host, Pulse, Tears of the Black Tiger, and most recently 13 Assassins, along with many other titles. Ong-Bak, on view at TIFF in 2004, was a particular triumph for him, yielding over a million dollars in its first weekend of release and eventually garnering $4.5 million in the US. Even the heavy piracy of Ong-Bak Quinn takes as a positive sign, “a validation of the film’s value.”
Bill Kong, a legendary Hong Kong producer and a force behind Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon, along with Stephen Fung, director of Tai Chi 0 (above), filled out the panel. Overall, the discussion ranged widely, but one question kept cropping up. Why is it that Western films are widely popular in Asia, but Asian cinema is almost completely a niche market in the West? I didn’t hear a clear answer (though I’d start an answer with Western racial prejudice).
Kong noted that Asian filmmakers don’t have high expectations about penetrating the US market, but other panelists were more hopeful about crossover projects. Quinn pointed out that the festival circuit built an audience, and Roth thinks that Tarantino has been a major player in making Asian film more popular, especially with the Kill Bill duet. The fact that Russell Crowe plays a major part in The Man with the Iron Fist suggests that things may be changing.
Bigger than Bollywood
Mira Nair.
The East/West dynamic was also the focus of two other panels. “India: Lessons from Bollywood and the Independents” brought together a nearly all-female group of experts to discuss local financing and wider distribution. All were agreed that it was necessary to convince the world that Indian cinema was bigger than Bollywood. As director Dibakar Banarjee put it: “We need to open the third eye.”
The local industry has a certain comfortable inertia. A film might cost only $150,000, but it can collect 90% of its production costs upon its opening run, said Shailja Gupta, who has been both a director and production executive. Foreign distribution is a major risk at this budget level. So how does a project, particularly an independent film, get international traction?
Coproductions are an obvious path, and while they are still rare, the trend is emerging. The Indian government’s National Film Development Corporation Ltd. [13] has helped with coproductions since 2006, says Nina Lath Gupta, NDFC Managing Director. Such enterprises are rare and mostly involve France or Germany. By establishing the Film Bazaar in 2007, the NDFC acknowledged the importance of marketing as well as financing, and this is getting local filmmakers acquainted with the need to think more globally.
 [14]Another path to the overseas market was suggested by Guneet Monga (right). She is a producer on the network narrative Peddlers [15] and the two-part gangster saga Gangs of Wasseypur [16]; both earned very good buzz at TIFF. Monga pointed out that sales agents can help shape projects for international distribution.Working with Elle Driver [17], she was able to generate three versions of Gangs, targeted for different regions. Moreover, sales agents can help a film by avoiding the old practice of selling it as a single package. Instead, the agent can pre-sell it with a minimum guarantee and negotiate territorial rights further down the line.
[14]Another path to the overseas market was suggested by Guneet Monga (right). She is a producer on the network narrative Peddlers [15] and the two-part gangster saga Gangs of Wasseypur [16]; both earned very good buzz at TIFF. Monga pointed out that sales agents can help shape projects for international distribution.Working with Elle Driver [17], she was able to generate three versions of Gangs, targeted for different regions. Moreover, sales agents can help a film by avoiding the old practice of selling it as a single package. Instead, the agent can pre-sell it with a minimum guarantee and negotiate territorial rights further down the line.
Mira Nair, distinguished director of Salaam Bombay and Monsoon Wedding, has long enjoyed worldwide exposure, of course. She shared her thoughts on how filmmakers could follow their visions and still, as she put it, “put bums on seats.” That’s accomplished by not worrying about distribution but devoting energies to creative choices–such as she undertook in The Reluctant Fundamentalist [18], her first foray into the thriller genre.
During the India panel, moderator Meenakshi Shedde asked if China might become a coproduction partner for local films. This is currently not happening, but the question reflects the significance of the People’s Republic on the global film scene. Earlier in the day, a panel on “Financing Between Asia and the West,” moderated by Patrick Frater, concentrated mostly on China as the leading edge of the region. Once more, the question of coproductions was central.
“Coproduction is a reality now for global filmmaking,” declared Peter Shiao, CEO of Orb Media Group [19]. But the power of China in the new media landscape has created a false optimism among Western entrepreneurs. Shiao warned newcomers that coproductions can’t be fulfilled in good faith with perfunctory gestures, such as including a Chinese actor in a secondary role. (The Expendables 2 was mentioned in this connection.) Aspiring filmmakers need to grasp and follow the China Coproduction Film Office regulations [20] straightforwardly.
Solid coproductions are rare, agreed Bruno Wu [21], founder and chair of many top Chinese media groups. He pointed out that what works in China won’t necessarily work in the rest of the world, but what works in the rest of the world is likely to work in China. So the Chinese investor needs to look at projects that will play internationally. He gave as examples his firms’ deals with Justin Lin and John Woo, who have reliably won global audiences. Along similar lines, Stuart Ford [22], founder and CEO of IM Global [23], suggested that a good alternative to coproduction involves soliciting equity investment from China for Western films. For example, Chinese investors in Paranoia, a $40 million production, acquired mainland distribution rights as part of the deal.
The soundness of investing in Western films seems borne out by local box-office figures. Seventy percent of China’s market receipts come from English-language imports; the several hundred domestic films produced earn only twenty percent. And theatrical receipts provide, according to Peter Shiao, ninety percent of a film’s earnings. Windows in the Western sense don’t exist, and there’s no legitimate home video market. Gradually local filmmakers are experimenting with Western ancillary tactics; Painted Skin: The Resurrection recently tried out apps and games.
China-based Video on Demand is more promising. In a few years, Wu expects there to be several million addressable HD cable homes, and providing entertainment on demand might provide a way around the national quota system for film import. There is no quota restraining VOD distribution, and as it takes hold, it might reduce piracy.
A killer app? (as in killing off business?)
Jonathan Sehring and Winnie Lau at the VOD panel at TIFF, 9 September 2012.
Speaking of VOD, in early September I signed up. I did it partly because there was one title I needed to see immediately: Keanu Reeves’ Side by Side, the documentary about the digital vs. film controversy. More abstractly, I had been learning a little about VOD when I recast and expanded my blogs on digital exhibition for Pandora’s Digital Box, and I was curious about how VOD worked in practice.
After a period of turmoil, the US film industry has integrated VOD into its system of non-theatrical ancillaries. Before, we had DVD and Blu-ray, both rental and retail, along with movie channels like HBO and Sundance available on subscription cable. Eventually movies would show up on basic-cable channels. There was also “pay per view” via cable, a one-off transaction now known as Pay TV VOD.
Now, the internet has expanded the options.
*Electronic Sell-Through (EST) allows the consumer to download a film and own it. This service is available through iTunes, Amazon, and other outlets.
*iVOD (internet VOD) is a one-off rental, to be run immediately or within a specified time period. To check the 1.77 aspect ratio on Dial M for Murder [25], I rented it for 24 hours on iTunes.
*Subscription VOD (SVOD), which you get with Netflix, Hulu, Amazon, and other providers. This option provides a library of titles available at any time for a monthly fee. SVOD is comparable to cable-television subscriptions, and it’s becoming very popular, as all-you-can-eat options tend to be.
In addition, another option hovers over the business:
*Premium VOD (PVOD) consists of a one-off rental available sooner than the traditional home-video window. The transmission would be via cable or satellite, not the Net, and the price point has typically been $30 for one viewing. The studios tried out PVOD with DirecTV in 2011, with apparently unencouraging results. Worse, last year’s Tower Heist fracas [26], during which Universal planned to put the film on PVOD 30 days after theatrical release, triggered threats of boycotts from exhibitors. PVOD, however, is likely to reappear at some point because it can offset losses from the declining DVD market.
No surprise, then, that one industry panel was called “VOD Killed the DVD Star.” The session assembled major players in that domain to discuss the present situation and the prospects for the future.
Much of the panel’s time was devoted to explaining why filmmakers needed to be flexible about accepting VOD as a legitimate complement to or substitute for theatrical release. VOD, they insisted, shouldn’t be seen as a dumping ground for weak or narrow-interest films. The reason: The consumer is king, and consumers want everything on demand.
Winnie Lau, Executive Vice-President for Sales and Acquisitions at Fortissimo [27], said that companies now recognized that consumers should be able to see a film on whatever platform they want. Given the high costs of a theatrical release, that option isn’t justifiable for many films. Philip Knatchbull, CEO of Curzon Artificial Eye [28], put the case more strongly, declaring that with the consumer in control, notions like windows and “on demand” are losing their usefulness. His view suits a company that, like IFC, has integrated video and theatrical distribution with theatre ownership and HD delivery. There are, he suggested, only home cinema and public cinema, and everyone in the film value chain should be aiming to reach millions of screens.
Tom Quinn of RADiUS was working for Magnolia when in 2005 Mark Cuban experimented with a multiple-platform release of Bubble. “His vision,” Quinn recalled, “was to make films available whenever people liked.” The Bubble experiment was problematic because it came out on film and on DVD simultaneously, but Quinn said that “the hotel VOD numbers were through the roof.” This summer, after twelve months of preparation, RADiUS has issued its first VOD titles, and Bachelorette, released earlier in September, won notice for earning about half a million dollars in its first weekend.
 [29]The prototype of longer-term VOD success is the later career of Edward Burns. Burns, who had his first success with the breakout indie movie The Brothers McMullen (1995), was lively and articulate. “VOD helped me stay in business.” He knew firsthand the slow rollout that characterized 35mm platform release in the 1990s, along with the months of press tours. In the years that followed, he realized that his movies–basically, as he put it, people bullshitting with one another around a kitchen table–had shrinking theatrical prospects. In 2007, he offered Purple Violets exclusively on iTunes. This came around the time that IFC and Magnolia were experimenting with day-and-date releasing on different platforms.
[29]The prototype of longer-term VOD success is the later career of Edward Burns. Burns, who had his first success with the breakout indie movie The Brothers McMullen (1995), was lively and articulate. “VOD helped me stay in business.” He knew firsthand the slow rollout that characterized 35mm platform release in the 1990s, along with the months of press tours. In the years that followed, he realized that his movies–basically, as he put it, people bullshitting with one another around a kitchen table–had shrinking theatrical prospects. In 2007, he offered Purple Violets exclusively on iTunes. This came around the time that IFC and Magnolia were experimenting with day-and-date releasing on different platforms.
Burns was satisfied with the results and built a production model around VOD. The cast and crew work for free and collectively own the film. Budgets can be low; he claimed last year [30] that Newlyweds cost only $100,000. Payments are deferred, and if a film breaks through, everyone makes money. His last three films, he reported, did. He compared the business model to that of an indie band. VOD gets his work to the people who watch HBO, Showtime, AMC. “That’s our audience.”
Burns is an unusual instance, since as one panelist pointed out, he has established his own brand. Still, other VOD releases can break out. The most widely publicized example is Margin Call, with about $4.5 million on VOD. Jonathan Sehring, President of IFC [31] and Sundance Selects [32], was a pioneer of alternative platforms, and he remarked that 4 Months, 3 Weeks, and 2 Days did better on VOD than in theatrical release (where it grossed $1.2 million). In a recent interview [33], Sehring indicates that the recent IFC release About Cherry as doing as well as Bachelorette on VOD and other revenue streams.
It seems, then, that these and other industry decision-makers see VOD as offering two avenues, depending on the film. VOD can provide a new window, to be added before or after or during theatrical release. Alternatively, VOD can replace theatrical, as it has done for Burns (who will still occasionally give a film like the upcoming Fitzgerald Family Christmas brief theatrical play). With this option, many films, both domestic and imported, will never see a theatrical release but they might make money on the less costly VOD platform.

The problem for the second strategy is finding a way to make the film stand out from the thousands of titles available in cable and VOD libraries. A theatrical release provides the “shop window,” as Knatchbull called it, but without that, the film needs other salient features–big stars or cult buzz–to attract the home viewer.
Despite the panel’s title, the guests didn’t predict that VOD would displace discs. In fact a couple of panelists agreed that DVD and Blu-ray would be around quite a while. Quinn (left) confessed that as someone who grew up with VHS he would always be collecting his favorite films on physical media.
There’s something else to consider: some dramatic disparities between VOD and DVD consumption. The differences are spelled out in a recent IHS Screen Digest report.
On one hand, the VOD audience has grown rapidly. The report counted transactions–buying a movie in any form–and came up with striking figures for the world’s top five regions.
2007: DVD retail and rental: 2.7 billion transactions; online VOD in all forms: 14.8 million transactions.
2011: DVD retail and rental: 2.58 billion transactions; online VOD in all forms: 1.4 billion transactions (nearly all SVOD).
The Screen Digest team estimates that 2012 will see an even bigger burst in online VOD, totaling 3.4 billion transactions, with nearly all that via subscription. (I’m in there somewhere.) By contrast, physical media sales and rentals are predicted to fall further, to 2.4 billion transactions.
The disparity lies in “monetization.” We have some access to weekend box office grosses, but almost none to income from DVD and VOD, so comparison is difficult. Still, everyone knows that DVD purchase and rental, along with pay TV licensing, yield the bulk of film revenues. In another research report, Screen Digest estimates that in the US the 2012 surge in VOD will yield only $1.72 billion. DVD will yield $11.1 billion, nearly ten times the VOD transactions. Even with the declining retail and rental prices of discs, VOD yields much less per transaction than DVD does, especially with subscription services leveling out the cost to consumers.
So did VOD kill, or at least wound, the DVD star? When measured in transactions, yes. In revenues, no. Moguls pay off their Ferraris in dollars, not transactions, so it seems that VOD would have to expand colossally, or raise prices, or both, to come close to achieving the returns of DVD.
It’s conceivable that VOD will cannibalize other windows, if you’ll excuse the mixed metaphor. DVD transactions were going downhill before the rise of VOD, but perhaps VOD will accelerate that plunge. iTunes already charges up to $20 for EST downloads of a new release. As consumers become used to storing their movie and TV collections digitally, the convenience of EST could hurt DVD sales.
Moreover, VOD has always threatened the theatrical market. That’s why exhibitors cried foul when Premium VOD was tried. But box-office grosses overall remain robust because ticket prices are constantly rising and 3D and Imax rely on upcharges. These revenues offer studios a good reason to maintain strict windows, at least for their most successful releases. Still, studios are very likely to continue to press for PVOD. And indie distributors have embraced VOD release exuberantly. Foreign and indie titles released on VOD before or during the theatrical run may steal business from art houses [34].
In sum, VOD might shake up the other platforms quite a bit. If your analogy is the music business, theatrical and DVD formats stand in for albums, while VOD is the online force that lowers consumers’ sense of a fair price point. There’s some discussion of raising prices for some iVOD and Pay TV VOD offerings to parity with theatrical ticket prices. I wonder if consumers will sit still for that. As a novice VOD’er who likes going out to see movies big, I probably wouldn’t. Unless Hulu’s Criterion library [35] discovered a lost Mizoguchi.
Assayas’ autobiography A Post-May Adolescence [36] has just been published in English translation. It includes two essays on Debord. At the same time, an anthology of critical essays on Assayas [37], edited by Kent Jones, has appeared in the sterling Austrian Film Museum series.
Patrick Frater reports on the TIFF Asian Film Summit at Film Business Asia [38].
My statistics on the progress of VOD come from “Movie Consumption Stabilizes,” IHS Screen Digest (April 2012): 95-98, and “Online Movie Consumption in the US,” IHS Screen Digest (May 2012): 116. See also Andrew Wallenstein’s Variety story [39], where we learn that Netflix’s subscription model is beating the pants off the competition. Thanks to David Hancock of IHS Screen Digest for further information.
As before, thanks to my Toronto hosts Cameron Bailey, Brad Deane, Christoph Straub, Andrew McIntosh, Andrea Picard, and all their colleagues.
TIFF leaves an indelible mark: The ankle of Crystal Decker, Marketing Manager of Well Go USA Entertainment [41], US distributor of Tai Chi 0.
P.S. 17 September: Thanks to Anuj Mehta for correction of a misspelled name.